
Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantcs Operational Semantics Operabonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Operational Semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics A programming language o Syntax o Semantics Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics A programming language Syntax Semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Formal semantics of a programming language o Operational semantics o Denotational semantics o Axiomatic semantics Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Formal semantics of a programming language Operational semantics Denotational semantics Axiomatic semantics Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Operational semantics Operational semantics defines program executions: o Sequence of steps,formulated as transitions of an abstract machine Configurations of the abstract machine include: o Expression/statement being evaluated/executed o States:abstract description of registers,memory and other data structures involved in computation Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Operational semantics Operational semantics defines program executions: Sequence of steps, formulated as transitions of an abstract machine Configurations of the abstract machine include: Expression/statement being evaluated/executed States: abstract description of registers, memory and other data structures involved in computation Operational Semantics
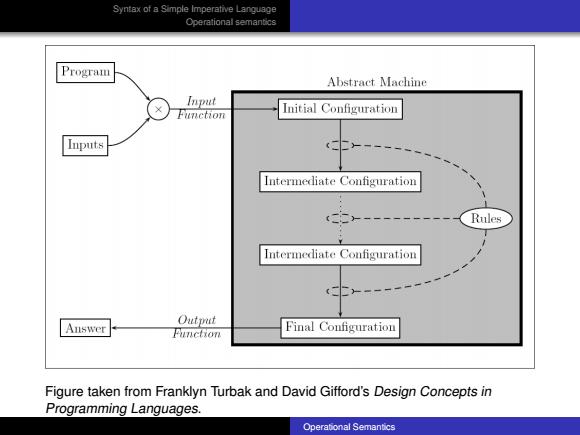
Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Cperational semantics Program Abstract Machine Input Function Initial Configuration Inputs Intermediate Configuration Rules Intermediate Configuration Auswer Output Function Final Configuration Figure taken from Franklyn Turbak and David Gifford's Design Concepts in Programming Languages. Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Figure taken from Franklyn Turbak and David Gifford’s Design Concepts in Programming Languages. Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Different approaches of operational semantics oSmall-step semantics: Describe each single step of the execution o Big-step semantics: Describe the overall result of the execution We will explain both in detail by examples Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Different approaches of operational semantics Small-step semantics: Describe each single step of the execution Big-step semantics: Describe the overall result of the execution We will explain both in detail by examples. Operational Semantics

Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics After this class... You should be able to: o write down the evaluation/execution steps,if given the operational semantics rules o formulate the operational semantics rule,if given the informal meaning of an expression/statement Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics After this class... You should be able to: write down the evaluation/execution steps, if given the operational semantics rules formulate the operational semantics rule, if given the informal meaning of an expression/statement Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Outline Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language 2 Operational semantics o Small-step operational semantics oStructural operational semantics(SOS) o Extensions:going wrong,local variable declaration,heap o Contextual semantics (a.k.a.reduction semantics) Big-step operational semantics Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Outline 1 Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language 2 Operational semantics Small-step operational semantics Structural operational semantics (SOS) Extensions: going wrong, local variable declaration, heap Contextual semantics (a.k.a. reduction semantics) Big-step operational semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp)e ::n x I e+e l e-e l... (BoolExp)b ::true I false I e=elee b bAb lbvb l... (Comm)c ::skip |X:=e C;C if b then c else c I while b do c Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp) e ::= n | x | e + e | e − e | . . . (BoolExp) b ::= true | false | e = e | e e | ¬b | b ∧ b | b ∨ b | . . . (Comm) c ::= skip | x := e | c ; c | if b then c else c | while b do c Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp)e ::n I x I e+e l e-e l... Here n ranges over the numerals 0,1,2,.... We distinguish between numerals,written n,0,1,2,...,and the natural numbers,written n,0,1,2,....The natural numbers are the normal numbers that we use in everyday life,while the numerals are just syntax for describing these numbers. We write Ln]to denote the meaning of n.We assume that Ln]=n, l0=0,l1J=1,.. The distinction is subtle,but important,because it is one manifestation of the difference between syntax and semantics. Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp) e ::= n | x | e + e | e − e | . . . Here n ranges over the numerals 0, 1, 2, . . . . We distinguish between numerals, written n, 0, 1, 2, . . . , and the natural numbers, written n, 0, 1, 2, . . . . The natural numbers are the normal numbers that we use in everyday life, while the numerals are just syntax for describing these numbers. We write bnc to denote the meaning of n. We assume that bnc = n, b0c = 0, b1c = 1, . . . . The distinction is subtle, but important, because it is one manifestation of the difference between syntax and semantics. Operational Semantics