
Control 9/25/19
Control 9 / 25 / 19

Print and None Demo
Print and None Demo

None Indicates that Nothing is Returned The special value None represents nothing in Python A function that does not explicitly return a value will return None Careful:None is not displayed by the interpreter as the value of an expression >>def does_not_return_square(x): XX ------- No return >>does_not_return_square(4)+----- None value is not displayed The name sixteen >>isixteen =does_not_return_square(4) is now bound to >>sixteen +4 the value None Traceback (most recent call last): File "",line 1,in TypeError:unsupported operand type(s)for +'NoneType'and 'int
>>> does_not_return_square(4) >>> sixteen + 4 Traceback (most recent call last): File "", line 1, in TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'NoneType' and 'int' >>> sixteen = does_not_return_square(4) None Indicates that Nothing is Returned ● The special value None represents nothing in Python ● A function that does not explicitly return a value will return None ● Careful: None is not displayed by the interpreter as the value of an expression >>> def does_not_return_square(x): ... x * x ... No return None value is not displayed The name sixteen is now bound to the value None
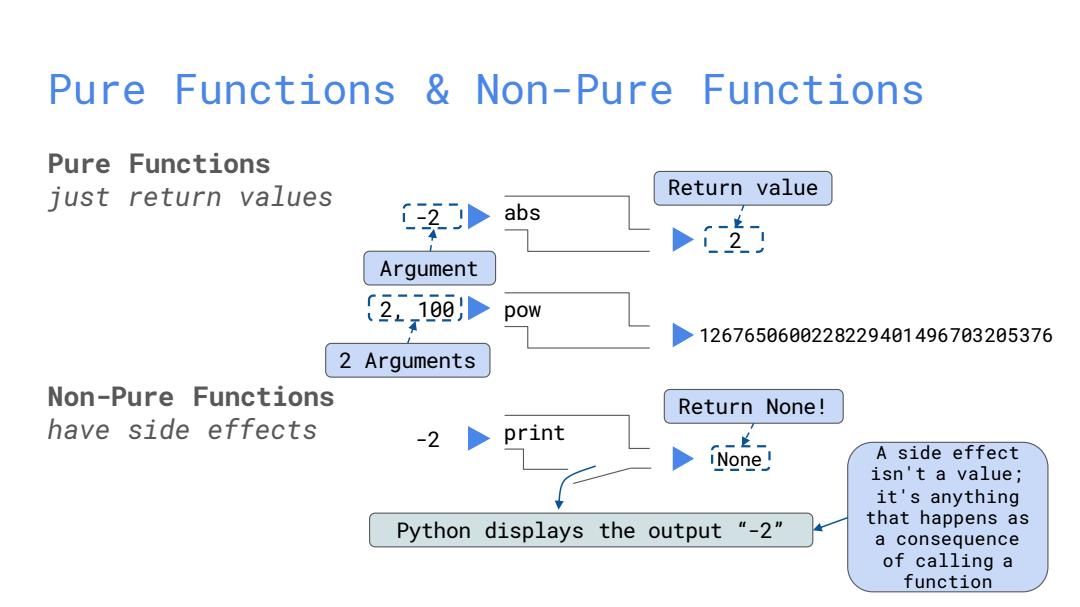
Pure Functions Non-Pure Functions Pure Functions just return values Return value abs 1支 Argument (2.0 pow 1267650600228229401496703205376 2 Arguments Non-Pure Functions Return None! have side effects -2 print -上- iNone A side effect isn't a value; it's anything Python displays the output "-2" that happens as a consequence of calling a function
Pure Functions & Non-Pure Functions Pure Functions just return values Non-Pure Functions have side effects -2 abs 2 Argument Return value 2, 100 pow 1267650600228229401496703205376 2 Arguments print -2 None Python displays the output “-2” Return None! A side effect isn't a value; it's anything that happens as a consequence of calling a function
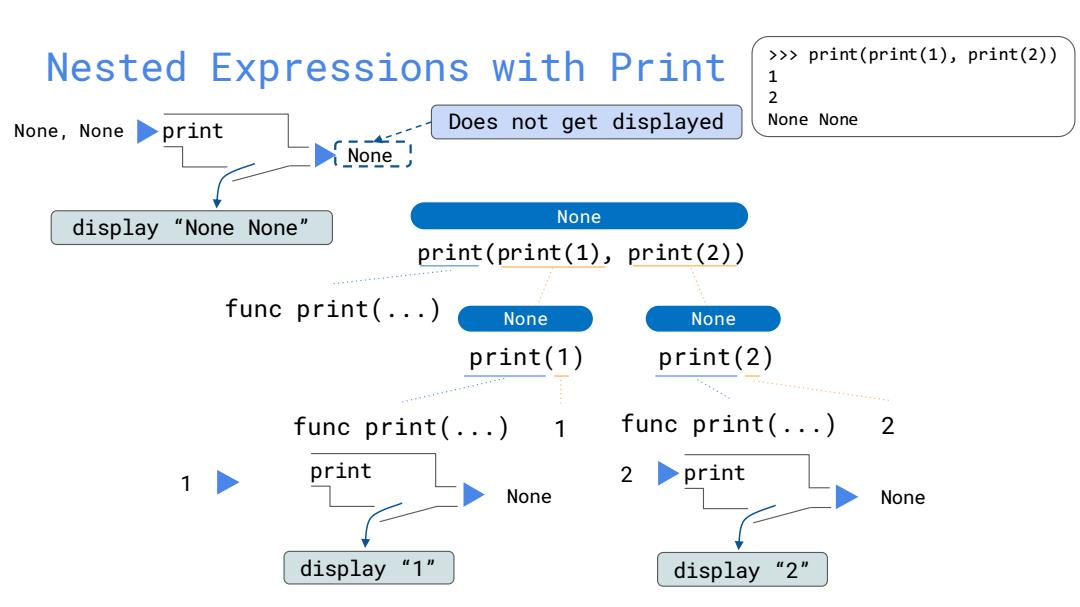
Nested Expressions with Print >>> print(print(1),print(2)) 1 2 None,Noneprint Does not get displayed None None None display "NoneNone" None print(print(1),print(2)) func print(...) None None print(1) print(2) func print(...) 1 func print(...) 2 1 print None None display“1" display "2
print(print(1), print(2)) Nested Expressions with Print >>> print(print(1), print(2)) 1 2 None None func print(...) print(1) func print(...) 1 None None print(2) func print(...) 2 print 1 None display “1” 2 print None display “2” None, None print None display “None None” None Does not get displayed

print vs return Demo
print vs return Demo

Control
Control

Control Expressions in programs evaluate to values Statements are executed to perform actions o Ex:assignment and def statements With what we have seen so far,a lot of useful programs have been left out ●For example:returning 'hot',‘warm',or‘cold'depending on an argument temp To do this we introduce the concept of control o Special expressions and statements can control how the program is executed by the interpreter
Control ● Expressions in programs evaluate to values ● Statements are executed to perform actions ○ Ex: assignment and def statements ● With what we have seen so far, a lot of useful programs have been left out ● For example: returning ‘hot’, ‘warm’, or ‘cold’ depending on an argument temp ● To do this we introduce the concept of control ○ Special expressions and statements can control how the program is executed by the interpreter

Conditional statements (if statements) Clause Syntax: if : Always start with if clause .Zero or more elif clauses elif : .Zero or one else clause,always else: at the end Execution Rule for Conditional Statements: Each header is considered in order 1.Evaluate the header's conditional expression if the header is not an else 2.If the expression evaluates to true or the header is an else,execute the suite and skip the remaining headers
Conditional statements (if statements) if : elif : else: Clause Syntax: ● Always start with if clause ● Zero or more elif clauses ● Zero or one else clause, always at the end Execution Rule for Conditional Statements: Each header is considered in order 1. Evaluate the header’s conditional expression if the header is not an else 2. If the expression evaluates to true or the header is an else, execute the suite and skip the remaining headers

if examples Demo
if examples Demo