
提纲 Overview of Mass Storage Structure Disk Structure Disk Scheduling(磁盘调度) Disk Management Swap-Space Management RAID(磁盘阵列)Structure 小结和作业 4口”4814在,4色,主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 提纲 Overview of Mass Storage Structure Disk Structure Disk Scheduling (磁盘调度) Disk Management Swap-Space Management RAID (磁盘阵列) Structure 小结和作业
Overview of Mass Storage Structure Magnetic disks(磁盘)provide bulk of secondary storage of modern computers Drives rotate at 60 to 200 times per second Transfer rate(传输速率)is rate at which data flow between drive and computer Positioning time(random-access time)is time to move disk arm to desired cylinder(seek time)and time for desired sector to rotate under the disk head (rotational latency) Head crash results from disk head making contact with the disk surface That's bad Disks can be removable 口”4814在年生”主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Overview of Mass Storage Structure ▶ Magnetic disks (磁盘) provide bulk of secondary storage of modern computers ▶ Drives rotate at 60 to 200 times per second ▶ Transfer rate (传输速率) is rate at which data flow between drive and computer ▶ Positioning time (random-access time) is time to move disk arm to desired cylinder (seek time) and time for desired sector to rotate under the disk head (rotational latency) ▶ Head crash results from disk head making contact with the disk surface ▶ That’s bad ▶ Disks can be removable
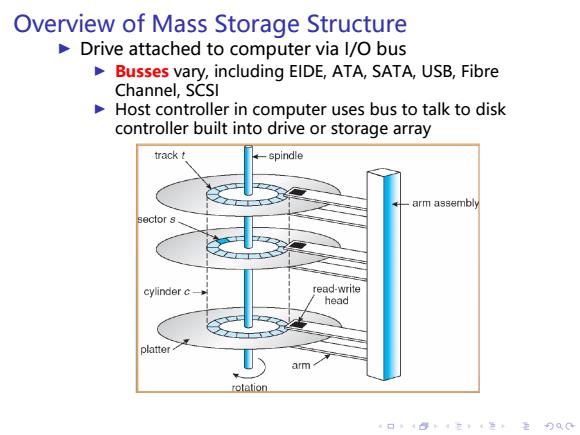
Overview of Mass Storage Structure Drive attached to computer via l/O bus Busses vary,including EIDE,ATA,SATA,USB,Fibre Channel,SCSI Host controller in computer uses bus to talk to disk controller built into drive or storage array track t ←-spindle arm assembly Bector s cylinder c- read-write head platter arm rotation 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Overview of Mass Storage Structure ▶ Drive attached to computer via I/O bus ▶ Busses vary, including EIDE, ATA, SATA, USB, Fibre Channel, SCSI ▶ Host controller in computer uses bus to talk to disk controller built into drive or storage array
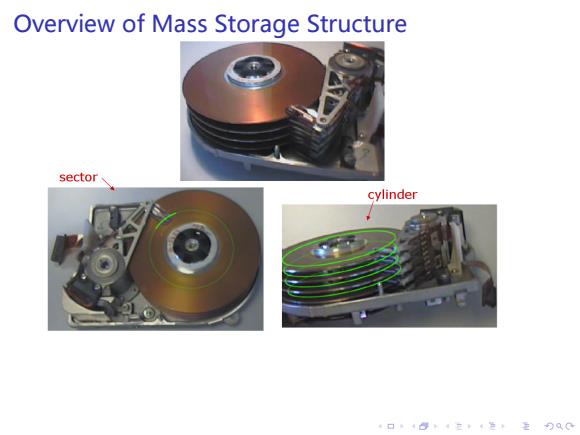
Overview of Mass Storage Structure sector、 cylinder 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Overview of Mass Storage Structure
Overview of Mass Storage Structure Magnetic tape(磁带) An early secondary-storage medium Relatively permanent and holds large quantities of data Access time slow Random access ~1000 times slower than disk Mainly used for backup,storage of infrequently-used data,transfer medium between systems Kept in spool and wound or rewound past read-write head Once data under head,transfer rates comparable to disk 20-200GB typical storage Common technologies are 4mm,8mm,19mm,LTO-2 and SDLT Oper “口4814在1生主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Overview of Mass Storage Structure ▶ Magnetic tape (磁带) ▶ An early secondary-storage medium ▶ Relatively permanent and holds large quantities of data ▶ Access time slow ▶ Random access ∼1000 times slower than disk ▶ Mainly used for backup, storage of infrequently-used data, transfer medium between systems ▶ Kept in spool and wound or rewound past read-write head ▶ Once data under head, transfer rates comparable to disk ▶ 20-200GB typical storage ▶ Common technologies are 4mm, 8mm, 19mm, LTO-2 and SDLT Oper

Outline Disk Structure “口4814在:4生”主QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline Disk Structure
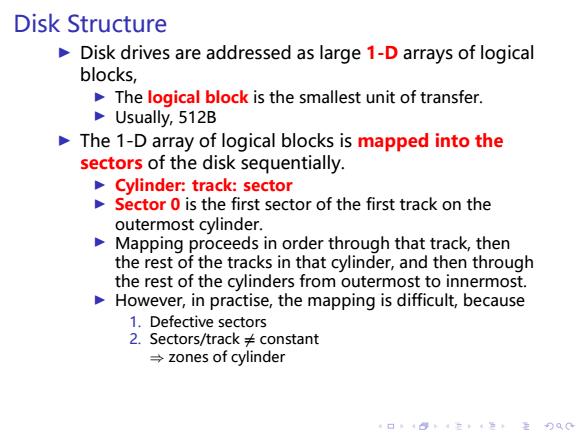
Disk Structure Disk drives are addressed as large 1-D arrays of logical blocks, The logical block is the smallest unit of transfer. Usually,512B The 1-D array of logical blocks is mapped into the sectors of the disk sequentially. Cylinder:track:sector Sector 0 is the first sector of the first track on the outermost cylinder. Mapping proceeds in order through that track,then the rest of the tracks in that cylinder,and then through the rest of the cylinders from outermost to innermost. However,in practise,the mapping is difficult,because 1.Defective sectors 2.Sectors/track constant →zones of cylinder 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Disk Structure ▶ Disk drives are addressed as large 1-D arrays of logical blocks, ▶ The logical block is the smallest unit of transfer. ▶ Usually, 512B ▶ The 1-D array of logical blocks is mapped into the sectors of the disk sequentially. ▶ Cylinder: track: sector ▶ Sector 0 is the first sector of the first track on the outermost cylinder. ▶ Mapping proceeds in order through that track, then the rest of the tracks in that cylinder, and then through the rest of the cylinders from outermost to innermost. ▶ However, in practise, the mapping is difficult, because 1. Defective sectors 2. Sectors/track ̸= constant ⇒ zones of cylinder

Outline Disk Scheduling(磁盘调度) 4口”484在4色,主月QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Outline Disk Scheduling (磁盘调度)

Disk Scheduling(磁盘调度) The OS is responsible for using hardware efficiently For the disk drives,this means having a fast access time and disk bandwidth. Access time has two major components 1.Seek time is the time for the disk to move the heads to the cylinder containing the desired sector. Minimize seek time Seek time seek distance 2.Rotational latency is the additional time waiting for the disk to rotate the desired sector to the disk head. Disk bandwidth(磁盘带宽)is the total number of bytes transferred,divided by the total time between the first request for service and the completion of the last transfer. 口”484在年生”主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Disk Scheduling (磁盘调度) ▶ The OS is responsible for using hardware efficiently. For the disk drives, this means having a fast access time and disk bandwidth. ▶ Access time has two major components 1. Seek time is the time for the disk to move the heads to the cylinder containing the desired sector. ▶ Minimize seek time ▶ Seek time ≈ seek distance 2. Rotational latency is the additional time waiting for the disk to rotate the desired sector to the disk head. ▶ Disk bandwidth (磁盘带宽) is the total number of bytes transferred, divided by the total time between the first request for service and the completion of the last transfer

Disk Scheduling(磁盘调度) Request queue(请求队列) empty or not How? Several algorithms exist to schedule the servicing of disk I/O requests. 1.FCFS 2.SSTF (shortest-seek-time-first) 3.SCAN(elevator algorithm) 4.C-SCAN 5.C-L00K We illustrate them with a request queue(0-199). 98,183,37,122,14,124,65,67 Head points to 53 initially 口”4814在年生”主)QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Disk Scheduling (磁盘调度) ▶ Request queue (请求队列) ▶ empty or not ▶ How? Several algorithms exist to schedule the servicing of disk I/O requests. 1. FCFS 2. SSTF (shortest-seek-time-first) 3. SCAN (elevator algorithm) 4. C-SCAN 5. C-LOOK ▶ We illustrate them with a request queue (0-199). 98, 183, 37, 122, 14, 124, 65, 67 Head points to 53 initially