
上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 生物技术与人类 周选围 上海交通大学农业与生物学院 植物生物技术研究中心 画天字卷业与生 通 大 xuanweizhou@163.com 学 TISCHOOL OF AGRICULTURE AND BIOLOG m■原m几《
生物技术与人类 周 选 围 上海交通大学 农业与生物学院 植物生物技术研究中心 xuanweizhou@163.com
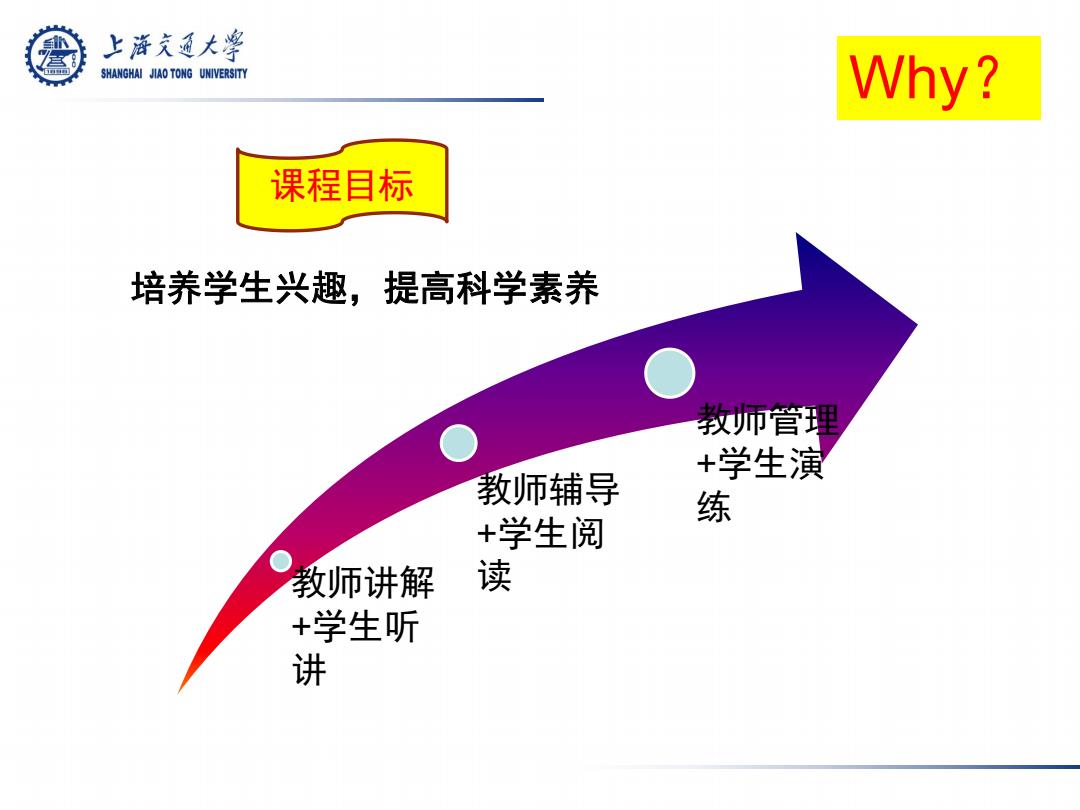
上游充通大兽 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Why? 课程目标 培养学生兴趣,提高科学素养 教师管理 +学生演 教师辅导 练 +学生阅 教师讲解 读 +学生听 讲
课程目标 培养学生兴趣,提高科学素养 教师讲解 +学生听 讲 教师辅导 +学生阅 读 教师管理 +学生演 练 Why?
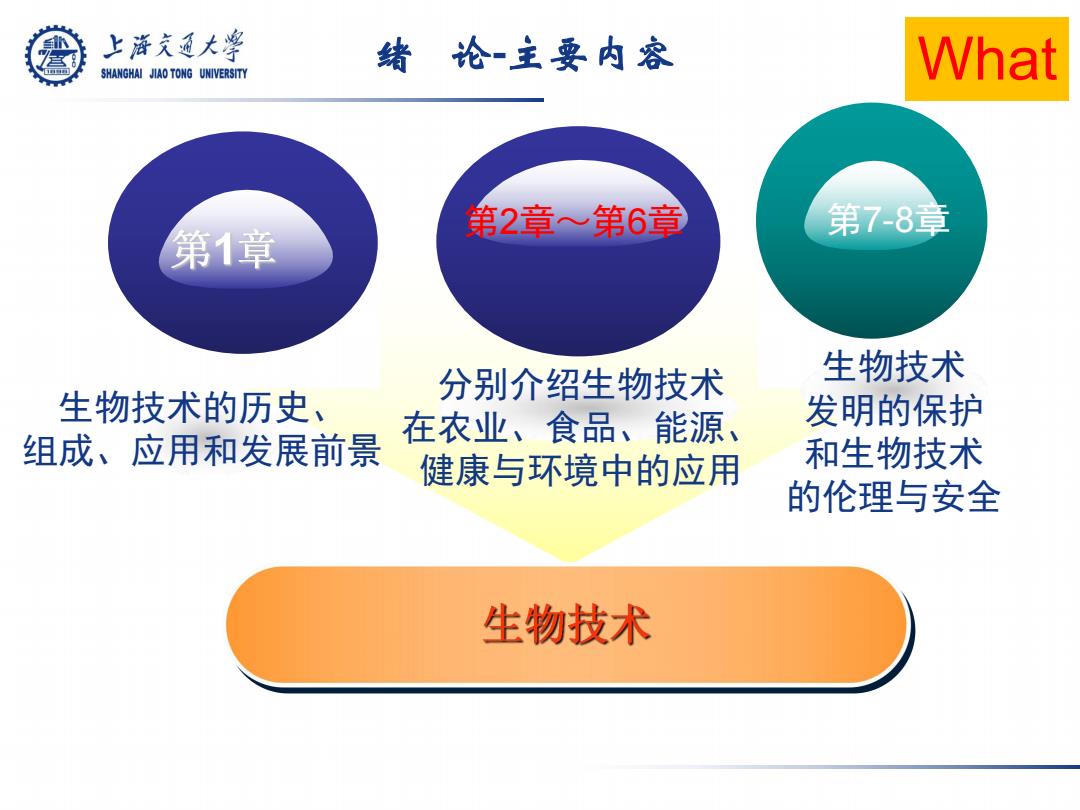
上游充通大兽 绪论-主要内容 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY What 第2章≈第6章 第7-8章 第1章 分别介绍生物技术 生物技术 生物技术的历史、 发明的保护 组成、应用和发展前景 在农业、食品、能源、 健康与环境中的应用 和生物技术 的伦理与安全 生物技术
绪 论-主要内容 生物技术的历史、 组成、应用和发展前景 分别介绍生物技术 在农业、食品、能源、 健康与环境中的应用 第2章~第6章 第7-8章 生物技术 发明的保护 和生物技术 的伦理与安全 What
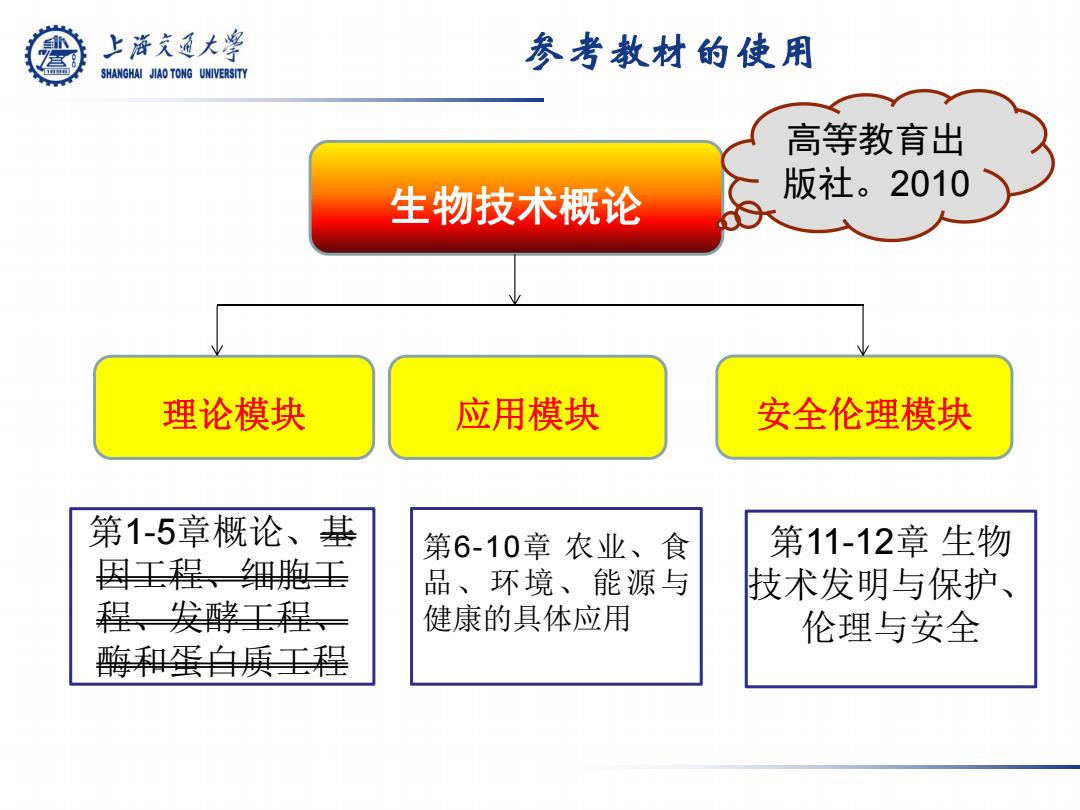
上游文通大学 参考教材的使用 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 高等教育出 生物技术概论 版社。2010 理论模块 应用模块 安全伦理模块 第1-5章概论、基 第6-10章农业、食 第11-12章生物 因王程、细胞王 品、环境、 能源与 技术发明与保护、 程、发酵王程、 健康的具体应用 伦理与安全 酶和蛋白质王程
参考教材的使用 生物技术概论 理论模块 应用模块 安全伦理模块 第1-5章概论、基 因工程、细胞工 程、发酵工程、 酶和蛋白质工程 第6-10章 农业、食 品、环境、能源与 健康的具体应用 第11-12章 生物 技术发明与保护、 伦理与安全 高等教育出 版社。2010
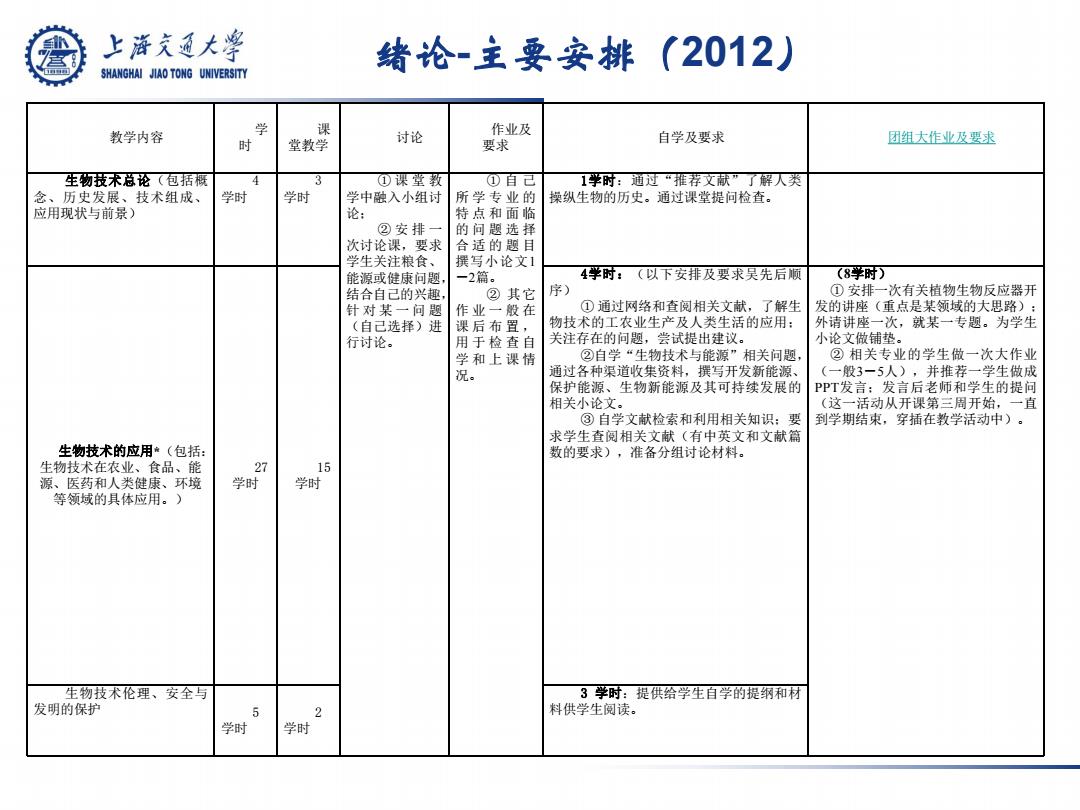
上游文通大学 绪论-主要安排(2012) SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 教学内容 学 课 时 堂教学 讨论 作业及 要求 自学及要求 团组大作业及要求 生物技禾总论(包括概 3 ①课堂教 ①自己 1华时:迪过“雅荐文献”了解人类 念、历史发展、技术组成、 学时 学时 学中融入小组讨 所学专业的 操纵生物的历史。通过课堂提问检查。 应用现状与前景) 论: 特点和面临 ②安排一 的问题选择 次讨论课,要求 合适的题目 学生关注粮食、 撰写小论文1 能源或健康问题, 一2篇。 4学时:(以下安排及要求吴先后顺 (8乎时) 结合自己的兴趣, ②其它 序) ①安排一次有关植物生物反应器开 针对某一问题 作业一般在 ①通过网络和查阅相关文献,了解生 发的讲座(重点是某领域的大思路): (自已选择)进 课后布置, 物技术的工农业生产及人类生活的应用: 外请讲座一次,就某一专题。为学生 行讨论。 用于检查自 关注存在的问题,尝试提出建议。 小论文做铺垫。 学和上课情 ②自学“生物技术与能源”相关问题, ②相关专业的学生做一次大作业 通过各种渠道收集资料,撰写开发新能源、 (一般3一5人),并推荐一学生做成 保护能源、生物新能源及其可持续发展的 PPT发言:发言后老师和学生的提问 相关小论文。 (这一活动从开课第三周开始,一直 ③自学文献检索和利用相关知识:要 到学期结束,穿插在教学活动中)。 求学生查阅相关文献(有中英文和文献篇 生物技术的应用(包括: 数的要求),准备分组讨论材料。 生物技术在农业、食品、能 27 15 源、医药和人类健康、环境 学时 学时 等领域的具体应用。) 生物技术伦理、安全与 3学时:提供给学生自学的提纲和材 发明的保护 5 料供学生阅读。 学时 学时2
绪论-主要安排(2012) 教学内容 学 时 课 堂教学 讨论 作业及 要求 自学及要求 团组大作业及要求 生物技术总论(包括概 念、历史发展、技术组成、 应用现状与前景) 4 学时 3 学时 ① 课 堂 教 学中融入小组讨 论; ② 安 排 一 次讨论课,要求 学生关注粮食、 能源或健康问题, 结合自己的兴趣, 针 对 某 一 问 题 (自己选择)进 行讨论。 ① 自 己 所 学 专 业 的 特 点 和 面 临 的 问 题 选 择 合 适 的 题 目 撰写小论文1 -2篇。 ② 其它 作 业 一 般 在 课 后 布 置 , 用 于 检 查 自 学 和 上 课 情 况。 1学时:通过“推荐文献”了解人类 操纵生物的历史。通过课堂提问检查。 生物技术的应用*(包括: 生物技术在农业、食品、能 源、医药和人类健康、环境 等领域的具体应用。) 27 学时 15 学时 4学时:(以下安排及要求吴先后顺 序) ① 通过网络和查阅相关文献,了解生 物技术的工农业生产及人类生活的应用; 关注存在的问题,尝试提出建议。 ②自学“生物技术与能源”相关问题, 通过各种渠道收集资料,撰写开发新能源、 保护能源、生物新能源及其可持续发展的 相关小论文。 ③ 自学文献检索和利用相关知识;要 求学生查阅相关文献(有中英文和文献篇 数的要求),准备分组讨论材料。 (8学时) ① 安排一次有关植物生物反应器开 发的讲座(重点是某领域的大思路); 外请讲座一次,就某一专题。为学生 小论文做铺垫。 ② 相关专业的学生做一次大作业 (一般3-5人),并推荐一学生做成 PPT发言;发言后老师和学生的提问 (这一活动从开课第三周开始,一直 到学期结束,穿插在教学活动中)。 生物技术伦理、安全与 发明的保护 5 学时 2 学时 3 学时:提供给学生自学的提纲和材 料供学生阅读

上游充通大兽 绪论-学习方法 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY How? 课题听讲 课外阅读 讨论发言 作业考试 导 读 练 做 听 看 讲 评 学而不思则罔,思而不学则殆
绪论-学习方法 导 读 练 做 课题听讲 听 课外阅读 看 讲 评 讨论发言 作业考试 学而不思则罔,思而不学则殆 How?

上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 师生双边活动 教师活动 讲解引导 课外辅导 组织讨论 总结讲评 教学 目标 学生活动 课堂听讲 课外阅读 课堂演讲 作业讨论
师生双边活动

上游文通大学 教学主要手段和方法方法 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 生物技术概论 教学录像 ①Genetically.arcanum基因的秘密 2 Discovery-Life is no picnic 发明与生活 补充阅读材料 教材1本; ③科学史上100最伟大的发现-遗传学 (自由观看) 10篇选择文献 ④生物科学100重大发现生物学(自 参考教材5本 由观看) (中2+英8) ⑤孟山都眼中的世界(中文字幕) ⑥人类基因组动画(1)(2) 27篇Nature文献 ⑦转基因食物
教学主要手段和方法-方法 教材1本; 参考教材5本 教学录像 ① Genetically.arcanum 基因的秘密 ② Discovery- Life is no picnic 发明与生活 ③ 科学史上100最伟大的发现-遗传学 (自由观看) ④ 生物科学100重大发现-生物学(自 由观看) ⑤ 孟山都眼中的世界(中文字幕) ⑥ 人类基因组动画(1)(2) ⑦ 转基因食物 补充阅读材料 10篇选择文献 (中2+英8) 27篇Nature 文献

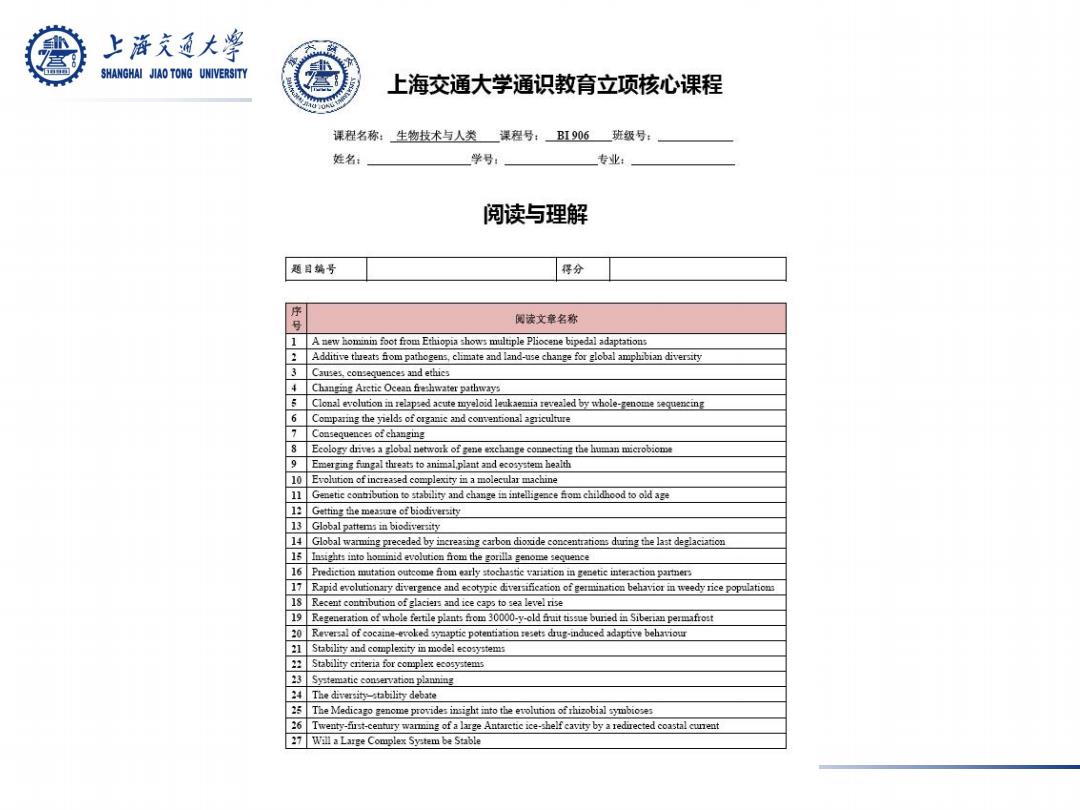
上游文通大学 经典阅读 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive threats from pathogens,climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes,consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant and ecosystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic contribution to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age 12 Getting the measure of biodiversity 13 Global patterns in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice populations 18 Recent contribution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plants from 30000-y-old fruit tissue buried in Siberian permafrost 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour
1 A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive threats from pathogens, climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes, consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant and ecosystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic contribution to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age 12 Getting the measure of biodiversity 13 Global patterns in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice populations 18 Recent contribution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plants from 30000-y-old fruit tissue buried in Siberian permafrost 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour 经典阅读
上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 上海交通大学通识教育立项核心课程 课程名称:生物技术与人类 课程号:BI906班级号: 姓名: 学号: 专业: 阅读与理解 题目编号 得分 序 阅读文章名称 1 A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive theats firom pathogens,climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes,consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agiculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange conneeting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant andcoystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic conmibution to stability and change in intelligenceom childhood to old age 12 Getting the measue of biodiversity 13 Global pattems in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice population 18 Recent conmibution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plantom0000-y-old fruitise bured Siberian permafrot 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked symaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour 2】Stabili时y and complexity in model 22 Stability criteria for complex ecosystems 23 Systematic conservation planning 24 The diversitytability debate The Medicag genome provides inight into theeoution of thizobial symbioe 26 Twenty-furst-century warming of a large Antarctic ice-shelf cavity by a redirected coastal curent Will a Large Complex System be Stable