
Outline Accessing SQL From a Programming Language Functions and Procedures ■Triggers ■Recursive Queries Advanced Aggregation Features Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.2 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Outline ▪ Accessing SQL From a Programming Language ▪ Functions and Procedures ▪ Triggers ▪ Recursive Queries ▪ Advanced Aggregation Features

Accessing SQL from a Programming Language A database programmer must have access to a general-purpose programming language for at least two reasons Not all queries can be expressed in SQL,since SQL does not provide the full expressive power of a general-purpose language. 图 Non-declarative actions--such as printing a report,interacting with a user,or sending the results of a query to a graphical user interface-- cannot be done from within SQL. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.3 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Accessing SQL from a Programming Language ▪ Not all queries can be expressed in SQL, since SQL does not provide the full expressive power of a general-purpose language. ▪ Non-declarative actions -- such as printing a report, interacting with a user, or sending the results of a query to a graphical user interface -- cannot be done from within SQL. A database programmer must have access to a general-purpose programming language for at least two reasons

Accessing SQL from a Programming Language(Cont.) There are two approaches to accessing SQL from a general-purpose programming language A general-purpose program --can connect to and communicate with a database server using a collection of functions Embedded SQL--provides a means by which a program can interact with a database server. The SQL statements are translated at compile time into function calls. At runtime,these function calls connect to the database using an API that provides dynamic SQL facilities. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.4 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Accessing SQL from a Programming Language (Cont.) ▪ A general-purpose program -- can connect to and communicate with a database server using a collection of functions ▪ Embedded SQL -- provides a means by which a program can interact with a database server. • The SQL statements are translated at compile time into function calls. • At runtime, these function calls connect to the database using an API that provides dynamic SQL facilities. There are two approaches to accessing SQL from a general-purpose programming language
JDBC Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC
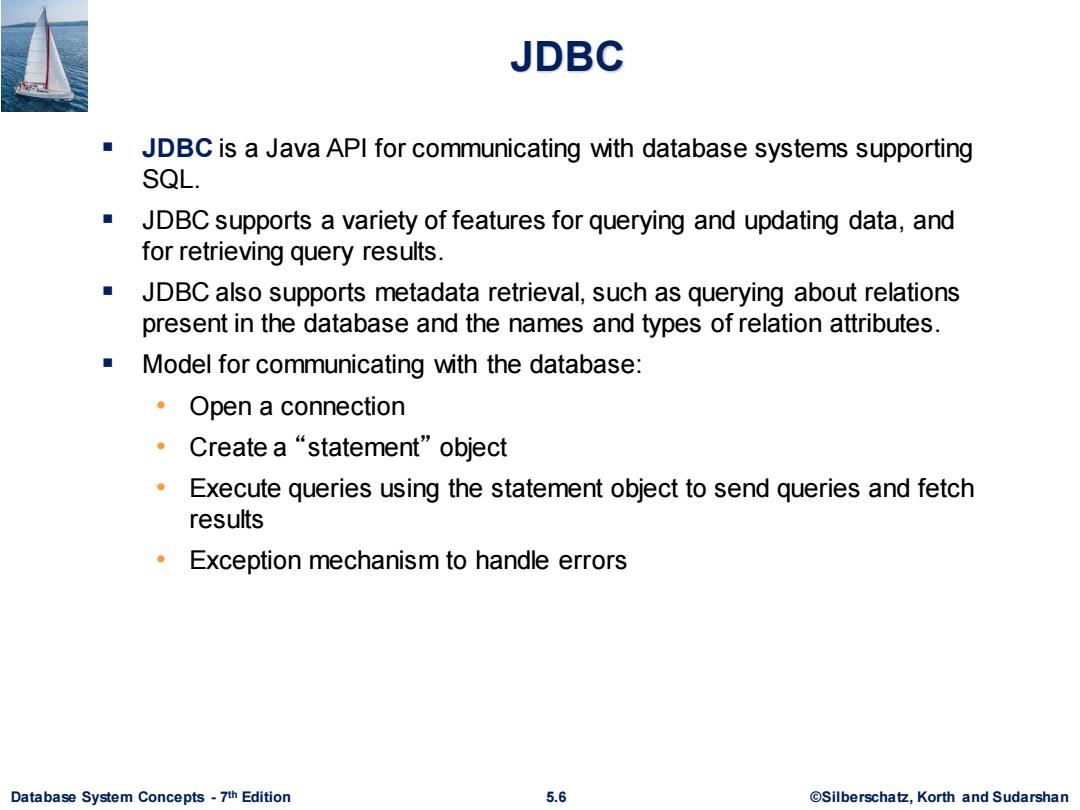
JDBC JDBC is a Java API for communicating with database systems supporting SQL. ■ JDBC supports a variety of features for querying and updating data,and for retrieving query results. JDBC also supports metadata retrieval,such as querying about relations present in the database and the names and types of relation attributes. Model for communicating with the database: ·Open a connection ·Create a“statement'”object Execute queries using the statement object to send queries and fetch results Exception mechanism to handle errors Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.6 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC ▪ JDBC is a Java API for communicating with database systems supporting SQL. ▪ JDBC supports a variety of features for querying and updating data, and for retrieving query results. ▪ JDBC also supports metadata retrieval, such as querying about relations present in the database and the names and types of relation attributes. ▪ Model for communicating with the database: • Open a connection • Create a “statement” object • Execute queries using the statement object to send queries and fetch results • Exception mechanism to handle errors
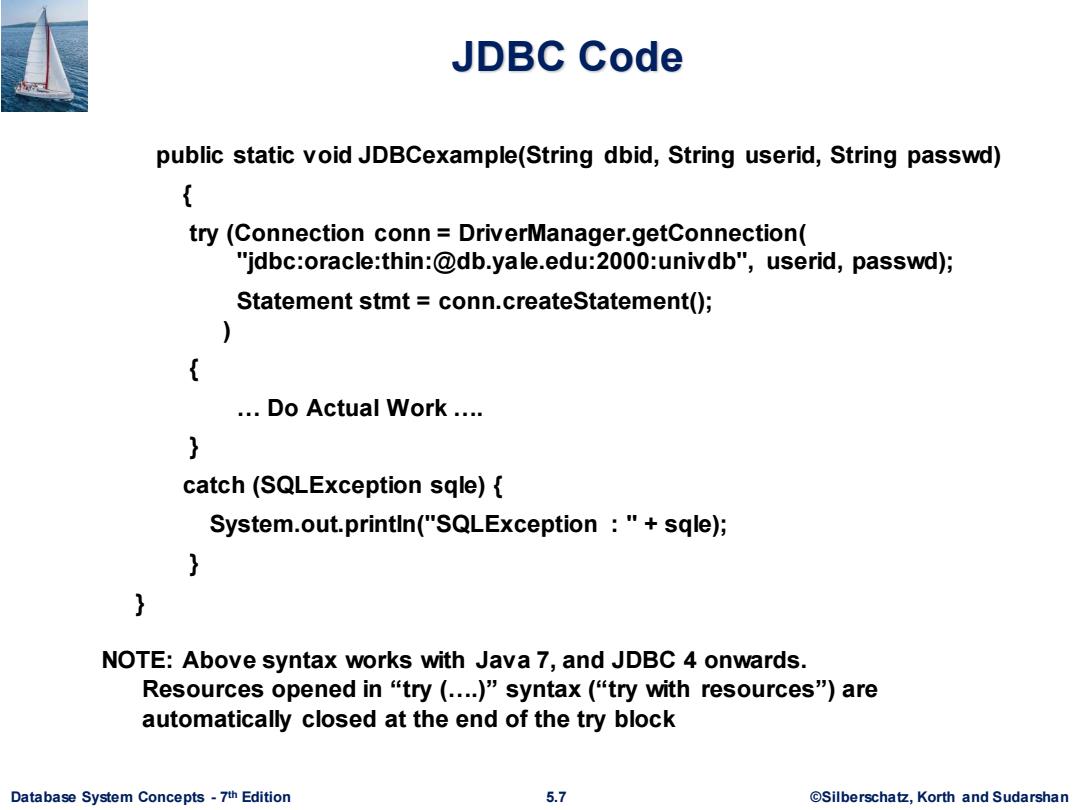
JDBC Code public static void JDBCexample(String dbid,String userid,String passwd) try (Connection conn DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:oracle:thin:@db.yale.edu:2000:univdb",userid,passwd); Statement stmt conn.createStatement(); ..Do Actual Work ... catch(SQLException sqle){ System.out.println("SQLException "sqle); NOTE:Above syntax works with Java 7,and JDBC 4 onwards. Resources opened in“try(..)”syntax(“try with resources")are automatically closed at the end of the try block Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.7 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC Code public static void JDBCexample(String dbid, String userid, String passwd) { try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:oracle:thin:@db.yale.edu:2000:univdb", userid, passwd); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); ) { … Do Actual Work …. } catch (SQLException sqle) { System.out.println("SQLException : " + sqle); } } NOTE: Above syntax works with Java 7, and JDBC 4 onwards. Resources opened in “try (….)” syntax (“try with resources”) are automatically closed at the end of the try block

JDBC Code for Older Versions of Java/JDBC public static void JDBCexample(String dbid,String userid,String passwd) { try Class.forName ("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); Connection conn DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:oracle:thin:@db.yale.edu:2000:univdb",userid,passwd); Statement stmt conn.createStatement(); ..Do Actual Work.... stmt.close(); conn.close(); catch(SQLException sqle){ System.out.println("SQLException "sqle); NOTE:Class.forName is not required from JDBC 4 onwards.The try with resources syntax in prev slide is preferred for Java 7 onwards. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.8 Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC Code for Older Versions of Java/JDBC public static void JDBCexample(String dbid, String userid, String passwd) { try { Class.forName ("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:oracle:thin:@db.yale.edu:2000:univdb", userid, passwd); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); … Do Actual Work …. stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (SQLException sqle) { System.out.println("SQLException : " + sqle); } } NOTE: Class.forName is not required from JDBC 4 onwards. The try with resources syntax in prev slide is preferred for Java 7 onwards
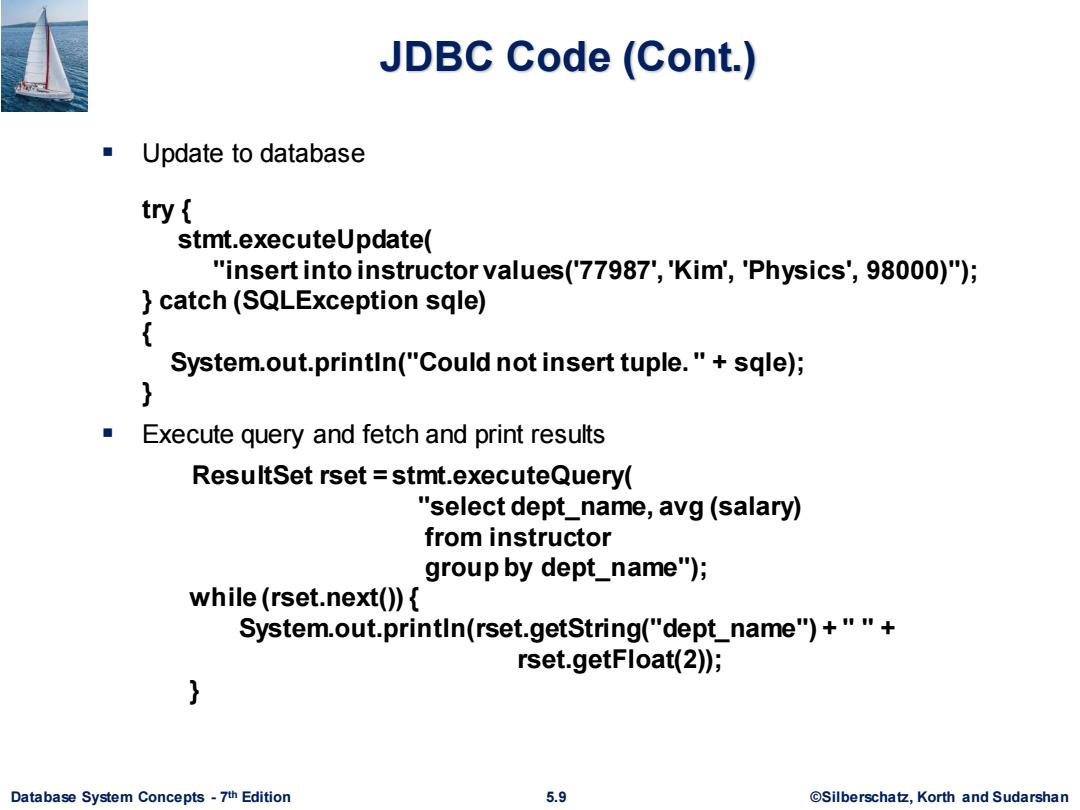
JDBC Code(Cont.) Update to database try stmt.executeUpdate( "insert into instructor values('77987','Kim','Physics',98000)"); catch(SQLException sqle) System.out.println("Could not insert tuple."+sqle); } Execute query and fetch and print results ResultSet rset =stmt.executeQuery( "select dept_name,avg (salary) from instructor group by dept_name"); while(rset.next()){ System.out.println(rset.getString("dept_name")+""+ rset.getFloat(2)); } Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.9 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC Code (Cont.) ▪ Update to database try { stmt.executeUpdate( "insert into instructor values('77987', 'Kim', 'Physics', 98000)"); } catch (SQLException sqle) { System.out.println("Could not insert tuple. " + sqle); } ▪ Execute query and fetch and print results ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery( "select dept_name, avg (salary) from instructor group by dept_name"); while (rset.next()) { System.out.println(rset.getString("dept_name") + " " + rset.getFloat(2)); }

JDBC SUBSECTIONS Connecting to the Database Shipping SQL Statements to the Database System Exceptions and Resource Management Retrieving the Result of a Query Prepared Statements ■ Callable Statements Metadata Features ■ Other Features Database Access from Python Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.10 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC SUBSECTIONS ▪ Connecting to the Database ▪ Shipping SQL Statements to the Database System ▪ Exceptions and Resource Management ▪ Retrieving the Result of a Query ▪ Prepared Statements ▪ Callable Statements ▪ Metadata Features ▪ Other Features ▪ Database Access from Python

JDBC Code Details ■Getting result fields: 9 rs.getString("dept_name")and rs.getString(1)equivalent if dept_name is the first argument of select result. Dealing with Null values inta rs.getint("a"); if(rs.wasNull())Systems.out.println("Got null value"); Database System Concepts-7th Edition 5.11 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 5.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition JDBC Code Details ▪ Getting result fields: • rs.getString(“dept_name”) and rs.getString(1) equivalent if dept_name is the first argument of select result. ▪ Dealing with Null values int a = rs.getInt(“ a ”); if (rs.wasNull()) Systems.out.println(“Got null value”);