
提纲 background Contiguous Memory Allocation(连续内存分配) Swapping Paging(分页) Structure of the Page Table Segmentation(分段) Segmentation with paging(段页式) 小结 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 提纲 background Contiguous Memory Allocation (连续内存分配) Swapping Paging (分页) Structure of the Page Table Segmentation (分段) Segmentation with paging (段页式) 小结

Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution,loading linking 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution, loading & linking
Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution,loading linking 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution, loading & linking

Storage hierarchy I Storage hierarchy Registers Storage systems in a computer system can be organized in a Cache hierarchy(层次结构) Main memory Speed,access time Electronic disk Size,cost,cost per bit Volatility VS.persistency Magnetic disk Optical tapes Magnetic tapes Main memory is the only large storage area that the processor can access directly. MM is a scarce resource(稀缺资源) 口”484在4色”主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Storage hierarchy I Storage hierarchy ▶ Storage systems in a computer system can be organized in a hierarchy(层次结构) ▶ Speed, access time ▶ Size, cost, cost per bit ▶ Volatility VS. persistency Registers Cache Main memory Electronic disk Magnetic disk Optical tapes Magnetic tapes ▶ Main memory is the only large storage area that the processor can access directly. ▶ MM is a scarce resource(稀缺资源)

Memory VS.register Same:Access directly for CPU Register name Memory address Different:access speed,size Register,one cycle of the CPU clock Memory,Many cycles(2 or more),CPU stall Disadvantage: CPU needs to stall frequently this is intolerable Remedy cache 4口”4614在4生”主QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Memory VS. register ▶ Same: Access directly for CPU ▶ Register name ▶ Memory address ▶ Different: access speed, size ▶ Register, one cycle of the CPU clock ▶ Memory, Many cycles (2 or more), CPU stall ▶ Disadvantage: ▶ CPU needs to stall frequently & this is intolerable ▶ Remedy ▶ cache

Caching 多 Caching(高速缓存技术) Copying information into faster storage system When accessing,first check in the cache, if In:use it directly Not in:get from upper storage system,and leave a copy in the cache Using of caching Registers provide a high-speed cache for main memory Instruction cache data cache Main memory can be viewed as a fast cache for secondary storage 4口”4814在,4色,主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Caching ▶ Caching (高速缓存技术) ▶ Copying information into faster storage system ▶ When accessing, first check in the cache, ▶ if In: use it directly ▶ Not in: get from upper storage system, and leave a copy in the cache ▶ Using of caching ▶ Registers provide a high-speed cache for main memory ▶ Instruction cache & data cache ▶ Main memory can be viewed as a fast cache for secondary storage ▶ …

Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution,loading linking 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution, loading & linking
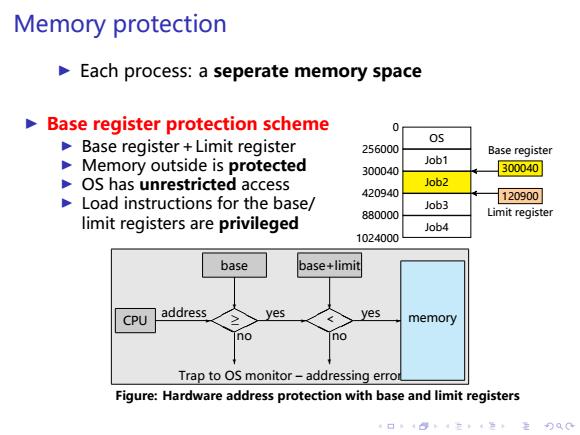
Memory protection Each process:a seperate memory space > Base register protection scheme Base register +Limit register 05 256000 Base register Memory outside is protected Job1 300040 300040 OS has unrestricted access Job2 420940 Load instructions for the base/ 120900 Job3 Limit register limit registers are privileged 880000 Job4 1024000 base base+limit CPU address yes yes memory no Trap to OS monitor-addressing error Figure:Hardware address protection with base and limit registers 4口148:4在,4生,月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Memory protection ▶ Each process: a seperate memory space ▶ Base register protection scheme ▶ Base register+Limit register ▶ Memory outside is protected ▶ OS has unrestricted access ▶ Load instructions for the base/ limit registers are privileged OS Job1 Job2 Job3 Job4 0 256000 300040 420940 880000 1024000 300040 Base register 120900 Limit register CPU address✲ base ❄ ✟ ✟ ❍❍✟ ✟ ❍❍ ❄ no ≥ yes ✲ Trap to OS monitor – addressing error base+limit ❄ ✟ ✟ ❍❍✟ ✟ ❍❍ ❄ no < yes ✲ memory Figure: Hardware address protection with base and limit registers

Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution,loading linking 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline background Storage hierarchy Memory protection Program execution, loading & linking
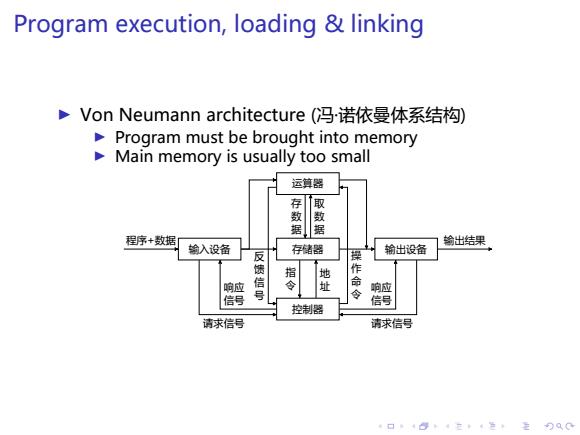
Program execution,loading linking Von Neumann architecture(G冯诺依曼体系结构) Program must be brought into memory Main memory is usually too small 运算器 存 据据 程序+数据 输出结果 输入设备 存储器 输出设备 反 指 地 冬 响应 信 令 址 命 响应 信号 信号 控制器 请求信号 请求信号 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Program execution, loading & linking ▶ Von Neumann architecture (冯·诺依曼体系结构) ▶ Program must be brought into memory ▶ Main memory is usually too small 控制器 存储器 地 址 指 令 运算器 取 数 据 存 数 据 输入设备 程序+数据 输出设备 输出结果 请求信号 请求信号 响应 信号 响应 信号 反 馈 信 号 操 作 命 令