
Introduction To Digital Signal Processing 主讲:张君 上游克大学
Introduction To Digital Signal Processing 主讲:张君
Block processing algorithms Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution Direct Form Convolution Table *LTI Form Matrix Form Flip-and-Slip Form Overlap-and Block Convolution Form 上浒充通大粤
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution Block processing algorithms Direct Form Convolution Table LTI Form Matrix Form Flip-and-Slip Form Overlap-and Block Convolution Form
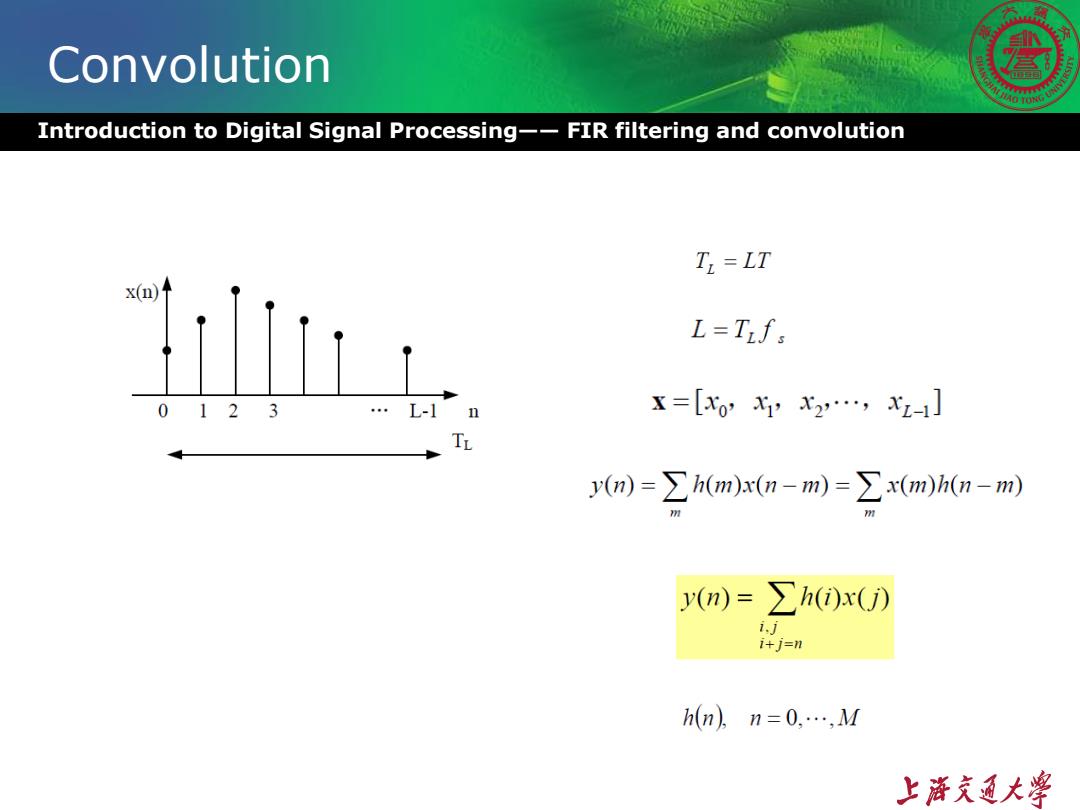
Convolution Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution T=LT x(n)↑ L=TLf: 012 …L-1 x=[xox,x2,,x-] TL y(m)=∑hm)ax(n-m)=∑r(m)h(n-m) yn)=∑h()x(U) i.j i+j=n h(n),n=0,…,M 上游充通大¥
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution Convolution
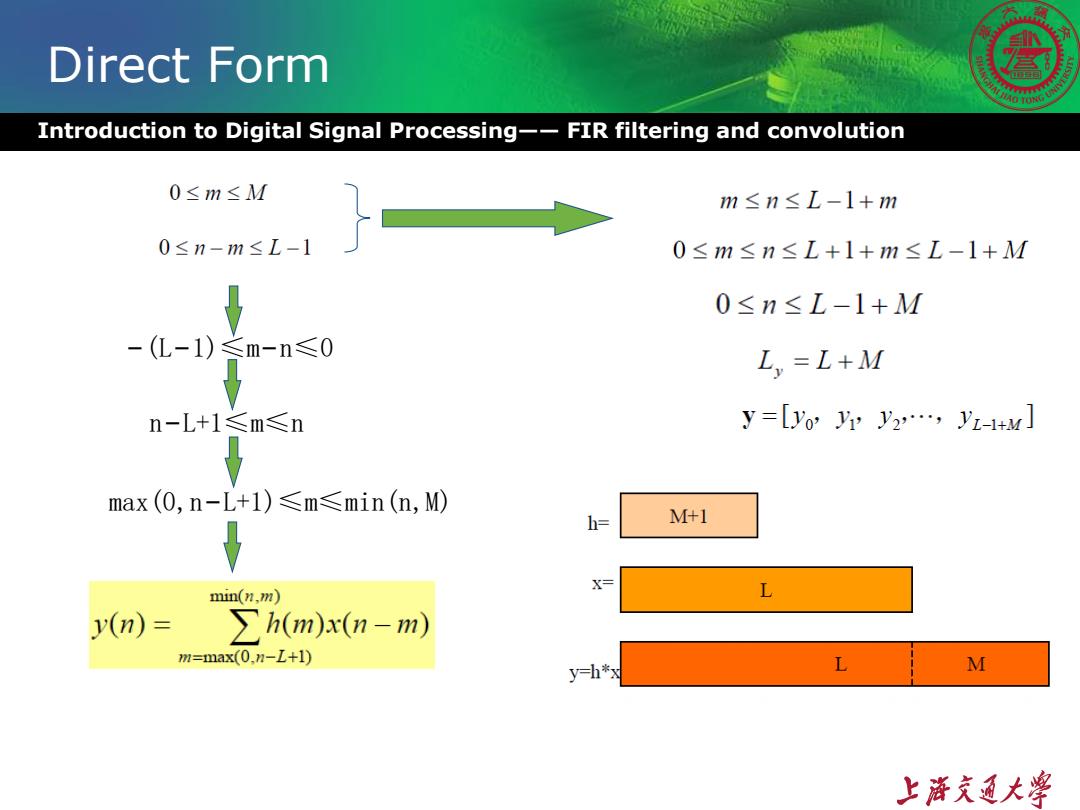
Direct Form Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution 0≤m≤M m≤n≤L-1+m 0≤n-m≤L-1 0≤m≤n≤L+1+m≤L-1+M 0≤n≤L-1+M -(L-1)≤m-n≤0 L =L+M n-L+1≤m≤n y=[yo yy y2,,y-tu max(0,n-L+l)≤m≤min(n,M) h= M+1 X= min(n,m) L y(n)= ∑h(m)x(n-m) m=max(0.n-L+1) y=h*x L M 上游充通大¥
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution Direct Form −(L−1)≤m−n≤0 n−L+1≤m≤n max(0,n−L+1)≤m≤min(n,M)
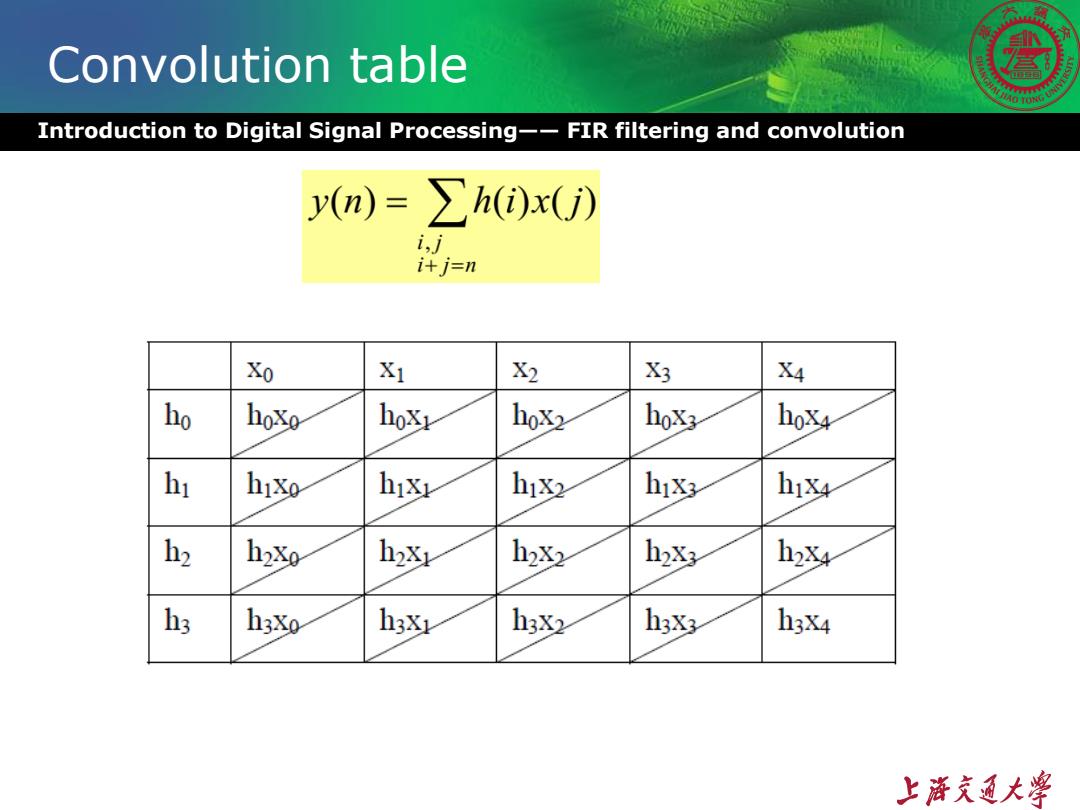
Convolution table Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution y(n)=∑h(i)x(ji》 i,j i+j=n Xo X1 X2 X3 X4 ho hoxo hoxr hox2 hox, hox4 hi hiXo hixr hixz hix h1&4 h2 h2Xo h2xr h2X2 h2X3 h2X4 h3 h3Xo h38 h3X2 h3x3 h3x4 上游充通大¥
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution Convolution table

LTI form Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution ho h h2 h3 0 0 0 0 Xo xoho xohi Xoh2 Xoh3 0 0 0 0 X1 0 Xi ho Xihi X1 h2 Xi h3 0 0 0 X2 0 0 X2 ho X2 hi X2 h2 X2 h3 0 0 83 0 0 0 x3 ho X3 hi 3h2 &h3 0 X4 0 0 0 0 X4 ho X4hi X4 h2 X4h3 yo yi y2 y3 y4 ys y6 y1 上游充通大¥
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution LTI form
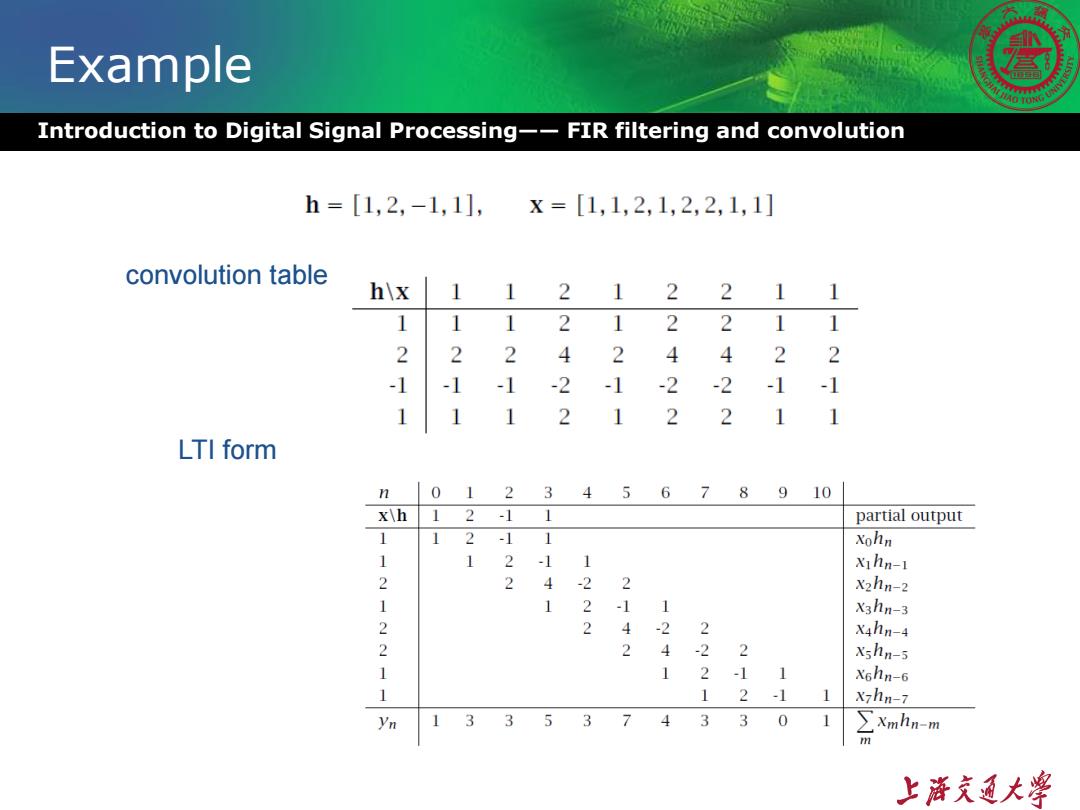
Example Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution h=[1,2,-1,1],X=[1,1,2,1,2,2,1,1] convolution table h\x1 12 12 21 1 1 1 12 122 11 2 2 2 4 2 4 4 2 2 -1 -1 -2 -1 -2 -2 -1 -1 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 LTI form n 0 123456 7 9 10 x\h 2 -1 1 partial output 1 1 2 -1 1 Xohn 1 1 2 -1 x1hn-1 2 4 -2 2 X2hn-2 1 -1 1 X3hn-3 2 2 -2 2 X4hn-4 2 2 4 -2 2 xshn-5 1 2 -1 1 X6hn-6 2 -1 X7hn-7 33537 4 3 3 0 ∑Xmhn-m 上游充通大
Example Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution convolution table LTI form

Transient and steady state Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution Input on transient Steady state Input off transient max(0,n-L+1)=0 min(n,M)-n max(0,n-L+1)=0 min(n,M)=M max(0,n-L+1)=m-L+1 min(n,M=M 上游充通大¥
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution Transient and steady state
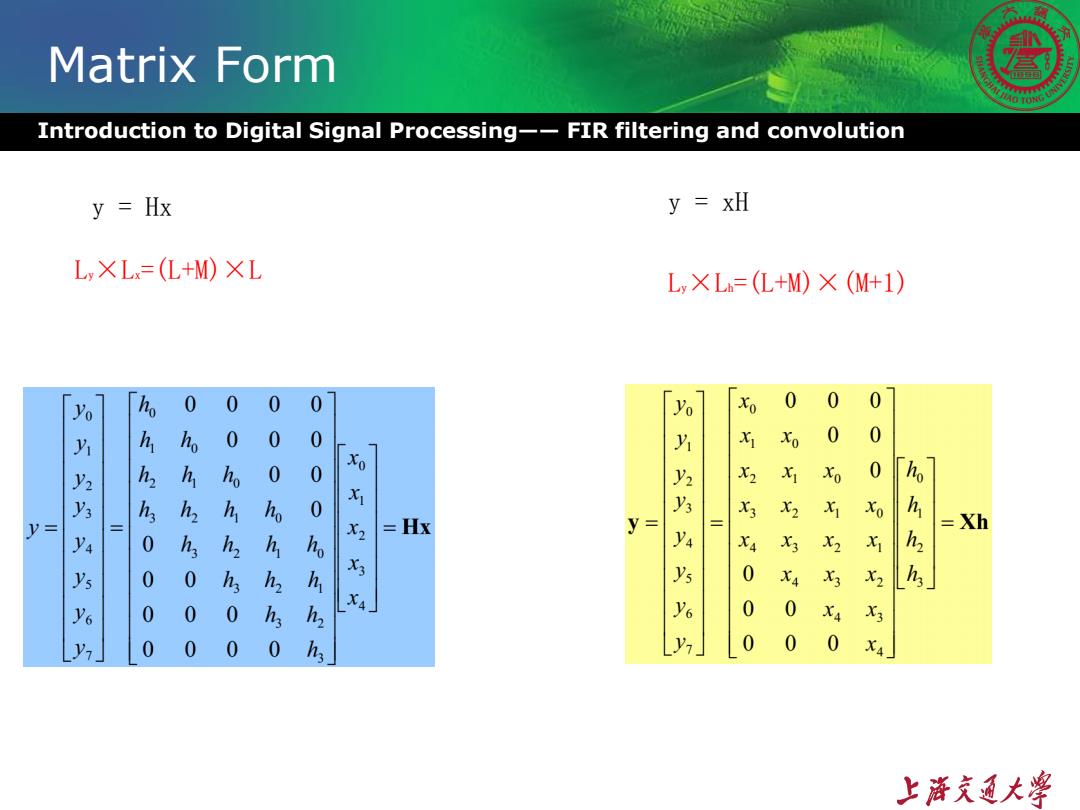
Matrix Form Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution y=Hx y xH L XL=(L+M)XL Ly×L=(L+M)×(M+1) o h 0 0 0 0 Xo 0 0 0 0 0 0 xo 0 0 h 0。 0 历乃乃乃归乃乐乃 Xo 0 X2 y= =Hx y= 七 =Xh 七3 X2 0 0 h 0 X3 0 0 0 40 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 上游充通大¥
Matrix Form Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution y = Hx Ly×Lx=(L+M)×L Ly×Lh=(L+M)×(M+1) y = xH
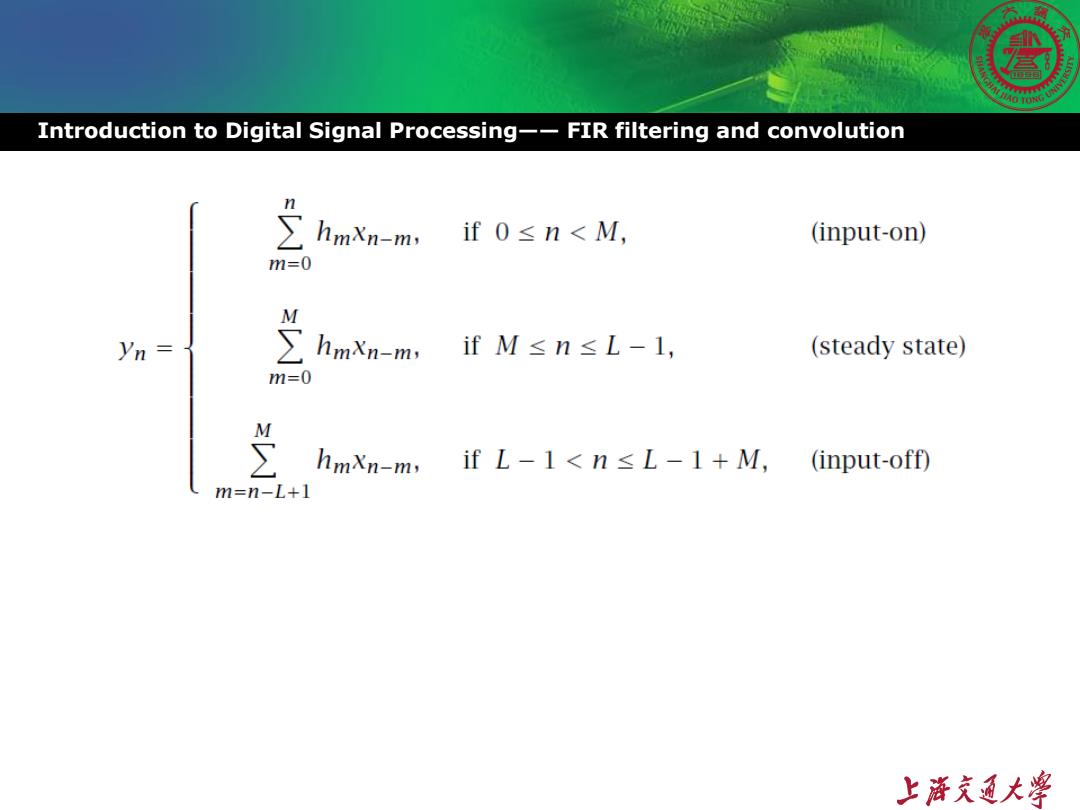
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing--FIR filtering and convolution n hmXn-m, if0≤n<M, (input-on) m=0 yn= ∑hmxn-m ,ifM≤n≤L-1, (steady state) m=0 M hmXn-m,if L-1<n<L-1+M, (input-off) m=n-L+1 上游充通大¥
Introduction to Digital Signal Processing—— FIR filtering and convolution