
Dynamic Program Analysis Jun Ma majun@nju.edu.cn
Dynamic Program Analysis majun@nju.edu.cn Jun Ma

Overview Static analysis A program that takes programs as input and produces useful results(without executing it). Dynamic analysis A program that monitors and alters program execution to produce useful results
Overview Static analysis A program that takes programs as input and produces useful results (without executing it). Dynamic analysis A program that monitors and alters program execution to produce useful results

Computer Systems as State Machine
Computer Systems as State Machine
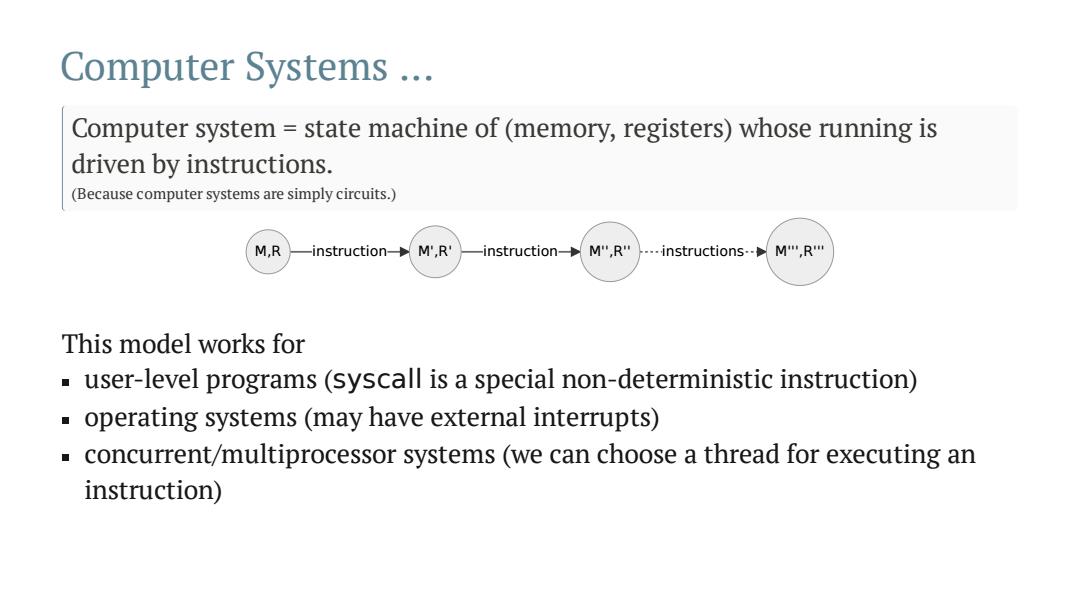
Computer Systems .. Computer system state machine of(memory,registers)whose running is driven by instructions. (Because computer systems are simply circuits.) M,R -instruction-M',R' instruction M",R" …instructions.-pM,R" This model works for user-level programs(syscall is a special non-deterministic instruction) operating systems(may have external interrupts) concurrent/multiprocessor systems (we can choose a thread for executing an instruction)
Computer Systems … Computer system = state machine of (memory, registers) whose running is driven by instructions. (Because computer systems are simply circuits.) M,R instruction M',R' instruction M'',R'' instructions M''',R''' This model works for user-level programs (syscall is a special non-deterministic instruction) operating systems (may have external interrupts) concurrent/multiprocessor systems (we can choose a thread for executing an instruction)

Dynamic Analysis A program that monitors and alters program execution to produce useful results. That is,a function f(T)to produce useful results given the execution trace T of a state machine(program/computer system). Only provides useful results for the given T usually complete but unsound complements static analyses SE tasks tolerate unsound and incomplete analyses as long as results are useful in engineering PL guys don't like this
Dynamic Analysis A program that monitors and alters program execution to produce useful results. That is, a function to produce useful results given the execution trace of a state machine (program/computer system). Only provides useful results for the given usually complete but unsound complements static analyses SE tasks tolerate unsound and incomplete analyses as long as results are useful in engineering PL guys don’t like this f(τ ) τ τ

Debuggers
Debuggers

The GNU Project Debugger(GDB) GDB,the GNU Project debugger,allows you to see what is going on "inside"another program while it executes-or what another program was doing at the moment it crashed. Start your program,specifying anything that might affect its behavior. Make your program stop on specified conditions. Examine what has happened when your program has stopped. Change things in your program,so you can experiment with correcting the effects of one bug and go on to learn about another
The GNU Project Debugger (GDB) GDB, the GNU Project debugger, allows you to see what is going on “inside” another program while it executes – or what another program was doing at the moment it crashed. Start your program, specifying anything that might affect its behavior. Make your program stop on specified conditions. Examine what has happened when your program has stopped. Change things in your program, so you can experiment with correcting the effects of one bug and go on to learn about another

GDB's Offer Lots of commands Execution controlr,c,f,n,s,si,.. Breakpoints b,hb,wa,... ·Program state display`p,x,i,bt`,… Program state modification set,... Black magic -reverse debugging: ■`record,rc,rn,rsi, Suffices for anything GDB captures the entire "state transition"procedure of a process
GDB’s Offer Lots of commands Execution control r, c, f, n, s, si ,… Breakpoints b, hb, wa , … Program state display p, x, i, bt , … Program state modification set , … Black magic - reverse debugging: record, rc, rn, rsi , … Suffices for anything GDB captures the entire “ state transition” procedure of a process ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` ` `

Debugger is ALL Dynamic Analyses Any practical dynamic analysis is a "simplified"(and more efficient)debugger. Virtually,we can do any observation or perturbation on a debugger Understanding program states info inferiors;thread 1;info registers;x/i srip Modifying program states ■`set var=value But single-step execution incurs 1000X slowdown and GB/s instruction log
Debugger is ALL Dynamic Analyses Any practical dynamic analysis is a “ simplified” (and more efficient) debugger. Virtually, we can do any observation or perturbation on a debugger Understanding program states info inferiors; thread 1; info registers; x/i $rip Modifying program states set var = value But single-step execution incurs 1000X slowdown and GB/s instruction log ` ` ` `

Implementing GDB The fundamental problem: How to pause program execution at an instruction (address)or statement? Dynamic program instrumentation patch the instruction!(quite clever idea) make the code writable(thus cannot breakpoint on ROM addresses) ■`mprotect() patch the instruction with a“debugger trap” int $3 (0xcc for x86)or 'ebreak (for risc-v) -OS will send a signal to the parent process(gdb) restore the instruction after hitting the breakpoint
Implementing GDB The fundamental problem: How to pause program execution at an instruction (address) or statement? Dynamic program instrumentation patch the instruction! (quite clever idea) make the code writable (thus cannot breakpoint on ROM addresses) mprotect() patch the instruction with a “debugger trap” int $3 ( 0xcc for x86) or ebreak (for risc-v) OS will send a signal to the parent process (gdb) restore the instruction after hitting the breakpoint ` ` ` ` ` ` ` `