
Lecture 19 -Scheme
Lecture 19 - Scheme

Scheme Scheme is a dialect of Lisp. It uses a lot of parentheses. LISP IS OVER HALFA I WONDER IF THE CYCLES THESE ARE YOUR CENTURY OLD AND IT WILL CONTINUE FOREVER. FATHER'S PARENTHESES STILL HAS THIS PERFECT, TIMELESS AIR ABOUT IT. ELEGANT A FEW CODERS FROMEACH WEAPONS NEW GENERATION RE- DISCOVERING THE LISP ARTS. FOR A MORE...CIVIUZED AGE 'The greatest single programming language ever designed." -Alan Kay,co-inventor of Smalltalk and OOP "The only computer language that is beautiful." -Neal Stephenson,John DeNero's favorite sci-fi author
Scheme Scheme is a dialect of Lisp. It uses a lot of parentheses. "The greatest single programming language ever designed." -Alan Kay, co-inventor of Smalltalk and OOP "The only computer language that is beautiful." -Neal Stephenson, John DeNero's favorite sci-fi author

Why another language? The goal of this class is not to teach Python,but rather to teach a variety of programming techniques and core concepts. How does learning another language help us? To see some key components across many programming languages. To see what paradigms certain languages prioritize. To learn how interpreters are implemented!
Why another language? The goal of this class is not to teach Python, but rather to teach a variety of programming techniques and core concepts. How does learning another language help us? ● To see some key components across many programming languages. ● To see what paradigms certain languages prioritize. ● To learn how interpretersare implemented!

Scheme Expressions
Scheme Expressions

Scheme expressions Scheme programs consist entirely of two types of expressions. Atomic expressions Self-evaluating:numbers,booleans 3,5.5,-10,#t,#f Symbols:names bound to values +modulo,list,x,foo,hello-world Combinations (
Scheme programs consist entirely of two types of expressions. Atomic expressions ● Self-evaluating: numbers, booleans 3, 5.5, -10, #t, #f ● Symbols: names bound to values +, modulo, list, x, foo, hello-world Combinations ( …) Scheme expressions
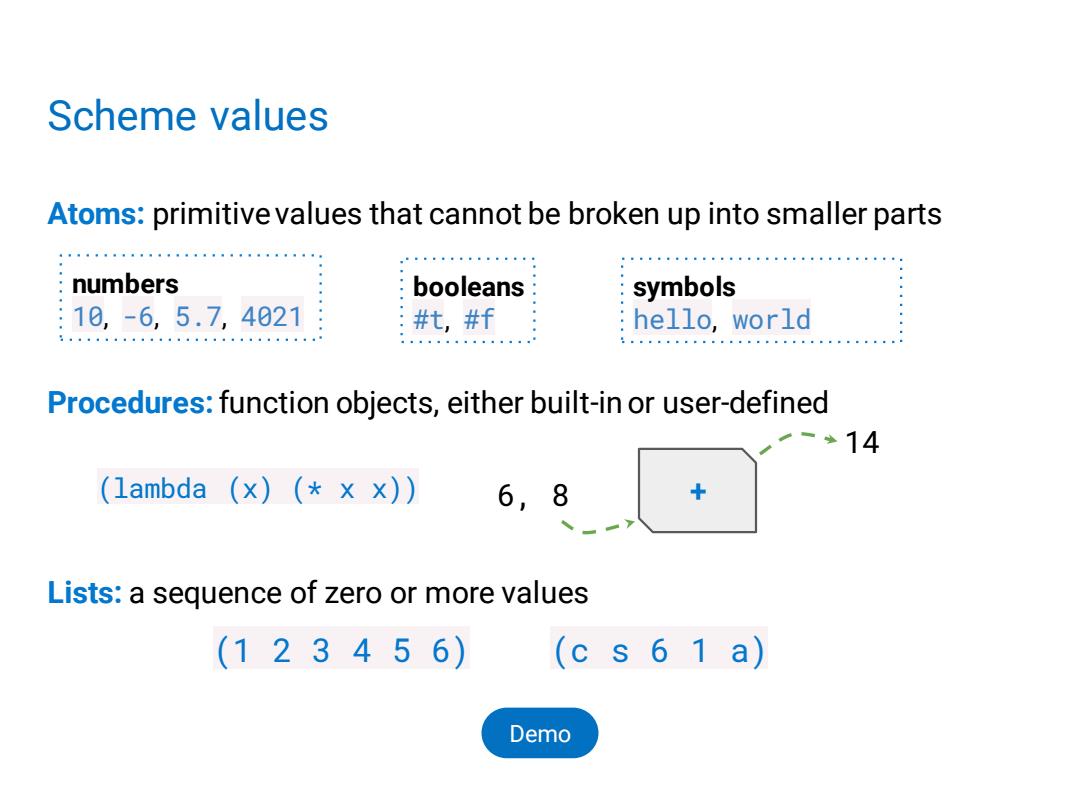
Scheme values Atoms:primitive values that cannot be broken up into smaller parts numbers booleans symbols :10,-6,5.7,4021 #t,#f hello,world Procedures:function objects,either built-in or user-defined 2-14 (1ambda (x)(xx)) 6, 8 Lists:a sequence of zero or more values (123456) (c s 6 1 a) Demo
Scheme values Atoms: primitive values that cannot be broken up into smaller parts Procedures:function objects, either built-in or user-defined Lists: a sequence of zero or more values numbers 10, -6, 5.7, 4021 symbols hello, world booleans #t, #f (1 2 3 4 5 6) (c s 6 1 a) 6, 8 + 14 (lambda (x) (* x x)) Demo
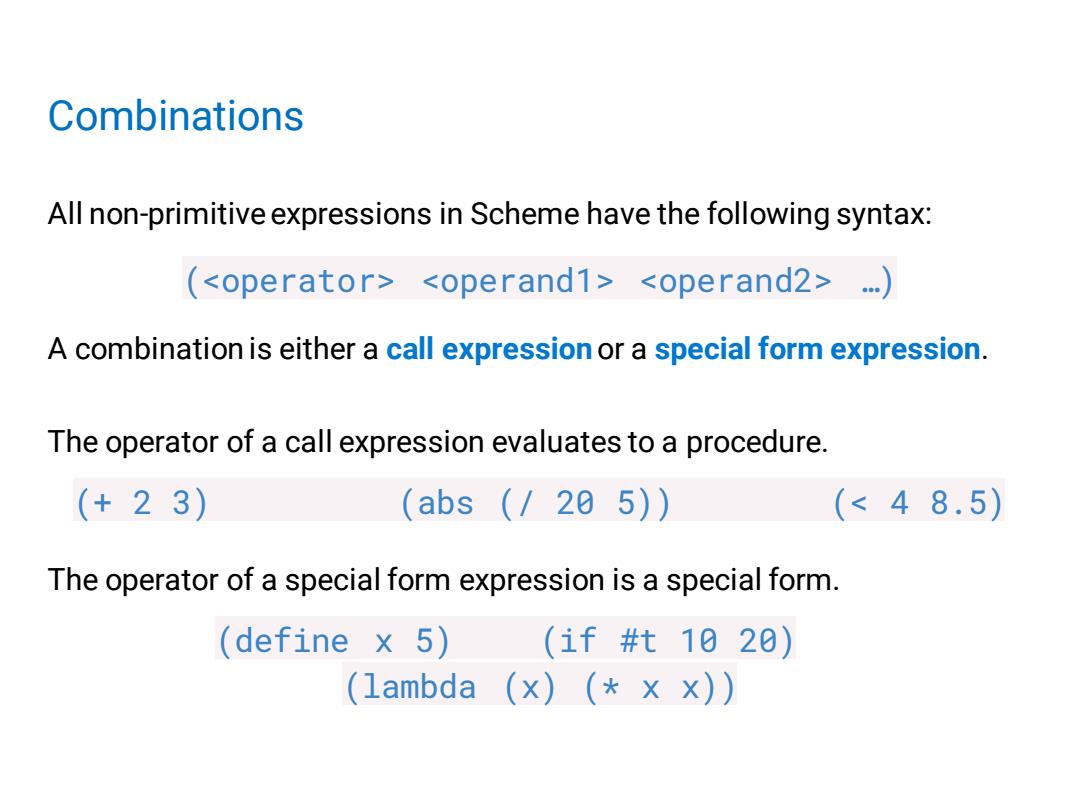
Combinations All non-primitive expressions in Scheme have the following syntax: (.. A combination is either a call expression or a special form expression. The operator of a call expression evaluates to a procedure. (+23) (abs(/285)) (<48.5) The operator of a special form expression is a special form. (define x 5) (1f#t1020) (1ambda (x)(xx))
Combinations All non-primitive expressions in Scheme have the following syntax: ( …) A combination is either a call expression or a special form expression. The operator of a call expression evaluates to a procedure. (+ 2 3) (abs (/ 20 5)) (< 4 8.5) The operator of a special form expression is a special form. (define x 5) (if #t 10 20) (lambda (x) (* x x))

Call expressions () A call expression applies a procedure to some arguments. How to evaluate call expressions: Step 1.Evaluate the operator to get a procedure. Step 2.Evaluate all operands left to right to get the arguments. Step 3.Apply the procedure to the arguments. (-(+7(*46)(*35) Key Evaluate (+7(*46)) (*35) 16 operator 7(*46)31 大3 5 15 Evaluate operand 4 6 24 Apply
(* 4 6) Call expressions ( …) A call expression applies a procedure to some arguments. How to evaluate call expressions: Step 1. Evaluate the operator to get a procedure. Step 2. Evaluate all operands left to right to get the arguments. Step 3. Apply the procedure to the arguments. (- (+ 7 (* 4 6)) (* 3 5)) - (+ 7 (* 4 6)) + 7 * 4 6 * 3 (* 3 5) 5 24 31 15 16 Key Evaluate operator Evaluate operand Apply

Special form expressions () Special forms have special behaviors that allow us to write complex programs. How to evaluate special form expressions: Each special form has its own rules! ● Some operands may not be evaluated. scm> (define x (/10 2)) X scm> (if(>18)(-34)(/10)) -1 scm> (1 ambda(xy)(+xy)) (lambda(xy)(+xy))
Special form expressions ( …) Special forms have special behaviors that allow us to write complex programs. How to evaluate special form expressions: ● Each special form has its own rules! ● Some operands may not be evaluated. scm> (define x (/ 10 2)) x scm> (if (> 1 0) (- 3 4) (/ 1 0)) -1 scm> (lambda (x y) (+ x y)) (lambda (x y) (+ x y))

Special Forms
Special Forms