
Chapter 9 Computer Networking Multimedia A TOP-DOWN APPROACH SEVENTH EDITION Networking KUROSE·ROSS A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We're making these slides freely available to all (faculty,students,readers). They're in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;and can add,modify. and delete slides (including this one)and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part.In return for use,we only ask the following: Computer If you use these slides(e.g.,in a class)that you mention their source Networking:A Top (after all,we'd like people to use our book!) If you post any slides on a ww site,that you note that they are adapted from(or perhaps identical to)our slides,and note our copyright of this Down Approach material. 7th edition Thanks and enjoy!JFK/KWR Jim Kurose,Keith Ross Al material copyright19-2016 Pearson/Addison Wesley J.F Kurose and K.W.Ross,All Rights Reserved April 2016 Multimedia Networking 9-1
Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the following: ▪ If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) ▪ If you post any slides on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our slides, and note our copyright of this material. Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR All material copyright 1996-2016 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved 7 th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Pearson/Addison Wesley April 2016 Chapter 9 Multimedia Networking Multimedia Networking 9-1

Multimedia networking:outline 9.I multimedia networking applications 9.2 streaming stored video 9.3 voice-over-IP 9.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 9.5 network support for multimedia Multimedia Networking 9-2
Multimedia networking: outline 9.1 multimedia networking applications 9.2 streaming stored video 9.3 voice-over-IP 9.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 9.5 network support for multimedia Multimedia Networking 9-2
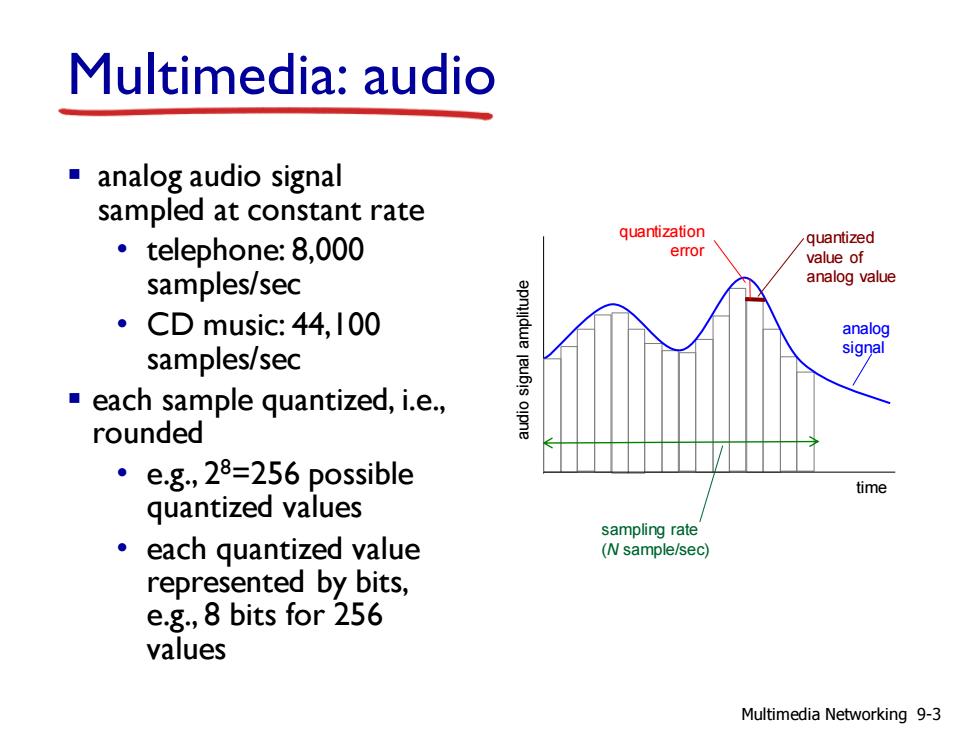
Multimedia:audio analog audio signal sampled at constant rate quantization ·telephone:8,000 quantized error value of samples/sec analog value ·CD music:44,I00 analog samples/sec signal each sample quantized,i.e., rounded ·eg,28=256 possible time quantized values sampling rate 。each quantized value (N sample/sec) represented by bits, e.g.,8 bits for 256 values Multimedia Networking 9-3
Multimedia: audio ▪ analog audio signal sampled at constant rate • telephone: 8,000 samples/sec • CD music: 44,100 samples/sec ▪ each sample quantized, i.e., rounded • e.g., 28=256 possible quantized values • each quantized value represented by bits, e.g., 8 bits for 256 values time audio signal amplitude analog signal quantized value of analog value quantization error sampling rate (N sample/sec) Multimedia Networking 9-3
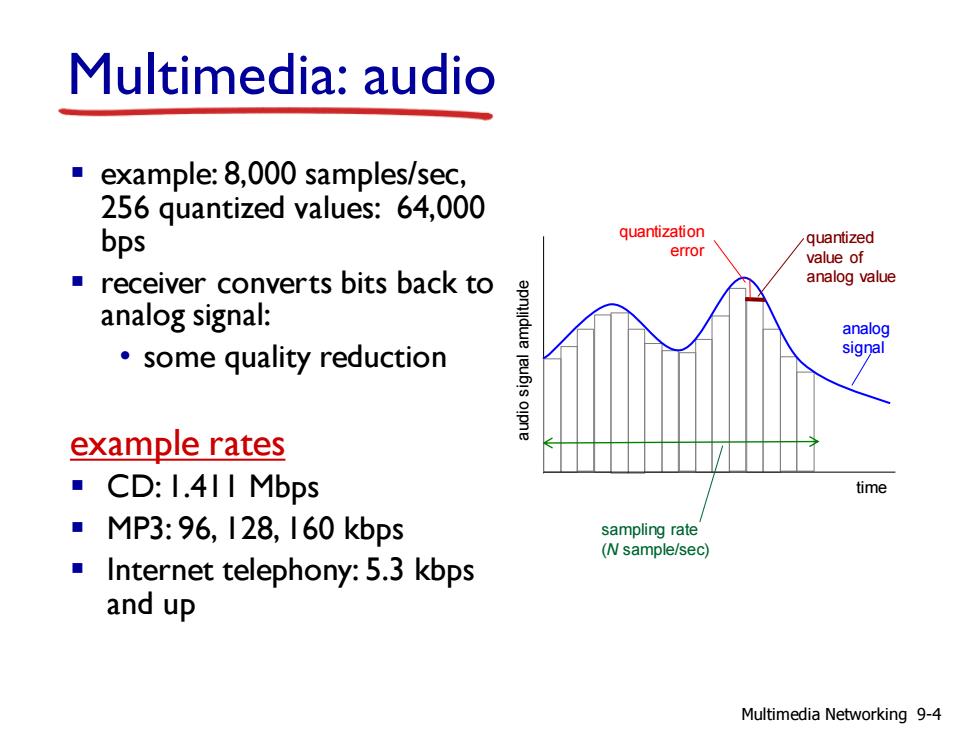
Multimedia:audio example:8,000 samples/sec, 256 quantized values:64,000 bps quantization quantized error value of receiver converts bits back to analog value analog signal: analog some quality reduction signal example rates ■CD:I.4 II Mbps time ■MP3:96,I28,160kbps sampling rate (N sample/sec) Internet telephony:5.3 kbps and up Multimedia Networking 9-4
Multimedia: audio ▪ example: 8,000 samples/sec, 256 quantized values: 64,000 bps ▪ receiver converts bits back to analog signal: • some quality reduction example rates ▪ CD: 1.411 Mbps ▪ MP3: 96, 128, 160 kbps ▪ Internet telephony: 5.3 kbps and up time audio signal amplitude analog signal quantized value of analog value quantization error sampling rate (N sample/sec) Multimedia Networking 9-4
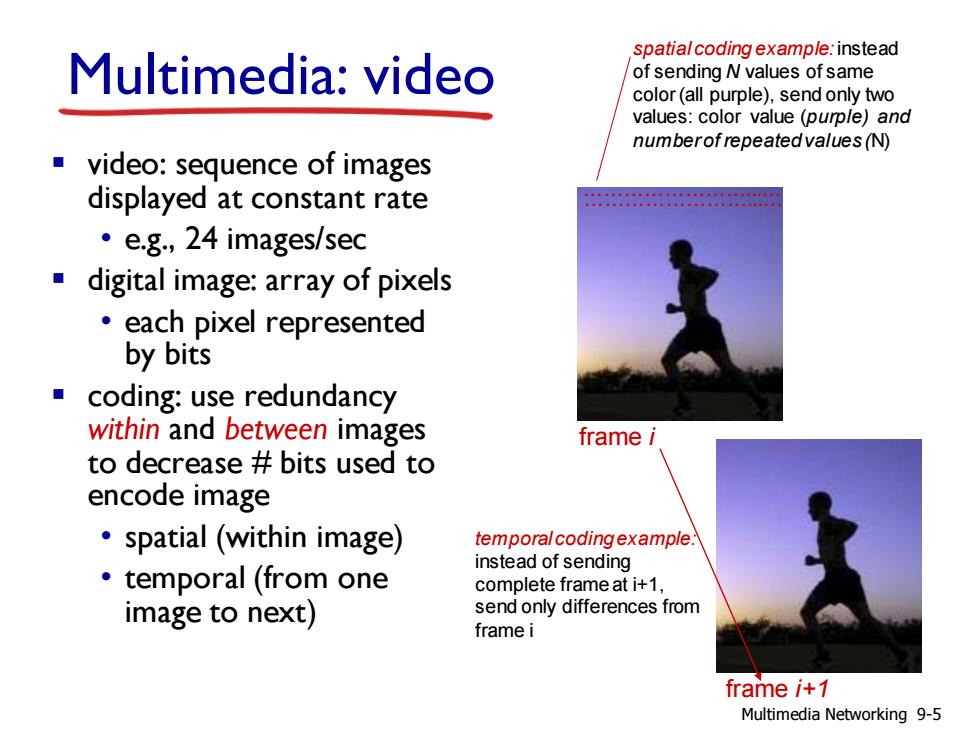
spatial coding example:instead Multimedia:video of sending N values of same color(all purple),send only two values:color value (purple)and numberof repeated values(N) video:sequence of images displayed at constant rate ·e.g,24 images/sec digital image:array of pixels each pixel represented by bits coding:use redundancy within and between images frame i to decrease bits used to encode image spatial (within image) temporal coding example. instead of sending ·temporal(from one complete frame at i+1, image to next) send only differences from frame i frame i+1 Multimedia Networking 9-5
▪ video: sequence of images displayed at constant rate • e.g., 24 images/sec ▪ digital image: array of pixels • each pixel represented by bits ▪ coding: use redundancy within and between images to decrease # bits used to encode image • spatial (within image) • temporal (from one image to next) Multimedia: video ……………………...… spatial coding example: instead of sending N values of same color (all purple), send only two values: color value (purple) and number of repeated values (N) ……………………...… frame i frame i+1 temporal coding example: instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i Multimedia Networking 9-5
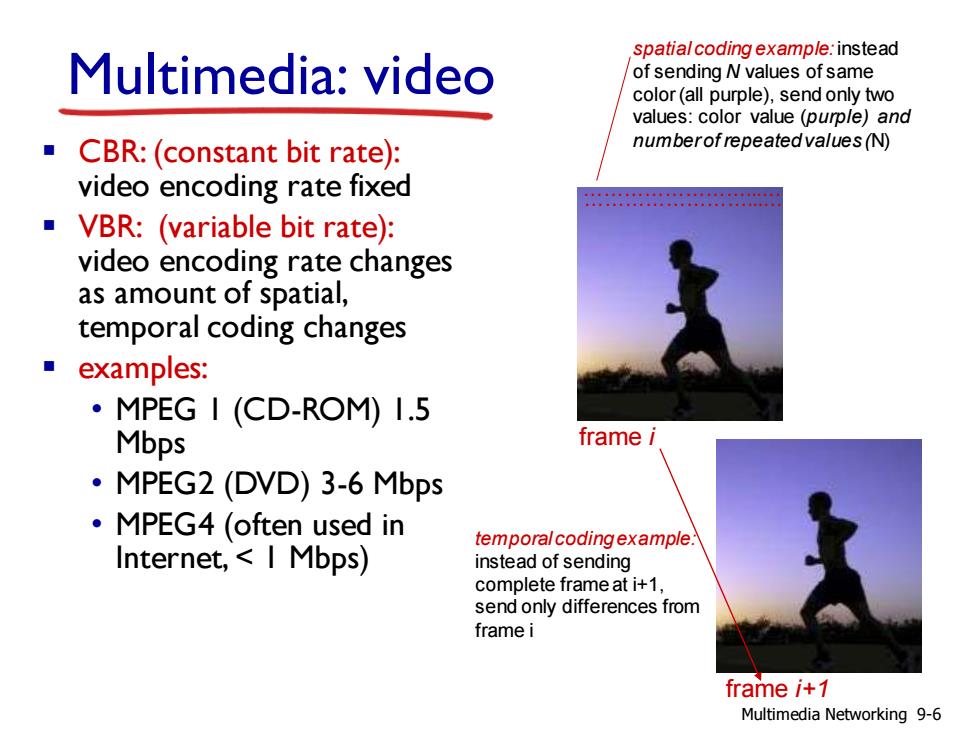
spatial coding example:instead Multimedia:video of sending N values of same color (all purple),send only two values:color value (purple)and CBR:(constant bit rate): numberof repeatedvalues(N) video encoding rate fixed 288800228022008890090 VBR:(variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes examples: ·MPEG I(CD-ROM)I.5 Mbps frame i ·MPEG2(DVD)3-6MbPs ·MPEG4(often used in temporal coding example Internet,I Mbps) instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i frame i+1 Multimedia Networking 9-6
Multimedia: video ……………………...… spatial coding example: instead of sending N values of same color (all purple), send only two values: color value (purple) and number of repeated values (N) ……………………...… frame i frame i+1 temporal coding example: instead of sending complete frame at i+1, send only differences from frame i ▪ CBR: (constant bit rate): video encoding rate fixed ▪ VBR: (variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes ▪ examples: • MPEG 1 (CD-ROM) 1.5 Mbps • MPEG2 (DVD) 3-6 Mbps • MPEG4 (often used in Internet, < 1 Mbps) Multimedia Networking 9-6

Multimedia networking:3 application types streaming,stored audio,video streaming:can begin playout before downloading entire file stored (at server):can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client) e.g.,YouTube,Netflix,Hulu conversational voice/video over IP interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance ·eg,Skype streaming live audio,video e.g.,live sporting event (futbol) Multimedia Networking 9-7
Multimedia networking: 3 application types ▪ streaming, stored audio, video • streaming: can begin playout before downloading entire file • stored (at server): can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client) • e.g., YouTube, Netflix, Hulu ▪ conversational voice/video over IP • interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance • e.g., Skype ▪ streaming live audio, video • e.g., live sporting event (futbol) Multimedia Networking 9-7

Multimedia networking:outline 9.I multimedia networking applications 9.2 streaming stored video 9.3 voice-over-IP 9.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 9.5 network support for multimedia Multimedia Networking 9-8
Multimedia networking: outline 9.1 multimedia networking applications 9.2 streaming stored video 9.3 voice-over-IP 9.4 protocols for real-time conversational applications 9.5 network support for multimedia Multimedia Networking 9-8
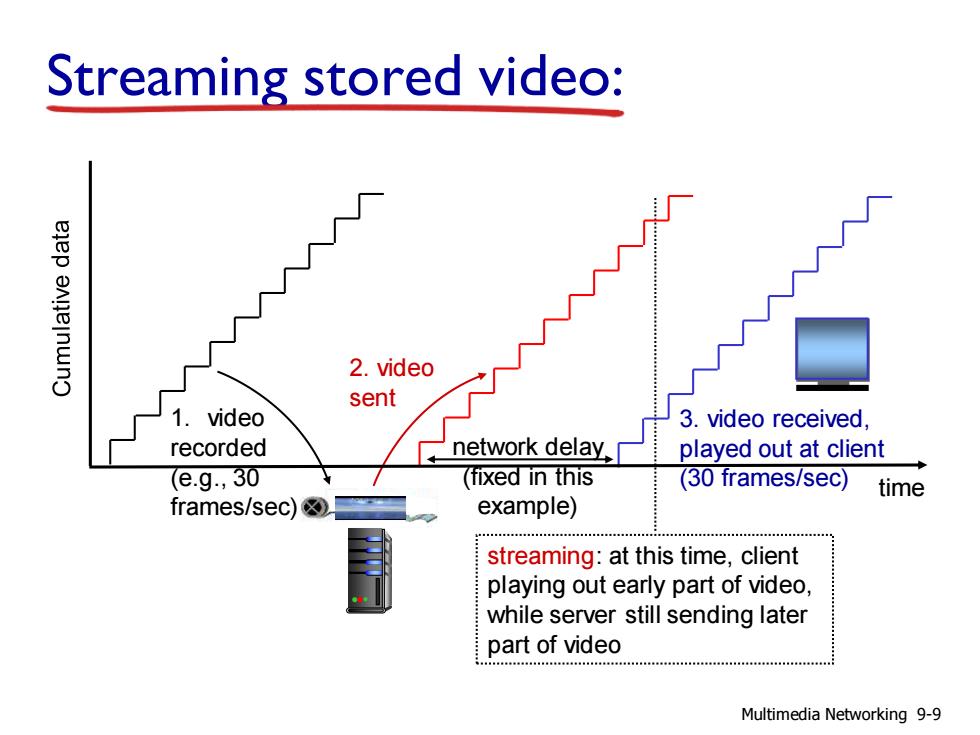
Streaming stored video: ejep enneinwno 2.video sent 1.video 3.video received, recorded network delay played out at client (e.g,30 (fixed in this (30 frames/sec) time frames/sec) example) streaming:at this time,client playing out early part of video while server still sending later part of video Multimedia Networking 9-9
Streaming stored video: 1. video recorded (e.g., 30 frames/sec) 2. video sent streaming: at this time, client playing out early part of video, while server still sending later part of video network delay (fixed in this example) time 3. video received, played out at client (30 frames/sec) Multimedia Networking 9-9

Streaming stored video:challenges continuous playout constraint:once client playout begins,playback must match original timing ...but network delays are variable (jitter),so will need client-side buffer to match playout requirements other challenges: client interactivity:pause,fast-forward,rewind, jump through video video packets may be lost,retransmitted Multimedia Networking 9-10
Streaming stored video: challenges ▪ continuous playout constraint: once client playout begins, playback must match original timing • … but network delays are variable (jitter), so will need client-side buffer to match playout requirements ▪ other challenges: • client interactivity: pause, fast-forward, rewind, jump through video • video packets may be lost, retransmitted Multimedia Networking 9-10