ToxicBacillary Dysentery
ToxicBacillary Dysentery

[Etiology]: Dysentery bacilli, genus shigella Gram gram-negative bacilli. Pili-associated with attachment Non-spore forming, non-microcapsule: Resistance tohumidity and cooling, andsensitive to common sterilizingagents
[Etiology] □ Dysentery bacilli, genus shigella □ Gram gram-negative bacilli □ Pili -associated with attachment □ Non-spore forming, non-microcapsule □ Resistance to humidity and cooling, and sensitive to common sterilizing agents
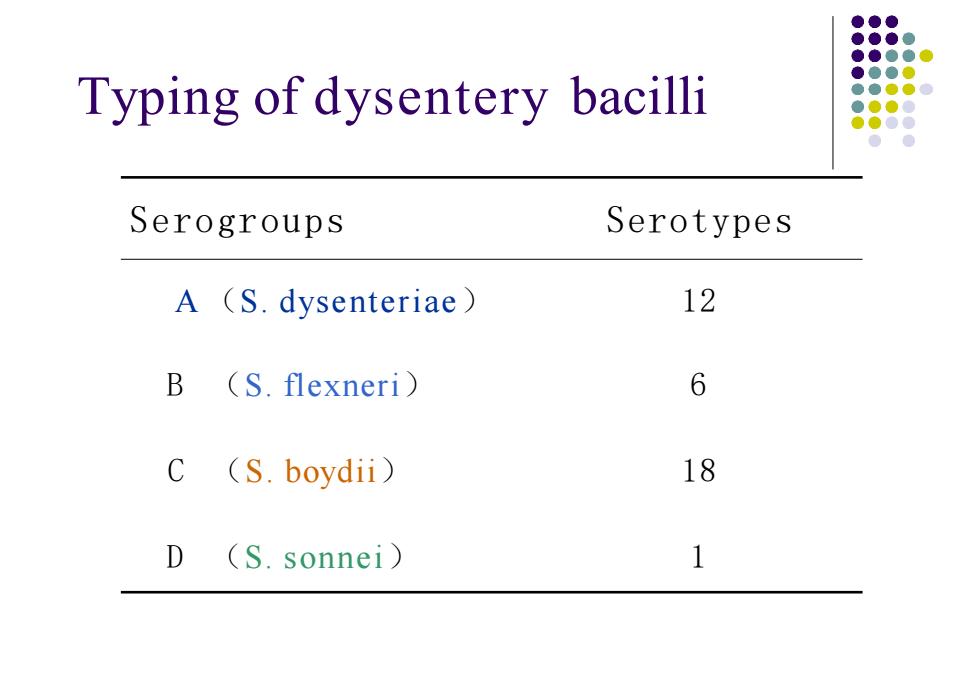
Typing of dysentery bacilliSerogroupsSerotypes12A (S.dysenteriae)6B(S. flexneri)C18(S. boydii)D1(S. sonnei)
Typing of dysentery bacilli Serogroups Serotypes A (S. dysenteriae) 12 B (S. flexneri) 6 C (S. boydii) 18 D (S. sonnei) 1

[Epidemiology.l.Sourceof infectionpatients and carriers2.Route of transmissionfecal-oralroute3.Susceptibility ofpopulationuniversal4.Epidemiological characteristics Epidemic seasons:Peak season:summer sporadicoccur inother seasons Peak age: 2~7 yrs
[Epidemiology] 1.Source of infection patients and carriers 2.Route of transmission fecal-oral route 3.Susceptibility ofpopulation universal 4.Epidemiological characteristics □ Epidemic seasons: □ Peak season: summer □ sporadic occur in other seasons □ Peak age:2~7 yrs

[Pathogenesis]The prerequisites ofToxic Bacillary Dysentery occurring:l. Toxicityinvasivenessattachment中penetration口multiplicationendotoxin日2. Host idiosyncrasy and responsivity
[Pathogenesis] The prerequisites of Toxic Bacillary Dysentery occurring: 1. Toxicity □ invasiveness □ attachment □ penetration □ multiplication □ endotoxin 2.Host idiosyncrasy and responsivity

Intestine (sigmoid colon andrectum)dysenterybacilliinvasivenessmultiplyinepithelia cell & proper laminaToxinsexotoxinendotoxinendotoxemiamucous hyperemia, edema, effusionbioactive compounds orPyrogen ofInflammatory Mediators (SIRS)WBCsuperficial mucosal necrosis and ulcermicro-circulatory failureChill, fever Septic Shock, cerebraledema,abdominalpain, diarrhea,DIC,MOFSstoolmixed withblood& pus,tenesmus
dysente ry bacilli Intestine (sigmoid colon and rectum) invasiveness multiply in epithelia cell & proper lamina Toxins endotoxin exotoxin endotoxemia mucous hyperemia, edema, effusion bioactive compounds or Inflammatory Mediators (SIRS) superficial mucosal necrosis and ulcer micro-circulatory failure abdominal pain, diarrhea, stool mixed with blood & pus, tenesmus Pyrogen of WBC Chill, fever Septic Shock, cerebral edema, DIC, MOFS

1Construction of Normal MicrocirculatoryStagnantmicro-circulatoryMicrocirculationIschemiaStageHypoxicFailurestageStageMicrocirculationFailureStages
Microcirculation Failure Stages Construction of Normal Microcirculatory Microcirculation Ischemia Stage Stagnant Hypoxic Stage micro-circulatory Failure stage

[Pathology] Intestinaltract:hyperemia,edemaleukocyte infiltration System:cellular swelling of capillary endothelial cellplasmexhidrosistissueedema, punctatehemorrhagethrombogenesisin capillarycerebraledema and brainstemedema,neurocytedegeneration
[P ath olo gy] □ Intestinal tract: hyperemia, e d e m a leukocyte infiltration □ System: cellularswelling of capillary endothelial cell plasmexhidrosis tissue edema, punctate hemorrhage thrombogenesisin capillary cerebral edema and brainstem edema, neurocyte degeneration

[ClinicalmanifestationsIncubationperiod: 1~2days(Itcan be as short as several hours)The patternsof onsetClinical types ShocktypeCerebral type口 Mixed type
[Clinical manifestations] Incubation period: 1~2days (Itcan be as short as several hours) The patterns of onset Clinical types □ Shock type □ Cerebral type □ Mixed type