
Chapter 31:Information Retrieval Database System Concepts,7th Ed. @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use
Database System Concepts, 7th Ed. ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Chapter 31: Information Retrieval

Outline Relevance Ranking Using Terms Relevance Using Hyperlinks Synonyms.,Homonyms,and Ontologies Indexing of Documents Measuring Retrieval Effectiveness ■Veb Search Engines Information Retrieval and Structured Data Directories Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.2 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Outline ▪ Relevance Ranking Using Terms ▪ Relevance Using Hyperlinks ▪ Synonyms., Homonyms, and Ontologies ▪ Indexing of Documents ▪ Measuring Retrieval Effectiveness ▪ Web Search Engines ▪ Information Retrieval and Structured Data ▪ Directories

Information Retrieval Systems Information retrieval(IR)systems use a simpler data model than database systems Information organized as a collection of documents Documents are unstructured,no schema Information retrieval locates relevant documents,on the basis of user input such as keywords or example documents ·e.g.,find documents containing the words“database systems” Can be used even on textual descriptions provided with non-textual data such as images Web search engines are the most familiar example of IR systems Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.3 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Information Retrieval Systems ▪ Information retrieval (IR) systems use a simpler data model than database systems • Information organized as a collection of documents • Documents are unstructured, no schema ▪ Information retrieval locates relevant documents, on the basis of user input such as keywords or example documents • e.g., find documents containing the words “database systems” ▪ Can be used even on textual descriptions provided with non-textual data such as images ▪ Web search engines are the most familiar example of IR systems
Information Retrieval Systems (Cont.) Differences from database systems IR systems don't deal with transactional updates (including concurrency control and recovery) 。 Database systems deal with structured data,with schemas that define the data organization IR systems deal with some querying issues not generally addressed by database systems Approximate searching by keywords Ranking of retrieved answers by estimated degree of relevance Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.4 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Information Retrieval Systems (Cont.) ▪ Differences from database systems • IR systems don’t deal with transactional updates (including concurrency control and recovery) • Database systems deal with structured data, with schemas that define the data organization • IR systems deal with some querying issues not generally addressed by database systems ▪ Approximate searching by keywords ▪ Ranking of retrieved answers by estimated degree of relevance

Keyword Search In full text retrieval,all the words in each document are considered to be keywords. We use the word term to refer to the words in a document Information-retrieval systems typically allow query expressions formed using keywords and the logical connectives and,or,and not Ands are implicit,even if not explicitly specified Ranking of documents on the basis of estimated relevance to a query is critical Relevance ranking is based on factors such as Term frequency -Frequency of occurrence of query keyword in document Inverse document frequency -How many documents the query keyword occurs in 》Fewer→give more importance to keyword Hyperlinks to documents -More links to a document>document is more important Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.5 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Keyword Search ▪ In full text retrieval, all the words in each document are considered to be keywords. • We use the word term to refer to the words in a document ▪ Information-retrieval systems typically allow query expressions formed using keywords and the logical connectives and, or, and not • Ands are implicit, even if not explicitly specified ▪ Ranking of documents on the basis of estimated relevance to a query is critical • Relevance ranking is based on factors such as Term frequency – Frequency of occurrence of query keyword in document Inverse document frequency – How many documents the query keyword occurs in » Fewer ➔ give more importance to keyword Hyperlinks to documents – More links to a document ➔ document is more important
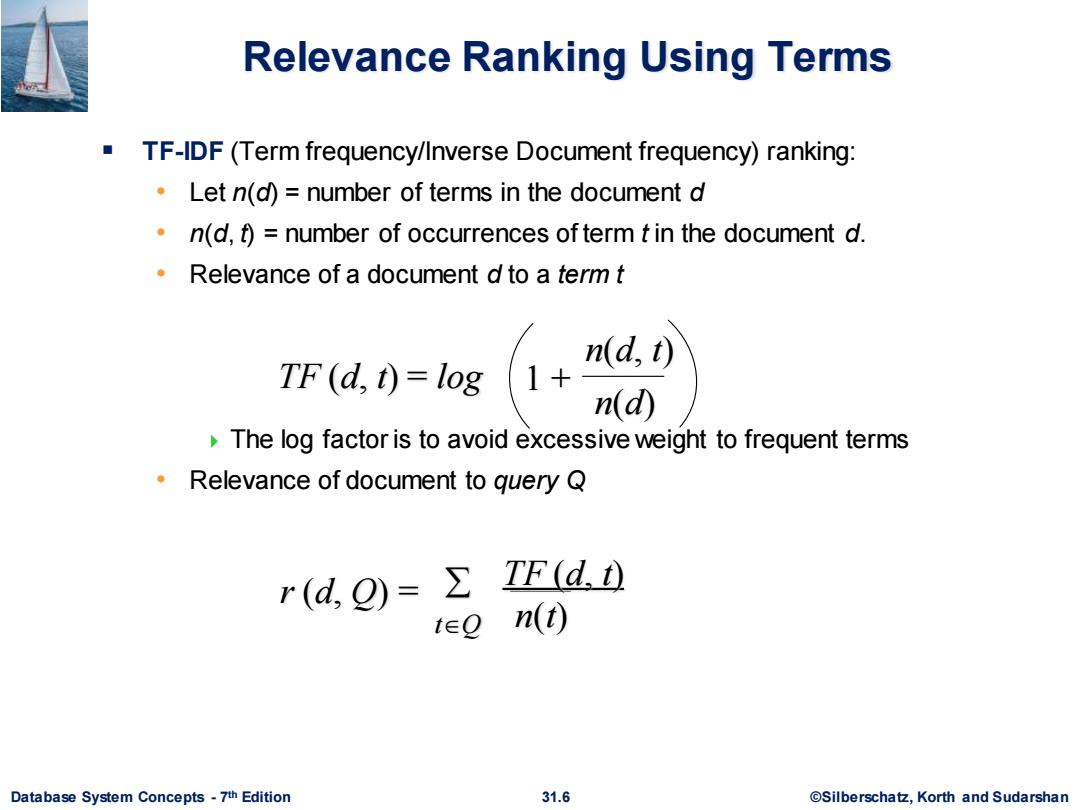
Relevance Ranking Using Terms TF-IDF (Term frequency/Inverse Document frequency)ranking: Let n(d)=number of terms in the document d n(d,)number of occurrences ofterm t in the document d. Relevance of a document d to a term t n(d,t) TF (d,t)=log 1+ n(d) The log factor is to avoid excessive weight to frequent terms Relevance of document to query Q r(d,Q)=∑ TF(d.t) t∈Q n(t) Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relevance Ranking Using Terms ▪ TF-IDF (Term frequency/Inverse Document frequency) ranking: • Let n(d) = number of terms in the document d • n(d, t) = number of occurrences of term t in the document d. • Relevance of a document d to a term t The log factor is to avoid excessive weight to frequent terms • Relevance of document to query Q n(d) n(d, t) TF (d, t) = log 1 + r (d, Q) = TF (d, t) tQ n(t)

Relevance Ranking Using Terms(Cont.) Most systems add to the above model Words that occur in title,author list,section headings,etc.are given greater importance Words whose first occurrence is late in the document are given lower importance ·Very common words such as“a”,“an”,“the”,“it'etc.are eliminated Called stop words Proximity:if keywords in query occur close together in the document, the document has higher importance than if they occur far apart Documents are returned in decreasing order of relevance score Usually only top few documents are returned,not all Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.7 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relevance Ranking Using Terms (Cont.) ▪ Most systems add to the above model • Words that occur in title, author list, section headings, etc. are given greater importance • Words whose first occurrence is late in the document are given lower importance • Very common words such as “a”, “an”, “the”, “it” etc. are eliminated ▪ Called stop words • Proximity: if keywords in query occur close together in the document, the document has higher importance than if they occur far apart ▪ Documents are returned in decreasing order of relevance score • Usually only top few documents are returned, not all

Similarity Based Retrieval Similarity based retrieval-retrieve documents similar to a given document Similarity may be defined on the basis of common words E.g.,find k terms in A with highest TF(d,t)/n (t)and use these terms to find relevance of other documents. Relevance feedback:Similarity can be used to refine answer set to keyword query User selects a few relevant documents from those retrieved by keyword query,and system finds other documents similar to these Vector space model:define an n-dimensional space,where n is the number of words in the document set. Vector for document d goes from origin to a point whose i th coordinate is TF(d,t)/n(t) The cosine of the angle between the vectors of two documents is used as a measure of their similarity. Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.8 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Similarity Based Retrieval ▪ Similarity based retrieval - retrieve documents similar to a given document • Similarity may be defined on the basis of common words ▪ E.g., find k terms in A with highest TF (d, t ) / n (t ) and use these terms to find relevance of other documents. ▪ Relevance feedback: Similarity can be used to refine answer set to keyword query • User selects a few relevant documents from those retrieved by keyword query, and system finds other documents similar to these ▪ Vector space model: define an n-dimensional space, where n is the number of words in the document set. • Vector for document d goes from origin to a point whose i th coordinate is TF (d,t ) / n (t ) • The cosine of the angle between the vectors of two documents is used as a measure of their similarity

Relevance Using Hyperlinks Number of documents relevant to a query can be enormous if only term frequencies are taken into account ■Using term frequencies makes“spamming”easy E.g.,a travel agency can add many occurrences of the words "travel"to its page to make its rank very high Most of the time people are looking for pages from popular sites Idea:use popularity of Web site (e.g.,how many people visit it)to rank site pages that match given keywords Problem:hard to find actual popularity of site ·Solution:next slide Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.9 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relevance Using Hyperlinks ▪ Number of documents relevant to a query can be enormous if only term frequencies are taken into account ▪ Using term frequencies makes “spamming” easy ▪ E.g., a travel agency can add many occurrences of the words “travel” to its page to make its rank very high ▪ Most of the time people are looking for pages from popular sites ▪ Idea: use popularity of Web site (e.g., how many people visit it) to rank site pages that match given keywords ▪ Problem: hard to find actual popularity of site • Solution: next slide

Relevance Using Hyperlinks (Cont.) Solution:use number of hyperlinks to a site as a measure of the popularity or prestige of the site Count only one hyperlink from each site (why?-see previous slide) Popularity measure is for site,not for individual page But,most hyperlinks are to root of site Also,concept of"site"difficult to define since a URL prefix like cs.yale.edu contains many unrelated pages of varying popularity ■Refinements When computing prestige based on links to a site,give more weight to links from sites that themselves have higher prestige Definition is circular Set up and solve system of simultaneous linear equations Above idea is basis of the Google PageRank ranking mechanism Database System Concepts-7th Edition 31.10 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 31.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Relevance Using Hyperlinks (Cont.) ▪ Solution: use number of hyperlinks to a site as a measure of the popularity or prestige of the site • Count only one hyperlink from each site (why? - see previous slide) • Popularity measure is for site, not for individual page ▪ But, most hyperlinks are to root of site ▪ Also, concept of “site” difficult to define since a URL prefix like cs.yale.edu contains many unrelated pages of varying popularity ▪ Refinements • When computing prestige based on links to a site, give more weight to links from sites that themselves have higher prestige ▪ Definition is circular ▪ Set up and solve system of simultaneous linear equations • Above idea is basis of the Google PageRank ranking mechanism