正在加载图片...
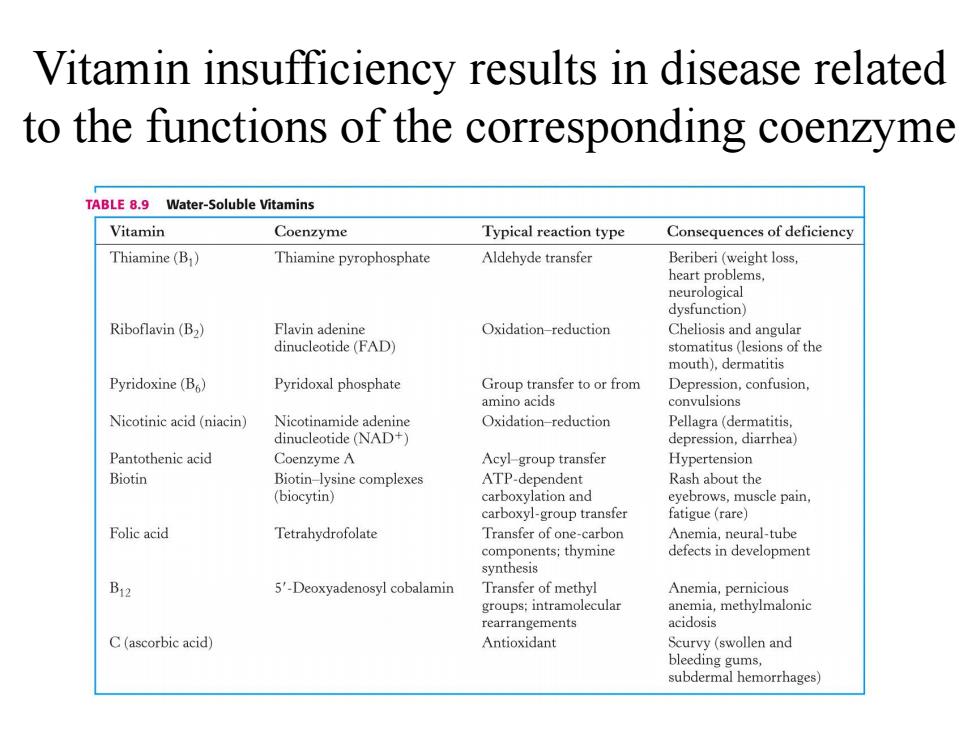
Vitamin insufficiency results in disease related to the functions of the corresponding coenzyme TABLE 8.9 Water-Soluble Vitamins Vitamin Coenzyme Typical reaction type Consequences of deficiency Thiamine(B) Thiamine pyrophosphate Aldehyde transfer Beriberi(weight loss. heart problems, neurological dysfunction) Riboflavin(B2) Flavin adenine Oxidation-reduction Cheliosis and angular dinucleotide(FAD) stomatitus(lesions of the mouth),dermatitis Pyridoxine(B6) Pyridoxal phosphate Group transfer to or from Depression,confusion, amino acids convulsions Nicotinic acid (niacin) Nicotinamide adenine Oxidation-reduction Pellagra(dermatitis, dinucleotide (NAD+) depression,diarrhea) Pantothenic acid Coenzyme A Acyl-group transfer Hypertension Biotin Biotin-lysine complexes ATP-dependent Rash about the (biocytin) carboxylation and eyebrows,muscle pain, carboxyl-group transfer fatigue(rare) Folic acid Tetrahydrofolate Transfer of one-carbon Anemia,neural-tube components;thymine defects in development synthesis b12 5'-Deoxyadenosyl cobalamin Transfer of methyl Anemia,pernicious groups:intramolecular anemia,methylmalonic rearrangements acidosis C(ascorbic acid) Antioxidant Scurvy (swollen and bleeding gums, subdermal hemorrhages) Vitamin insufficiency results in disease related to the functions of the corresponding coenzyme