正在加载图片...
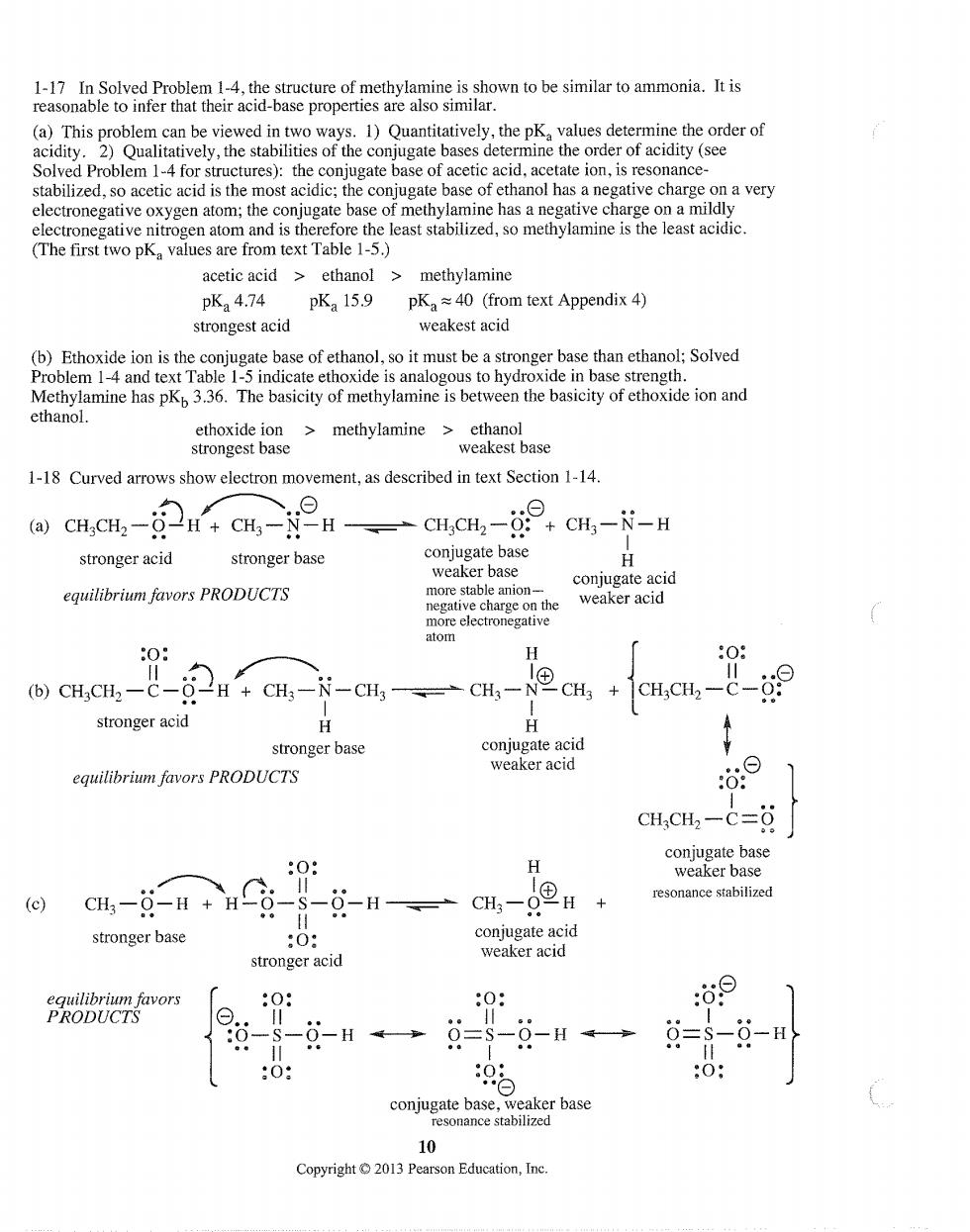
1-17 In Solved Problem 1-4,the structure of methylamine is shown to be similar to ammonia.It is reasonable to infer that their acid-base properties are also similar. rate bases determine the order of acidity (see Solved Problem 1-4 for structures):the conjugate base of acetic acid,acetate ion,is resonance- stabilized.so acetic acid is the most acidic:the conjugate base of ethanol has a negative charge on a very electronegative oxygen atom;the conjugate base of methylamine has a negative charge on a mildly electronegative nitrogen atom and is therefore the least stabilized,so methylamine is the least acidic. (The first two pK values are from text Table 1-5.) acetic acid>ethanol>methylamine pK24.74 pKa 15.9 pK40 (from text Appendix 4) strongest acid weakest acid (b)Ethoxide ion is the conjugate base of ethanol,so it must be a stronger base than ethanol;Solved Problem 1-4 and text Table 1-5 indicate ethoxide is analogous to hydroxide in base strength. Methylamine has pKp3.36.The basicity of methylamine is between the basicity of ethoxide ion and ethanol. ethoxide ion>methylamine cthanol strongest base weakest base 1-18 Curved arrows show electron movement,as described in text Section 1-14 CH.CH,CH-cH.cH CH-- stronger acid stronger base conjugat conjugate acid equilibrium favors PRODUCTS weaker acid 0: L (b)CHCH2一C-O CHs-N-CH- +cmcu,-- stronger acid H stronger base conjugate acid equilibrium favors PRODUCTS weaker acid CH.CH2-c=8 H resonance stabilized (c) CH,-g-H+H stronger base 0 conjugate acid stronger acid weaker acid 0 :0: 09 --H←→=-9-H→ g=-- 9.e :0: ) eaker base 10 Copyright01 Pearson Education,Ine