正在加载图片...
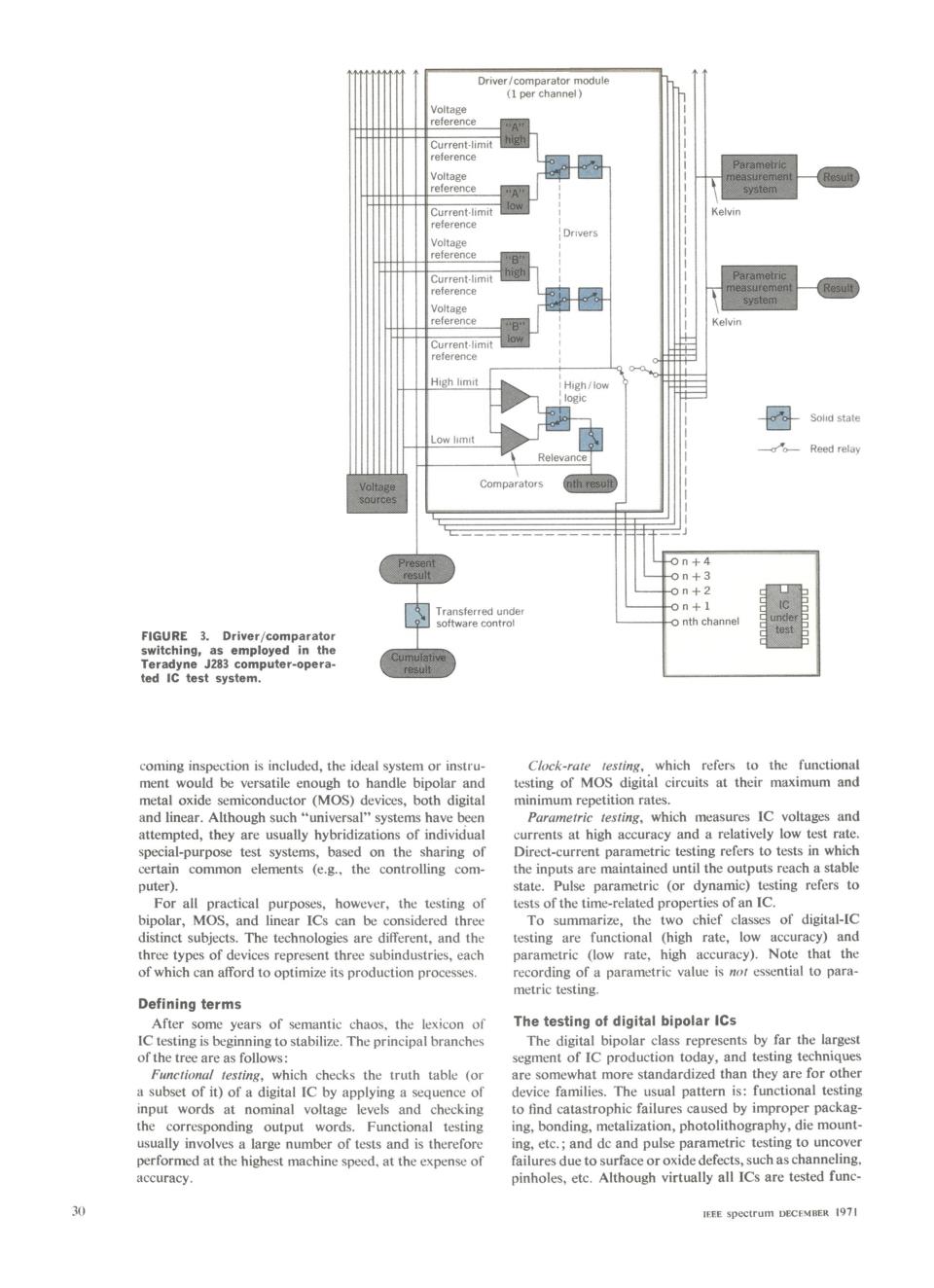
Driver/comparator module (1 per channel) Voltage reterence Current-limit hg reference Parametric Voltage measurement reference A system Current-limit Kelvin reterence Drivers Voltage reference Current-limit Parametric reterence Voltage system reference Kelvin Current-limit reference High limit High/iow logic Sold state Low limit Reed relay Relevance Voltage Comparators nth result 0n+4 0n+3 on+2 Transterred unde 0n+1 sottware contro! o nth channel FIGURE 3.Driver/comparator t switching,as employed in the Teradyne J283 computer-opera- ted Ic test system. coming inspection is included,the ideal system or instru- Clock-rate testing,which refers to the functional ment would be versatile enough to handle bipolar and testing of MOS digital circuits at their maximum and metal oxide semiconductor (MOS)devices,both digital minimum repetition rates. and linear.Although such"universal"systems have been Parametric testing,which measures IC voltages and attempted,they are usually hybridizations of individual currents at high accuracy and a relatively low test rate. special-purpose test systems,based on the sharing of Direct-current parametric testing refers to tests in which certain common elements (e.g.,the controlling com- the inputs are maintained until the outputs reach a stable puter). state.Pulse parametric (or dynamic)testing refers to For all practical purposes,however,the testing of tests of the time-related properties of an IC. bipolar,MOS,and linear ICs can be considered three To summarize,the two chief classes of digital-IC distinct subjects.The technologies are different.and the testing are functional (high rate,low accuracy)and three types of devices represent three subindustries,each parametric (low rate,high accuracy).Note that the of which can afford to optimize its production processes. recording of a parametric value is nor essential to para- metric testing. Defining terms After some years of semantic chaos,the lexicon of The testing of digital bipolar ICs IC testing is beginning to stabilize.The principal branches The digital bipolar class represents by far the largest of the tree are as follows: segment of IC production today,and testing techniques Functional testing,which checks the truth table (or are somewhat more standardized than they are for other a subset of it)of a digital IC by applying a sequence of device families.The usual pattern is:functional testing input words at nominal voltage levels and checking to find catastrophic failures caused by improper packag- the corresponding output words.Functional testing ing,bonding,metalization,photolithography,die mount- usually involves a large number of tests and is therefore ing,etc.and dc and pulse parametric testing to uncover performed at the highest machine speed,at the expense of failures due to surface or oxide defects,such as channeling accuracy. pinholes,etc.Although virtually all ICs are tested func- 30 IEEE spectrum DECEMBER 1971_-_~~~ ~( pe chanversl)eli ___reference z tv Kli Current-limit _ KlT reference Kelvin _V_oHltagehmit S w _ _ E Sobd state ....._refereance - Reed relay Transferred undee n + 1 l|software control _ nth channel _ FIGURE 3. Driver/comparator crier switching, as employed in the _ ___ Teradyne J283 computer-opera- _ ted IC test system. coming inspection is included, the ideal system or instru- Clock-rate testing, which refers to the functional ment would be versatile enough to handle bipolar and testing of MOS digitatl circuits at their maximum and metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) devices, both digital minimum repetition rates. and linear. Although such "universal" systems have been Parametric testing, which measures IC voltages and attempted, they are usually hybridizations of individual currents at high accuracy and a relatively low test rate. special-purpose test systems, based on the sharing of Direct-current parametric testing refers to tests in which certain common elements (e.g., the controlling com- the inputs are maintained until the outputs reach a stable puter). state. Pulse parametric (or dynamic) testing refers to For all practical purposes, however, the testing of tests ofthe time-related properties ofanlIC. bipolar, MOS, and linear ICs can be considered three To summarize, the two chief classes of digital-IC distinct subjects. The technologies are different, and the testing are functional (high rate, low accuracy) and three types of devices represent three subindustries, each parametric (low rate, high accuracy). Note that the of which can afford to optimize its production processes. recording of a parametric value is not essential to parametric testing. Defining terms After some years of semantic chaos, the lexicon of The testing of digital bipolar lCs IC testing is beginning to stabilize. The principal branches The digital bipolar class represents by far the largest ofthe tree are asrfollows: segment of IC production today, and testing techniques Functional testing, which checks the truth table (or are somewhat more standardized than they are for other a subset of it) of a digital IC by applying a sequence of device families. The usual pattern is: functional testing input words at nominal voltage levels and checking to find catastrophic failures caused by improper packagthe corresponding output words. Functional testing ing, bonding, metalization, photolithography, die mountusually involves a large number of tests and is therefore ing, etc.; and dc and pulse parametric testing to uncover performed at the highest machine speed, at the expense of failures due to surface or oxide defects, such as channeling. accuracy. pinholes, etc. Although virtually all ICs are tested funclogicIEEE spectrum DECEMBER t97a