正在加载图片...
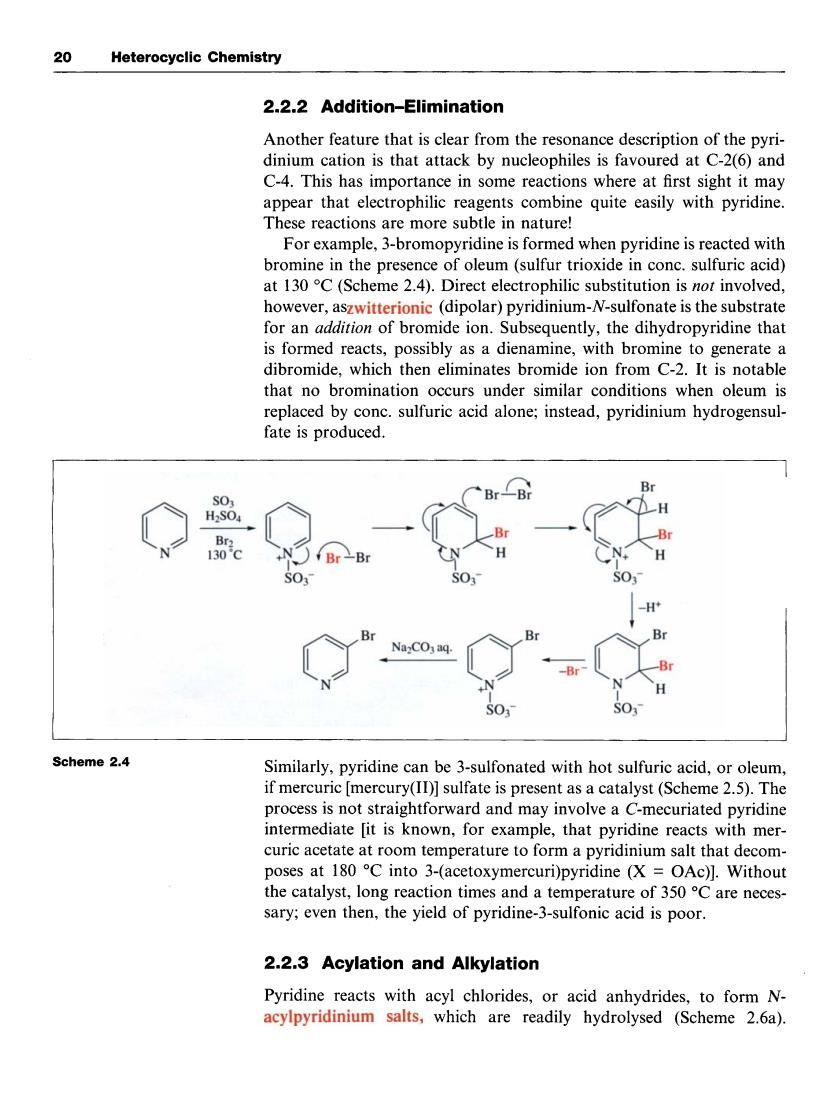
20 Heterocyclic Chemistry 2.2.2 Addition-Elimination Another feature that is clear from the resonance description of the pyri- dinium cation is that attack by nucleophiles is favoured at C-2(6)and C-4.This has importance in some reactions where at first sight it may appear that electrophilic reagents combine quite easily with pyridine These reactions are more subtle in nature! For example,3-bromopyridine is formed when pyridine is reacted with bromine in the presence of oleum(sulfur trioxide in conc.sulfuric acid) at 13C(Scheme).Direct electrophilic however,aszwitterionic (dipolar)pyridinium-N-sulfonate is the substrate for an addition of bromide ion.Subsequently,the dihydropyridine that that no bromination occurs under similar conditions when oleum is replaced by conc.sulfuric acid alone;instead,pyridinium hydrogensul- fate is produced. Br CB 29 Br 30 SO 0 B Na:COaq SO Scheme 2.4 Similarly,pyridine can be 3-sulfonated with hot sulfuric acid,or oleum if mercuric [mercury(ID)]sulfate is present as a catalyst(Scheme 2.5).Th process is not straightforward and may involve a C-mecuriated pyridine intermediate [it is known,for example,that pyridine reacts with mer- curic acetate at room temperature to form a pyridinium salt that decom- sary;even then,the yield of pyridine-3-sulfonic acid is poor. 2.2.3 Acylation and Alkylation Pyridine reacts with acyl chlorides,or acid anhydrides,to form N- acylpyridinium salts,which are readily hydrolysed (Scheme 2.6a). 20 Heterocyclic Chemistry 2.2.2 Addition-Elimination Another feature that is clear from the resonance description of the pyridinium cation is that attack by nucleophiles is favoured at C-2(6) and C-4. This has importance in some reactions where at first sight it may appear that electrophilic reagents combine quite easily with pyridine. These reactions are more subtle in nature! For example, 3-bromopyridine is formed when pyridine is reacted with bromine in the presence of oleum (sulfur trioxide in conc. sulfuric acid) at 130 "C (Scheme 2.4). Direct electrophilic substitution is not involved, however, aszwitterionic (dipolar) pyridinium-N-sulfonate is the substrate for an addition of bromide ion. Subsequently, the dihydropyridine that is formed reacts, possibly as a dienamine, with bromine to generate a dibromide, which then eliminates bromide ion from C-2. It is notable that no bromination occurs under similar conditions when oleum is replaced by conc. sulfuric acid alone; instead, pyridinium hydrogensulfate is produced. 0 N 0- +yJ 0-Br so,- n c&rBr H I S0,- Br soy- I -H+ I s0,- Scheme 2.4 Similarly, pyridine can be 3-sulfonated with hot sulfuric acid, or oleum, if mercuric [mercury(II)] sulfate is present as a catalyst (Scheme 2.5). The process is not straightforward and may involve a C-mecuriated pyridine intermediate [it is known, for example, that pyridine reacts with mercuric acetate at room temperature to form a pyridinium salt that decomposes at 180 "C into 3-(acetoxymercuri)pyridine (X = OAc)]. Without the catalyst, long reaction times and a temperature of 350 "C are necessary; even then, the yield of pyridine-3-sulfonic acid is poor. 2.2.3 Acylation and Alkylation Pyridine reacts with acyl chlorides, or acid anhydrides, to form Nacylpyridinium salts, which are readily hydrolysed (Scheme 2.6a)