正在加载图片...
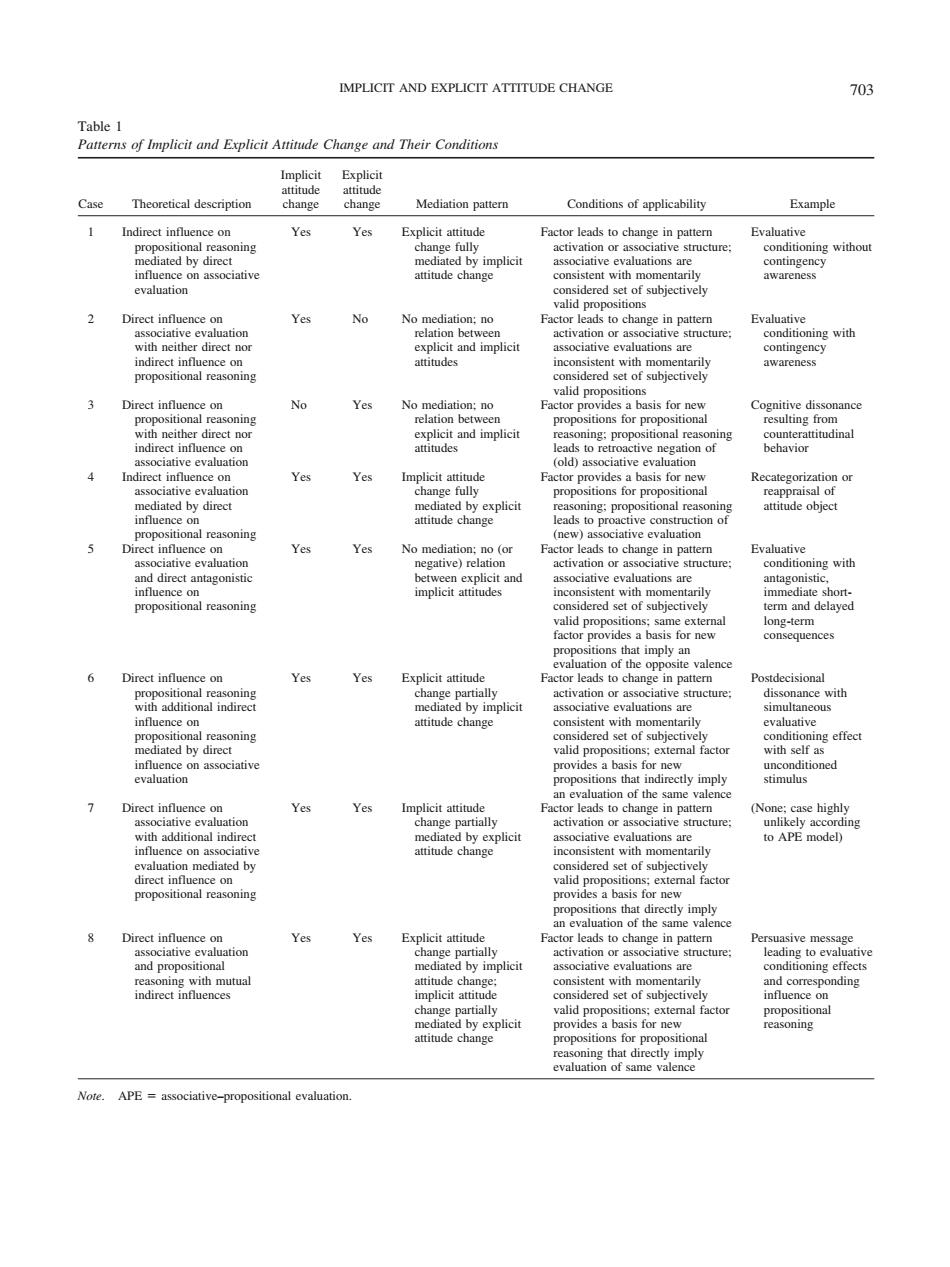
IMPLICIT AND EXPLICIT ATTITUDE CHANGE 703 Implicit Explicit Case Theoretical description change change Mediation pattern Conditions of applicability Indirect Yes Yes ning uatbrimplien luation Ne ain tions a No Yes s for prop old) Yes Yes Yes ons are Direct influence on Yes Explicit attitud lead nf ttitude chane easonin of subi of the Direct influence on Yes mplicitaitndey nal indire ons ar Yes Yes ind propo tual dered tly impl Note.APEaciative-propositionl evaluation. Table 1 Patterns of Implicit and Explicit Attitude Change and Their Conditions Case Theoretical description Implicit attitude change Explicit attitude change Mediation pattern Conditions of applicability Example 1 Indirect influence on propositional reasoning mediated by direct influence on associative evaluation Yes Yes Explicit attitude change fully mediated by implicit attitude change Factor leads to change in pattern activation or associative structure; associative evaluations are consistent with momentarily considered set of subjectively valid propositions Evaluative conditioning without contingency awareness 2 Direct influence on associative evaluation with neither direct nor indirect influence on propositional reasoning Yes No No mediation; no relation between explicit and implicit attitudes Factor leads to change in pattern activation or associative structure; associative evaluations are inconsistent with momentarily considered set of subjectively valid propositions Evaluative conditioning with contingency awareness 3 Direct influence on propositional reasoning with neither direct nor indirect influence on associative evaluation No Yes No mediation; no relation between explicit and implicit attitudes Factor provides a basis for new propositions for propositional reasoning; propositional reasoning leads to retroactive negation of (old) associative evaluation Cognitive dissonance resulting from counterattitudinal behavior 4 Indirect influence on associative evaluation mediated by direct influence on propositional reasoning Yes Yes Implicit attitude change fully mediated by explicit attitude change Factor provides a basis for new propositions for propositional reasoning; propositional reasoning leads to proactive construction of (new) associative evaluation Recategorization or reappraisal of attitude object 5 Direct influence on associative evaluation and direct antagonistic influence on propositional reasoning Yes Yes No mediation; no (or negative) relation between explicit and implicit attitudes Factor leads to change in pattern activation or associative structure; associative evaluations are inconsistent with momentarily considered set of subjectively valid propositions; same external factor provides a basis for new propositions that imply an evaluation of the opposite valence Evaluative conditioning with antagonistic, immediate shortterm and delayed long-term consequences 6 Direct influence on propositional reasoning with additional indirect influence on propositional reasoning mediated by direct influence on associative evaluation Yes Yes Explicit attitude change partially mediated by implicit attitude change Factor leads to change in pattern activation or associative structure; associative evaluations are consistent with momentarily considered set of subjectively valid propositions; external factor provides a basis for new propositions that indirectly imply an evaluation of the same valence Postdecisional dissonance with simultaneous evaluative conditioning effect with self as unconditioned stimulus 7 Direct influence on associative evaluation with additional indirect influence on associative evaluation mediated by direct influence on propositional reasoning Yes Yes Implicit attitude change partially mediated by explicit attitude change Factor leads to change in pattern activation or associative structure; associative evaluations are inconsistent with momentarily considered set of subjectively valid propositions; external factor provides a basis for new propositions that directly imply an evaluation of the same valence (None; case highly unlikely according to APE model) 8 Direct influence on associative evaluation and propositional reasoning with mutual indirect influences Yes Yes Explicit attitude change partially mediated by implicit attitude change; implicit attitude change partially mediated by explicit attitude change Factor leads to change in pattern activation or associative structure; associative evaluations are consistent with momentarily considered set of subjectively valid propositions; external factor provides a basis for new propositions for propositional reasoning that directly imply evaluation of same valence Persuasive message leading to evaluative conditioning effects and corresponding influence on propositional reasoning Note. APE associative–propositional evaluation. IMPLICIT AND EXPLICIT ATTITUDE CHANGE 703