
9 同济大学 经济与管理学院 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply 昵图闻www.nipic,com8r,y228o
Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply >>>Agenda ● Money Demand ● Theories of Money Demand ●】 Money Supply Theories of Money Supply ●】 2 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 2 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY Money Demand Theories of Money Demand Money Supply Theories of Money Supply Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply Agenda
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply 》》 Implication of Money Demand 1 Definition Money Demand Money demand refers to the need that people are willing to hold their income and assets in the form of money. Nominal money demand and real money demand real money demand=nominal money demand/price index Macro and micro money demand Subjective money demand and objective money demand 3 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 3 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Implication of Money Demand Money Demand Money demand refers to the need that people are willing to hold their income and assets in the form of money. Definition Nominal money demand and real money demand real money demand=nominal money demand/ price index Macro and micro money demand Subjective money demand and objective money demand Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply 》》 Factors that Determine the Demand for Money 1 the level of interest rates and financing conditions Money Demand Yields and investment environment the expectation of inflation and price level the income level and techniques of managing finance the velocity of money foreign interest rate the efficiency of the financial markets and transaction costs 4 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 4 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1 Factors that Determine the Demand for Money Money Demand the level of interest rates and financing conditions Yields and investment environment the expectation of inflation and price level the income level and techniques of managing finance the velocity of money the efficiency of the financial markets and transaction costs foreign interest rate Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply >>The Classical Theories of Money Demand 2 Theories of Money Demand 大卫,李嘉图 约翰·洛克 大卫·休谟 弗朗斯瓦·魁奈 大卫·李嘉图 5 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 5 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 2 The Classical Theories of Money Demand Theories of Money Demand Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply 约翰·洛克 大卫·休谟 弗朗斯瓦•魁奈 大卫·李嘉图

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply >>>The Classical Theories of Money Demand 2 The classical quantity theories of money demand Fisher's Equation of Exchange:MV=PT Theories of Money Demand The Cambridge cash-balance approach Md=kPY 6 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 6 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 2 The classical quantity theories of money demand Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply Theories of Money Demand The Classical Theories of Money Demand Fisher’s Equation of Exchange: MV=PT The Cambridge cash-balance approach : Md=kPY
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply >>Keynesian theory of Money Demand 2 (1)持有货币的三种动机 Theories of Money Demand 交易动机:为交易需要持有货币 预防动机:预防意料之外的支出 投机动机:为投机活动持有货币 (2)M=M1+M2=L1(Y)+L2(①) 7 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 7 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 2Theories of Money Demand Keynesian theory of Money Demand (2)M=M1+M2=L1 (Y)+L2 (i) (1)持有货币的三种动机 交易动机:为交易需要持有货币 预防动机:预防意料之外的支出 投机动机:为投机活动持有货币 Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply
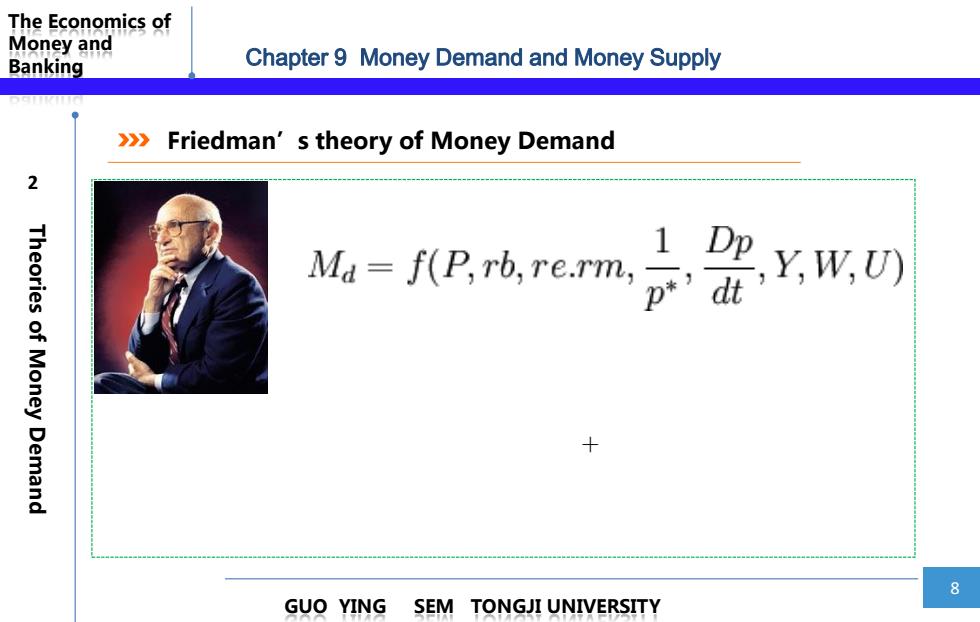
The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply 》》 Friedman's theory of Money Demand 2 Theories of Money Demand MP.rb.re.rm 1 Dp,Y,W,U) 8 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 8 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 2Theories of Money Demand Friedman’s theory of Money Demand + Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply >>>Quantity of Money Supply and Some Concepts Relating to it 3 Money stock and money flow Money Supply Money stock refers to the quantity of the money supply at a given point of time,while money flow is the total turnover of money calculated during a certain period. Money stock is often called balance while money flow is called turnover ■Mflow=Mstock*V 9 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 9 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 3Money Supply Quantity of Money Supply and Some Concepts Relating to it Money stock and money flow Money stock refers to the quantity of the money supply at a given point of time, while money flow is the total turnover of money calculated during a certain period. Money stock is often called balance while money flow is called turnover Mflow = Mstock * V Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply

The Economics of Money and Banking Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply 》》 Quantity of Money Supply and Some Concepts Relating to it 3 Nominal money supply and real money supply ■Mrs=Ms/P Exogenous and endogenous money supply The endogenous money supply refers to the case that money supply depends on real variables in an economic system,such as income,savings,investment,etc.rather than on monetary authorities. The exogenous money supply refers to the case that money supply is the subject to monetary policy of monetary authorities to a large extent. 10 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY
The Economics of Money and Banking 10 GUO YING SEM TONGJI UNIVERSITY 3Money Supply Quantity of Money Supply and Some Concepts Relating to it Nominal money supply and real money supply Mrs = Ms /P Exogenous and endogenous money supply The endogenous money supply refers to the case that money supply depends on real variables in an economic system, such as income, savings ,investment, etc. rather than on monetary authorities. The exogenous money supply refers to the case that money supply is the subject to monetary policy of monetary authorities to a large extent. Chapter 9 Money Demand and Money Supply