正在加载图片...
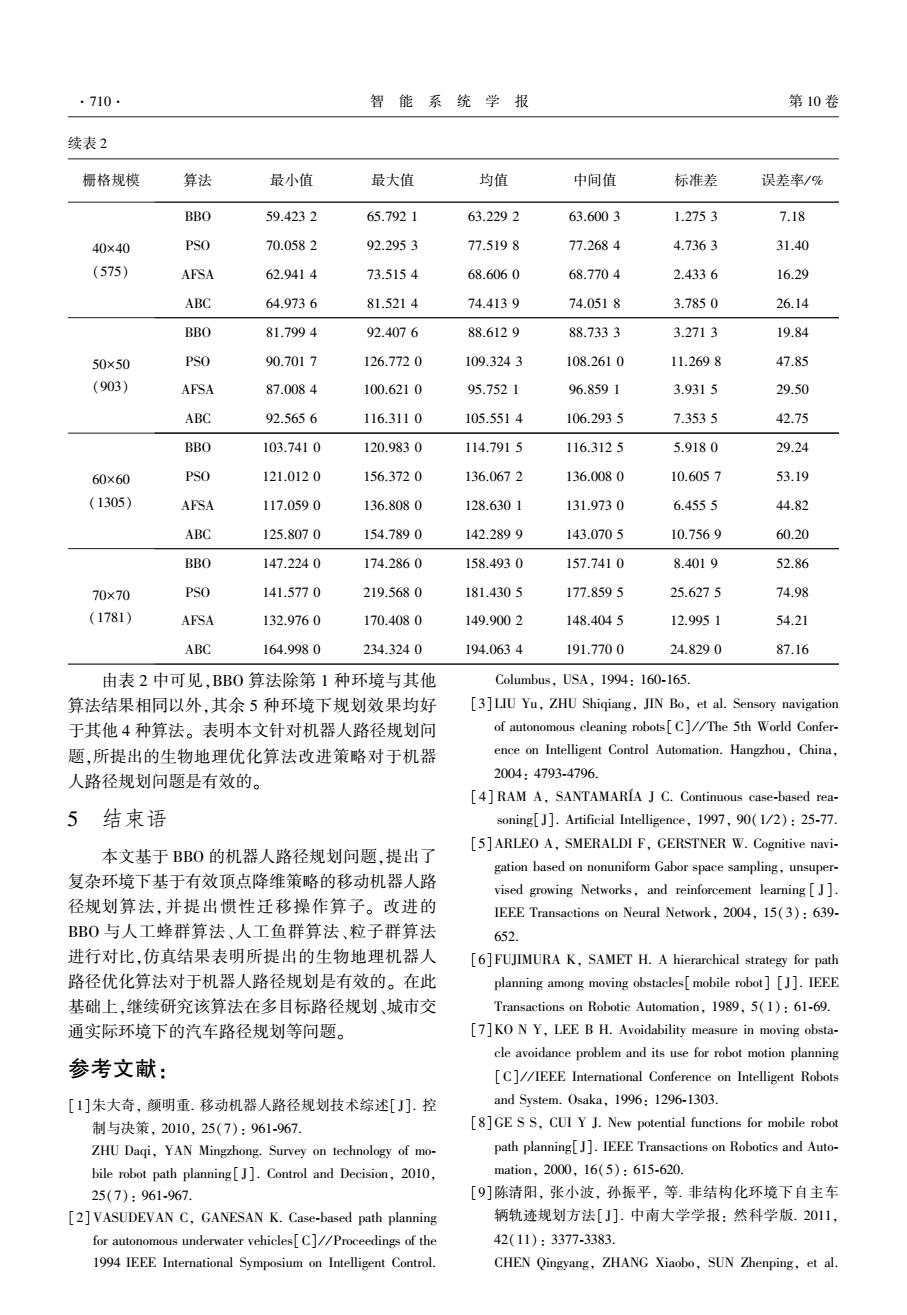
·710 智能系统学报 第10卷 续表2 栅格规模 算法 最小值 最大值 均值 中间值 标准差 误差率/% BBO 59.4232 65.7921 63.2292 63.6003 1.2753 7.18 40×40 PSO 70.0582 92.2953 77.5198 77.2684 4.7363 31.40 (575) AFSA 62.9414 73.5154 68.6060 68.7704 2.4336 16.29 ABC 64.9736 81.5214 74.4139 74.0518 3.7850 26.14 BBO 81.7994 92.4076 88.6129 88.7333 3.2713 19.84 50×50 PSO 90.7017 126.7720 109.3243 108.2610 11.2698 47.85 (903) AFSA 87.0084 100.6210 95.7521 96.8591 3.9315 29.50 ABC 92.5656 116.3110 105.5514 106.2935 7.3535 42.75 BBO 103.7410 120.9830 114.7915 116.3125 5.9180 29.24 60×60 PSO 121.0120 156.3720 136.0672 136.0080 10.6057 53.19 (1305) AFSA 117.0590 136.8080 128.6301 131.9730 6.4555 44.82 ABC 125.8070 154.7890 142.2899 143.0705 10.7569 60.20 BBO 147.2240 174.2860 158.4930 157.7410 8.4019 52.86 70×70 PSO 141.5770 219.5680 181.4305 177.8595 25.6275 74.98 (1781) AFSA 132.9760 170.4080 149.9002 148.4045 12.9951 54.21 ABC 164.9980 234.3240 194.0634 191.7700 24.8290 87.16 由表2中可见,BB0算法除第1种环境与其他 Columbus,USA,1994:160-165 算法结果相同以外,其余5种环境下规划效果均好 [3]LIU Yu,ZHU Shiqiang,JIN Bo,et al.Sensory navigation 于其他4种算法。表明本文针对机器人路径规划问 of autonomous cleaning robots[C]//The 5th World Confer- 题,所提出的生物地理优化算法改进策略对于机器 ence on Intelligent Control Automation.Hangzhou,China, 人路径规划问题是有效的。 2004:4793-4796. [4]RAM A,SANTAMARIA J C.Continuous case-based rea- 5结束语 soning[]]Artificial Intelligence,1997,90(1/2):25-77. [5]ARLEO A,SMERALDI F,GERSTNER W.Cognitive navi- 本文基于BBO的机器人路径规划问题,提出了 gation based on nonuniform Gabor space sampling,unsuper- 复杂环境下基于有效顶点降维策略的移动机器人路 vised growing Networks,and reinforcement learning[]. 径规划算法,并提出惯性迁移操作算子。改进的 IEEE Transactions on Neural Network,2004,15(3):639- BBO与人工蜂群算法、人工鱼群算法、粒子群算法 652. 进行对比,仿真结果表明所提出的生物地理机器人 [6]FUJIMURA K,SAMET H.A hierarchical strategy for path 路径优化算法对于机器人路径规划是有效的。在此 planning among moving obstacles[mobile robot][J].IEEE 基础上,继续研究该算法在多目标路径规划、城市交 Transactions on Robotic Automation,1989,5(1):61-69. 通实际环境下的汽车路径规划等问题。 [7]KO N Y,LEE B H.Avoidability measure in moving obsta- cle avoidance problem and its use for robot motion planning 参考文献: [C]//IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots [1]朱大奇,颜明重.移动机器人路径规划技术综述[J].控 and System.Osaka,1996:1296-1303. 制与决策.2010,25(7):961-967. [8]GE S S,CUI Y J.New potential functions for mobile robot ZHU Daqi,YAN Mingzhong.Survey on technology of mo- path planning[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Auto- bile robot path planning[J].Control and Decision,2010, mation,.2000,16(5):615-620. 25(7):961-967. [9]陈清阳,张小波,孙振平,等.非结构化环境下自主车 [2]VASUDEVAN C,GANESAN K.Case-based path planning 辆轨迹规划方法[J].中南大学学报:然科学版.2011, for autonomous underwater vehicles[C]//Proceedings of the 42(11):3377-3383. 1994 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control. CHEN Qingyang,ZHANG Xiaobo,SUN Zhenping,et al.续表 2 栅格规模 算法 最小值 最大值 均值 中间值 标准差 误差率/ % 40×40 (575) BBO 59.423 2 65.792 1 63.229 2 63.600 3 1.275 3 7.18 PSO 70.058 2 92.295 3 77.519 8 77.268 4 4.736 3 31.40 AFSA 62.941 4 73.515 4 68.606 0 68.770 4 2.433 6 16.29 ABC 64.973 6 81.521 4 74.413 9 74.051 8 3.785 0 26.14 50×50 (903) BBO 81.799 4 92.407 6 88.612 9 88.733 3 3.271 3 19.84 PSO 90.701 7 126.772 0 109.324 3 108.261 0 11.269 8 47.85 AFSA 87.008 4 100.621 0 95.752 1 96.859 1 3.931 5 29.50 ABC 92.565 6 116.311 0 105.551 4 106.293 5 7.353 5 42.75 60×60 (1305) BBO 103.741 0 120.983 0 114.791 5 116.312 5 5.918 0 29.24 PSO 121.012 0 156.372 0 136.067 2 136.008 0 10.605 7 53.19 AFSA 117.059 0 136.808 0 128.630 1 131.973 0 6.455 5 44.82 ABC 125.807 0 154.789 0 142.289 9 143.070 5 10.756 9 60.20 70×70 (1781) BBO 147.224 0 174.286 0 158.493 0 157.741 0 8.401 9 52.86 PSO 141.577 0 219.568 0 181.430 5 177.859 5 25.627 5 74.98 AFSA 132.976 0 170.408 0 149.900 2 148.404 5 12.995 1 54.21 ABC 164.998 0 234.324 0 194.063 4 191.770 0 24.829 0 87.16 由表 2 中可见,BBO 算法除第 1 种环境与其他 算法结果相同以外,其余 5 种环境下规划效果均好 于其他 4 种算法。 表明本文针对机器人路径规划问 题,所提出的生物地理优化算法改进策略对于机器 人路径规划问题是有效的。 5 结束语 本文基于 BBO 的机器人路径规划问题,提出了 复杂环境下基于有效顶点降维策略的移动机器人路 径规划算法,并提出惯性迁移操作算子。 改进的 BBO 与人工蜂群算法、人工鱼群算法、粒子群算法 进行对比,仿真结果表明所提出的生物地理机器人 路径优化算法对于机器人路径规划是有效的。 在此 基础上,继续研究该算法在多目标路径规划、城市交 通实际环境下的汽车路径规划等问题。 参考文献: [1]朱大奇, 颜明重. 移动机器人路径规划技术综述[ J]. 控 制与决策, 2010, 25(7): 961⁃967. ZHU Daqi, YAN Mingzhong. Survey on technology of mo⁃ bile robot path planning[ J]. Control and Decision, 2010, 25(7): 961⁃967. [2]VASUDEVAN C, GANESAN K. Case⁃based path planning for autonomous underwater vehicles[C] / / Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control. Columbus, USA, 1994: 160⁃165. [3]LIU Yu, ZHU Shiqiang, JIN Bo, et al. Sensory navigation of autonomous cleaning robots[C] / / The 5th World Confer⁃ ence on Intelligent Control Automation. Hangzhou, China, 2004: 4793⁃4796. [4] RAM A, SANTAMARÍA J C. Continuous case⁃based rea⁃ soning[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1997, 90(1 / 2): 25⁃77. [5]ARLEO A, SMERALDI F, GERSTNER W. Cognitive navi⁃ gation based on nonuniform Gabor space sampling, unsuper⁃ vised growing Networks, and reinforcement learning [ J ]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Network, 2004, 15(3): 639⁃ 652. [6]FUJIMURA K, SAMET H. A hierarchical strategy for path planning among moving obstacles[mobile robot] [J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotic Automation, 1989, 5(1): 61⁃69. [7]KO N Y, LEE B H. Avoidability measure in moving obsta⁃ cle avoidance problem and its use for robot motion planning [C] / / IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and System. Osaka, 1996: 1296⁃1303. [8]GE S S, CUI Y J. New potential functions for mobile robot path planning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Auto⁃ mation, 2000, 16(5): 615⁃620. [9]陈清阳, 张小波, 孙振平, 等. 非结构化环境下自主车 辆轨迹规划方法[ J]. 中南大学学报: 然科学版. 2011, 42(11): 3377⁃3383. CHEN Qingyang, ZHANG Xiaobo, SUN Zhenping, et al. ·710· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 10 卷