
ocation System Desn Experiments Coodusio 南京大学 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display Ke Sunt, Wei Wangt, Alex X.Liutt, Haipeng Dait Nanjing Universityt, Michigan State University Mobisys'18 June 3, 2018 Ke Sun, et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 1/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display Ke Sun† , Wei Wang† , Alex X.Liu†‡, Haipeng Dai† Nanjing University† , Michigan State University‡ Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 1 / 22
Motivaticn System Degn Experiments Coodusio 动京大盛 Motivation Traditional tapping-based interaction: o Require physical devices o Limit the freedom of user hands ·口0,4至·子2刀00 Ke Sun,et al. Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 2/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Motivation Traditional tapping-based interaction: Require physical devices Limit the freedom of user hands Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 2 / 22

Motivaticn System Degn Experiments Coodusio 和京大盛 Motivation Tapping-in-the-air: o Hands are free to interact with other objects Depth measurements provide different levels of feedbacks 4口…94至子·2刀00 Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 3/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Motivation Tapping-in-the-air: Hands are free to interact with other objects Depth measurements provide different levels of feedbacks Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 3 / 22
Motivation System Degn Experiments Coodusio 动京大盛 Limitation of Prior Arts Customized depth-cameras o Low accuracy: Centimeter-level accuracy (without different levels feedback) High lantency: Low frame rate and high computational requirements ·口0,4至·子2刀00 Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 4/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Limitation of Prior Arts Customized depth-cameras Low accuracy: Centimeter-level accuracy (without different levels feedback) High lantency: Low frame rate and high computational requirements Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 4 / 22

Motivation System Degn Experiments Coodusio 动京大盛 Problem Statement Can we suppport tapping-in-the-air without depth-cameras? and meet these design goals o High accuracy(mm-level) Low latency (20 ms) Different levels feedback(finger bending angle) Low computational cost (works on mobile devices) 4口0,4t4子2刀00 Ke Sun,et al. Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 5/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Problem Statement Can we suppport tapping-in-the-air without depth-cameras? and meet these design goals High accuracy (mm-level) Low latency (< 20 ms) Different levels feedback (finger bending angle) Low computational cost (works on mobile devices) Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 5 / 22
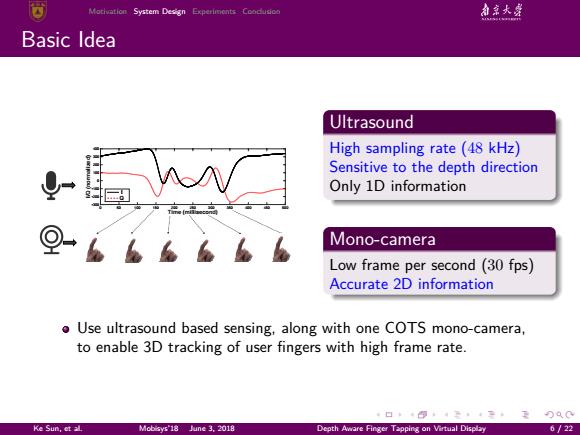
Motivation System Design Experiments Coodusic 和京大盛 Basic Idea Ultrasound High sampling rate(48 kHz) Sensitive to the depth direction Only 1D information Mono-camera Low frame per second(30 fps) Accurate 2D information o Use ultrasound based sensing,along with one COTS mono-camera, to enable 3D tracking of user fingers with high frame rate. ·口0,42,平·2刀00 Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 6/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Basic Idea Time (millisecond) 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 I/Q (normalized) -300 -200 -100 0 100 200 300 400 I Q Ultrasound High sampling rate (48 kHz) Sensitive to the depth direction Only 1D information Mono-camera Low frame per second (30 fps) Accurate 2D information Use ultrasound based sensing, along with one COTS mono-camera, to enable 3D tracking of user fingers with high frame rate. Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 6 / 22
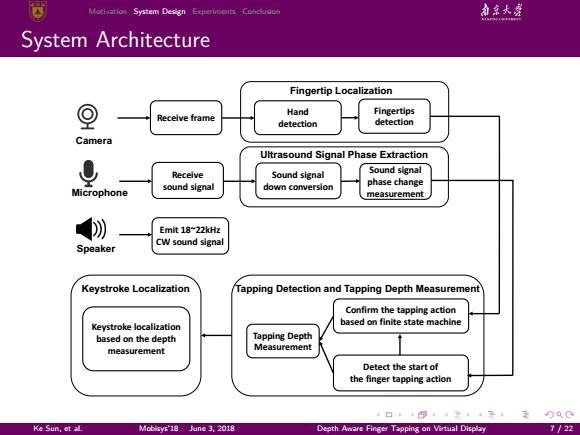
Motivation System Design Experimonts Coodusio 动京大盘 System Architecture Fingertip Localization Hand Fingertips Recelve frame detection detection Camera Ultrasound Signal Phase Extraction 0 Recelve Sound signal Sound signal phase change Microphone sound signal measurement 勿 Emit 18~22kHz Speaker CW sound signal Keystroke Localization Tapping Detection and Tapping Depth Measurement Confirm the tapping action Keystroke localization based on finite state machine based on the depth Tapping Depth measurement Measurement Detect the start of the finger tapping action Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 7/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion System Architecture Microphone Speaker Emit 18~22kHz CW sound signal Receive sound signal Sound signal down conversion Sound signal phase change measurement Detect the start of the finger tapping action Ultrasound Signal Phase Extraction Camera Receive frame Hand detection Fingertips detection Fingertip Localization Tapping Detection and Tapping Depth Measurement Confirm the tapping action based on finite state machine Tapping Depth Measurement Keystroke Localization Keystroke localization based on the depth measurement Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 7 / 22
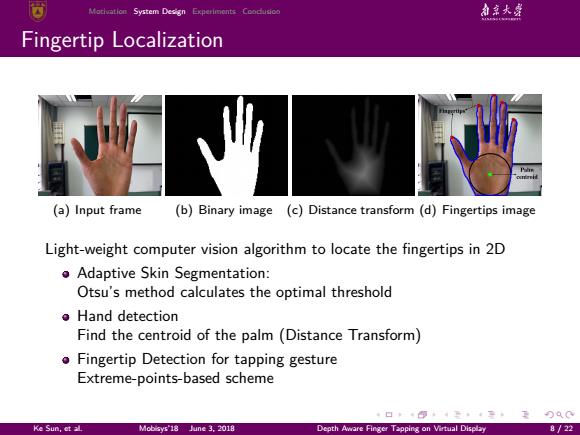
Motivation System Design Experiments Coodusic 和京大盛 Fingertip Localization (a)Input frame (b)Binary image (c)Distance transform (d)Fingertips image Light-weight computer vision algorithm to locate the fingertips in 2D Adaptive Skin Segmentation: Otsu's method calculates the optimal threshold o Hand detection Find the centroid of the palm (Distance Transform) Fingertip Detection for tapping gesture Extreme-points-based scheme ·口0,4至·子·2刀00 Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 8/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Fingertip Localization (a) Input frame (b) Binary image (c) Distance transform (d) Fingertips image Light-weight computer vision algorithm to locate the fingertips in 2D Adaptive Skin Segmentation: Otsu’s method calculates the optimal threshold Hand detection Find the centroid of the palm (Distance Transform) Fingertip Detection for tapping gesture Extreme-points-based scheme Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 8 / 22

Mothvation System Design Experimonts Coodusic 和京大盛 Ultrasound Signal Phase Extraction Tapping finger t40 I(normi密d o Phase-based distance measurement Measure phase changes caused by the movement 16 single frequencies(17~22 kHz)linear regression Challenge: o Phase changes caused by the finger movements is much smaller. o Multipath interference in finger movements is much more significant. Dao Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 9/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Ultrasound Signal Phase Extraction I (normalized) 700 900 1100 1300 1500 1700 Q (normalized) 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 Pushing hand Tapping finger I (normalized) 1000 1050 1100 1150 1200 Q (normalized) 900 950 1000 1050 1100 Tapping finger Tapping finger Phase-based distance measurement Measure phase changes caused by the movement 16 single frequencies (17 ∼ 22 kHz) linear regression Challenge: Phase changes caused by the finger movements is much smaller. Multipath interference in finger movements is much more significant. Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 9 / 22

Motivation System Design Experiments Coodusioo 动京大盛 Ultrasound Signal Phase Extraction 1150 1100 160 g 0 Extreme Point -Fake Extreme Point 600 Time (millisecond) Peak and Valley Estimation o Find the peak and valley Avoid the error-prone step of static vector estimation o Exclude the fake extreme points: o"Fingerlnterval":the magnitude gap of the finger "SpeedInterval":the speed of the finger Future:use modulated signal to locate the absolute distance and exclude other distance dynamic multipath 20a0 Ke Sun,et al Mobisys'18 June 3.2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 10/22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motivation System Design Experiments Conclusion Ultrasound Signal Phase Extraction Time (millisecond) 0 500 1000 1500 I/Q (normalized) 800 850 900 950 1000 1050 1100 1150 I Q Extreme Point Fake Extreme Point Peak and Valley Estimation Find the peak and valley Avoid the error-prone step of static vector estimation Exclude the fake extreme points: ”FingerInterval”: the magnitude gap of the finger ”SpeedInterval”: the speed of the finger Future: use modulated signal to locate the absolute distance and exclude other distance dynamic multipath Ke Sun, et al. Mobisys’18 June 3, 2018 Depth Aware Finger Tapping on Virtual Display 10 / 22