
重蹇等科大学 ongging Medical University DISEASES OF URINARY SYSTEM Depart.of pathol.CQMU
DISEASES OF URINARY SYSTEM Depart. of pathol.CQMU

倒重麦普种大号 gqing Med山eal Univers Glomerulonephritis-GN Secondary GN-caused by a variety of factors and in the course of a number of systemic diseases. SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus), hypertention,polyarteritis nodosa,diabetes. Primary GN-kedney is the only or the predominant organ invulved
Glomerulonephritis-GN Secondary GN—caused by a variety of factors and in the course of a number of systemic diseases . SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus), hypertention, polyarteritis nodosa, diabetes. Primary GN - kedney is the only or the predominant organ invulved

1.Pathogenesis of Glomerular Injury Antibody-Mediated Injury 1)In situ immune complex deposition a.anti-GBM Nephritis (Ab react directly with GBM Ag or planted Ag) b.Heymann Nephritis (Ab cross-react with the visceral epithelial cells and blush border Ag) 2)Circulating immune complex deposition Cell-Mediated immune Injury Macrophages,T cells Activation of Complement Pathway A common pathway of glomerular injury
1.Pathogenesis of Glomerular Injury Antibody-Mediated Injury 1)In situ immune complex deposition a. anti-GBM Nephritis ( Ab react directly with GBM Ag or planted Ag) b. Heymann Nephritis (Ab cross-react with the visceral epithelial cells and blush border Ag) 2)Circulating immune complex deposition Cell-Mediated immune Injury Macrophages, T cells Activation of Complement Pathway A common pathway of glomerular injury

重蹇暗科大图 2.Mechanisms and Mediators of glomerular damige Complement triggers attracts IC-complement cascade neutrophil Nephritic factors: Polymorphonuclear leukocytes Clotting factors:Fibrin,platelets C3 and Fc receptors
2.Mechanisms and Mediators of glomerular damige Complement : triggers attracts IC- complement cascade - neutrophil Nephritic factors: Polymorphonuclear leukocytes : Clotting factors: Fibrin , platelets C3 and Fc receptors

重蹇等科大学 3.Clinical Manifestations 1)acute nephritic syndrome:Hematuria. azotemia,red blood cell casts,variable proteinuria (3.5 gm/day proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia,hyperlipidemia,lipiduria 3)Asymptomatic hematuria or proteinuria; Glomerular hematuria:subnephrotic proteinuria
3.Clinical Manifestations 1)acute nephritic syndrome: Hematuria. azotemia, red blood cell casts, variable proteinuria (3.5 gm/day proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, lipiduria 3)Asymptomatic hematuria or proteinuria: Glomerular hematuria: subnephrotic proteinuria

圈重麦晋行大学 gqing Med山eal Univers 4)rapidly progressive nephritic syndrome: Acute nephritis,proteinuria,and acute renal failure 5)chronic nephritic syndrome:Azotemia uremia progressing for years
4)rapidly progressive nephritic syndrome: Acute nephritis, proteinuria, and acute renal failure 5)chronic nephritic syndrome: Azotemia uremia progressing for years

Primary Glomerular Disease Acute diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis** Poststreptococcal Non-poststreptococcal Rapidly progressive (crescentic~)glomerulonephritis** Membranous glomerulopathy Lipoid nephrosis (minimal change disease)** Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis ▣IgA nephropathy Focal proliferative glomerulonephritis Chronic glomerulonephritis**
Primary Glomerular Disease ◼ Acute diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis** Poststreptococcal Non-poststreptococcal ◼ Rapidly progressive (crescentic~) glomerulonephritis** ◼ Membranous glomerulopathy ◼ Lipoid nephrosis (minimal change disease)** ◼ Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis ◼ Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis ◼ IgA nephropathy ◼ Focal proliferative glomerulonephritis ◼ Chronic glomerulonephritis**

重蹇普科大学 Acute diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis post-infectious GN) It is seen most frequently in children 1-3 weeks after group A B-hemolytic streptococcal infection of pharynx or skin.It occurs mainly in children of primary school. This disease is characterized histologically by diffuse proliferation of glomerular cells, associated with influx of leukocytes
Acute diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis ( post-infectious GN) It is seen most frequently in children 1-3 weeks after group A β-hemolytic streptococcal infection of pharynx or skin. It occurs mainly in children of primary school. This disease is characterized histologically by diffuse proliferation of glomerular cells, associated with influx of leukocytes

霸重走等科大导 I.Pathogenesis exogenous antigens infectious agents Group AB- hemolytic streptococcal,other causative organisms and conditions including staphylococci,meningococci, pneumococci,viruses,toxoplasmosis,schitosomiasis,drugs. endogenous antigens DNA,immunoglobulins,IC, IgA
1. Pathogenesis exogenous antigens : infectious agents , Group A β- hemolytic streptococcal , other causative organisms and conditions including : staphylococci, meningococci, pneumococci, viruses, toxoplasmosis, schitosomiasis, drugs. endogenous antigens : DNA, immunoglobulins, IC, IgA
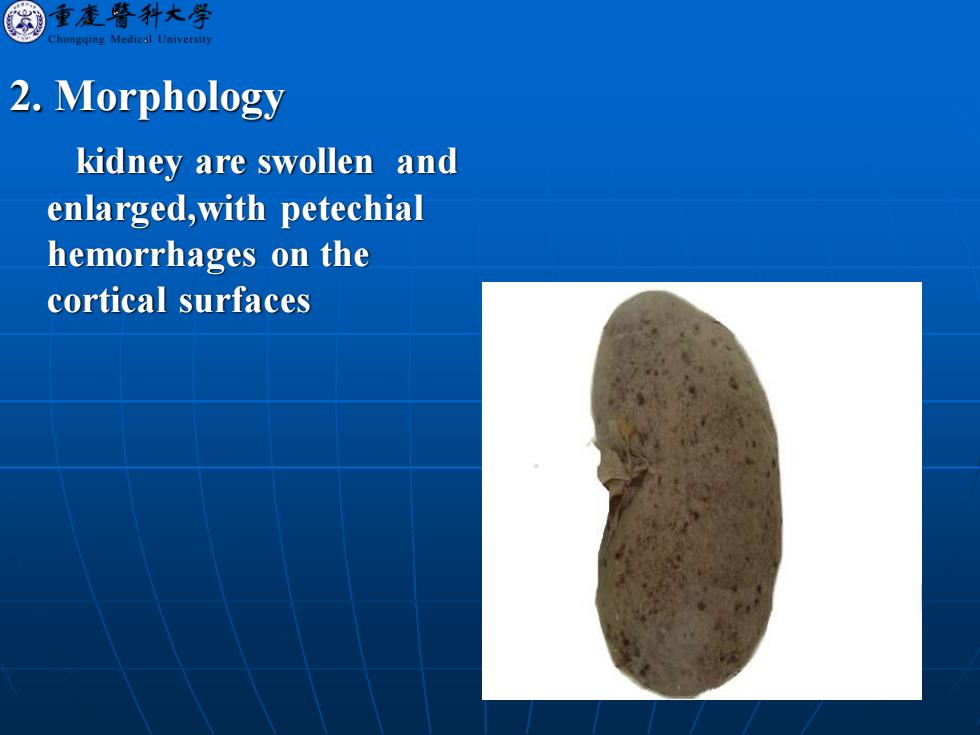
圈重麦晋行大学 gqing Med山l Universits 2.Morphology kidney are swollen and enlarged,with petechial hemorrhages on the cortical surfaces
2. Morphology kidney are swollen and enlarged,with petechial hemorrhages on the cortical surfaces