
Chapter 7 Pricing Strategies
Chapter 7 Pricing Strategies

一.Price Price is the sum of all the values that consumers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service. Price has been the major factor affecting buyer choice;nonprice factors have become increasingly important in buyer-choice behavior. Price is the only element in the marketing mix that produces revenues;all others represent costs
一.Price ◼ Price is the sum of all the values that consumers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service. ◼ Price has been the major factor affecting buyer choice; nonprice factors have become increasingly important in buyer-choice behavior. ◼ Price is the only element in the marketing mix that produces revenues; all others represent costs
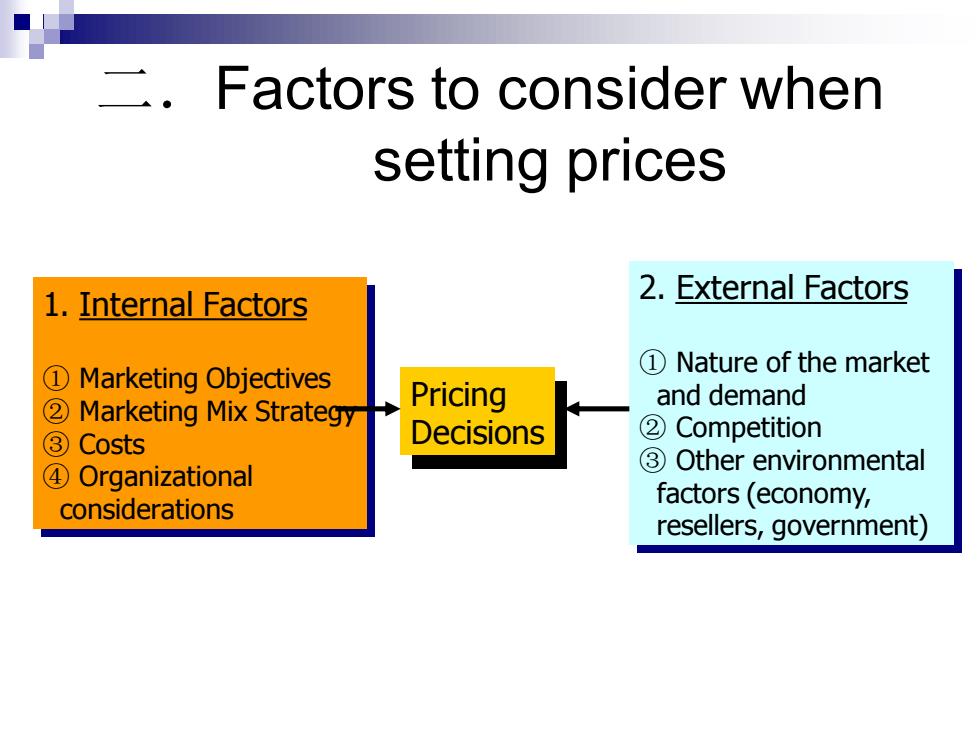
Factors to consider when setting prices 1.Internal Factors 2.External Factors D Marketing Objectives ①Nature of the market 2 Marketing Mix Strategy Pricing and demand ③Costs Decisions ②Competition ③Other environmental ④Organizational considerations factors (economy, resellers,government)
二.Factors to consider when setting prices 1. Internal Factors ① Marketing Objectives ② Marketing Mix Strategy ③ Costs ④ Organizational considerations 2. External Factors ① Nature of the market and demand ② Competition ③ Other environmental factors (economy, resellers, government) Pricing Decisions
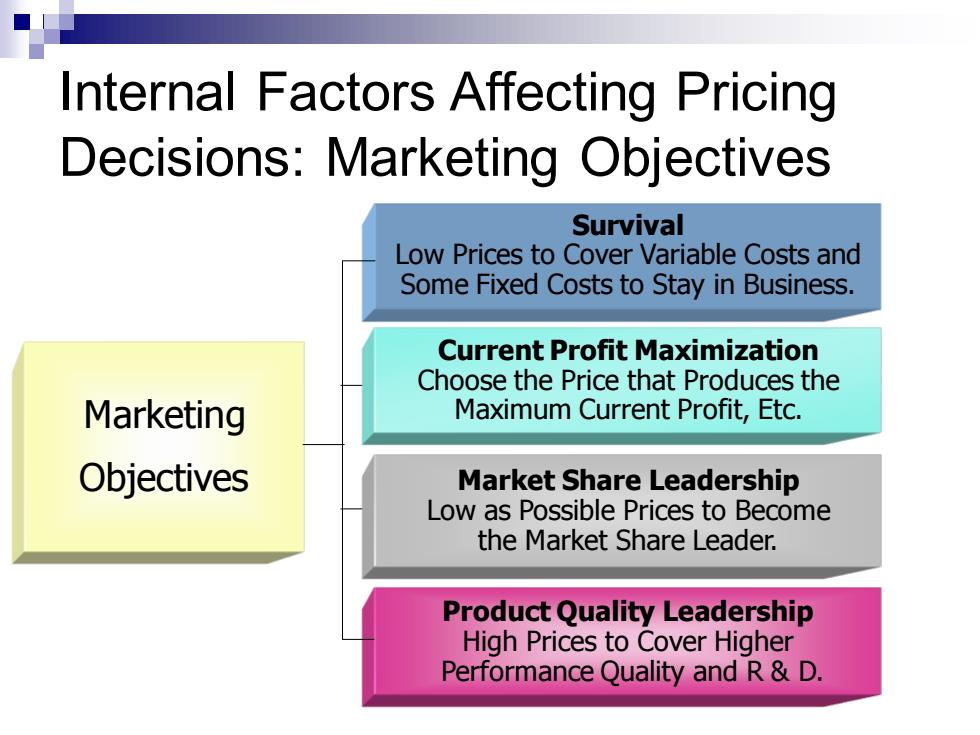
Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions:Marketing Objectives Survival Low Prices to Cover Variable Costs and Some Fixed Costs to Stay in Business. Current Profit Maximization Choose the Price that Produces the Marketing Maximum Current Profit,Etc. Objectives Market Share Leadership Low as Possible Prices to Become the Market Share Leader. Product Quality Leadership High Prices to Cover Higher Performance Quality and R&D
Marketing Objectives Survival Low Prices to Cover Variable Costs and Some Fixed Costs to Stay in Business. Current Profit Maximization Choose the Price that Produces the Maximum Current Profit, Etc. Market Share Leadership Low as Possible Prices to Become the Market Share Leader. Product Quality Leadership High Prices to Cover Higher Performance Quality and R & D. Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: Marketing Objectives

Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions:Marketing Objectives Other specific objectives include: Set prices low to prevent competition from entering the market, Prices might be reduced temporarily to create excitement or draw more customers. Nonprofit and public organization may have other pricing objectives such as: University aims for partial cost recovery, Hospital may aim for full cost recovery, Theater may price to fill maximum number of seats
Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: Marketing Objectives ◼ Other specific objectives include: Set prices low to prevent competition from entering the market, Prices might be reduced temporarily to create excitement or draw more customers. ◼ Nonprofit and public organization may have other pricing objectives such as: University aims for partial cost recovery, Hospital may aim for full cost recovery, Theater may price to fill maximum number of seats
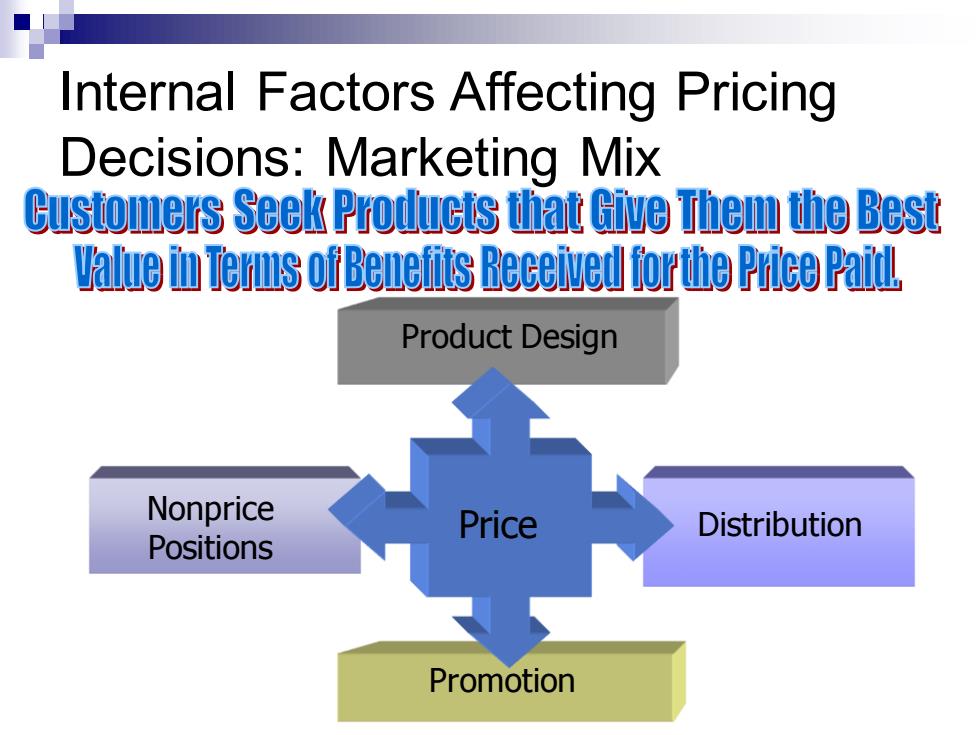
Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions:Marketing Mix Customers Seek Produets that Give Them the Best value i Terms of Benetits Received forthe Price Paid Product Design Nonprice Distribution Positions Promotion
Price Product Design Distribution Promotion Nonprice Positions Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: Marketing Mix
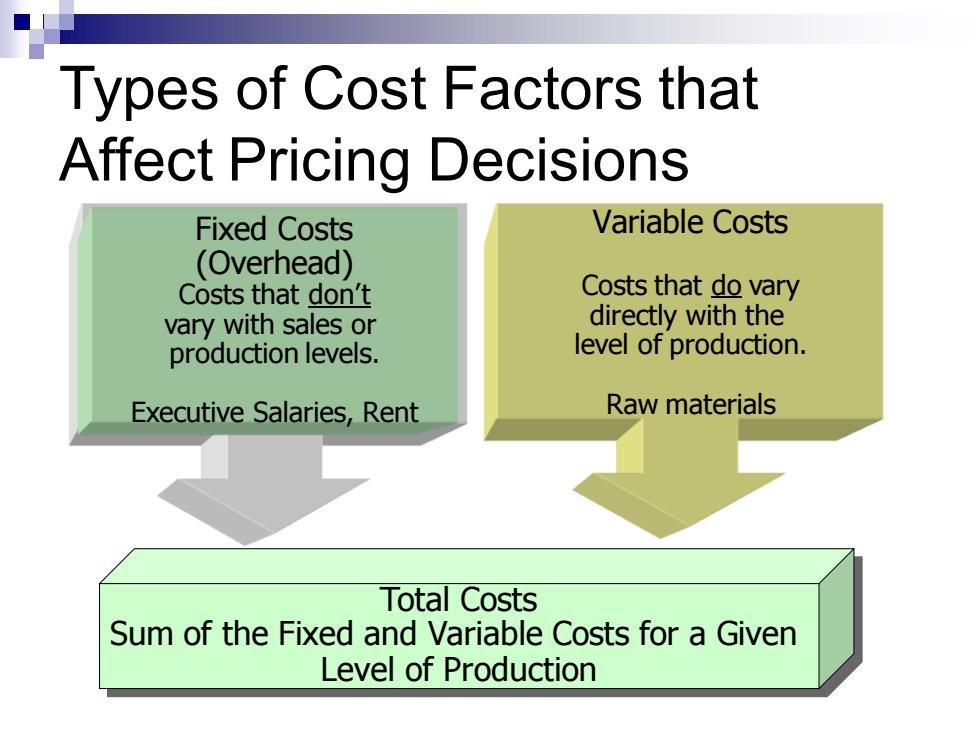
Types of Cost Factors that Affect Pricing Decisions Fixed Costs Variable Costs (Overhead) Costs that don't Costs that do vary vary with sales or directly with the production levels. level of production. Executive Salaries,Rent Raw materials Total Costs Sum of the Fixed and Variable Costs for a Given Level of Production
Types of Cost Factors that Affect Pricing Decisions Total Costs Sum of the Fixed and Variable Costs for a Given Level of Production Variable Costs Costs that do vary directly with the level of production. Raw materials Fixed Costs (Overhead) Costs that don’t vary with sales or production levels. Executive Salaries, Rent
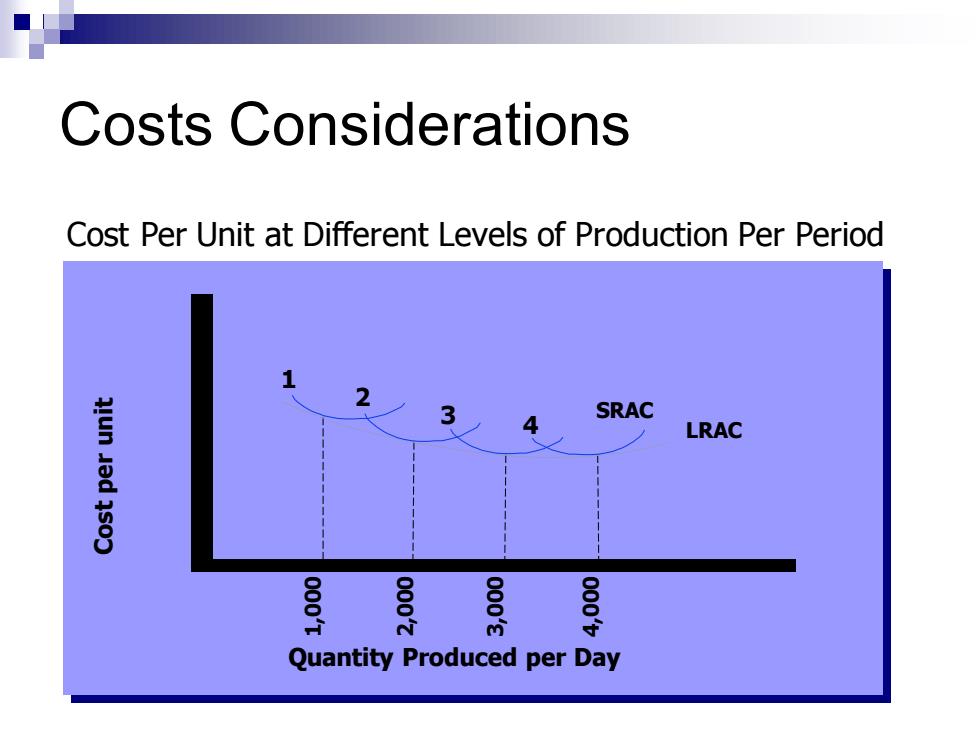
Costs Considerations Cost Per Unit at Different Levels of Production Per Period SRAC LRAC Quantity Produced per Day
Costs Considerations Cost per unit 1 2 3 4 SRAC LRAC Quantity Produced per Day 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 Cost Per Unit at Different Levels of Production Per Period

Types of Cost Factors that Affect Pricing Decisions As a firm gains experience in production,it learns how to do it better. The experience curve (or the learning curve)indicates that average cost drops with accumulated production experience. Strategy:company should price products low;sales increases;costs continue to decrease;and then lower prices further. Risks are present with this strategy
Types of Cost Factors that Affect Pricing Decisions ◼ As a firm gains experience in production, it learns how to do it better. ◼ The experience curve (or the learning curve) indicates that average cost drops with accumulated production experience. ◼ Strategy: company should price products low; sales increases; costs continue to decrease; and then lower prices further. ◼ Risks are present with this strategy
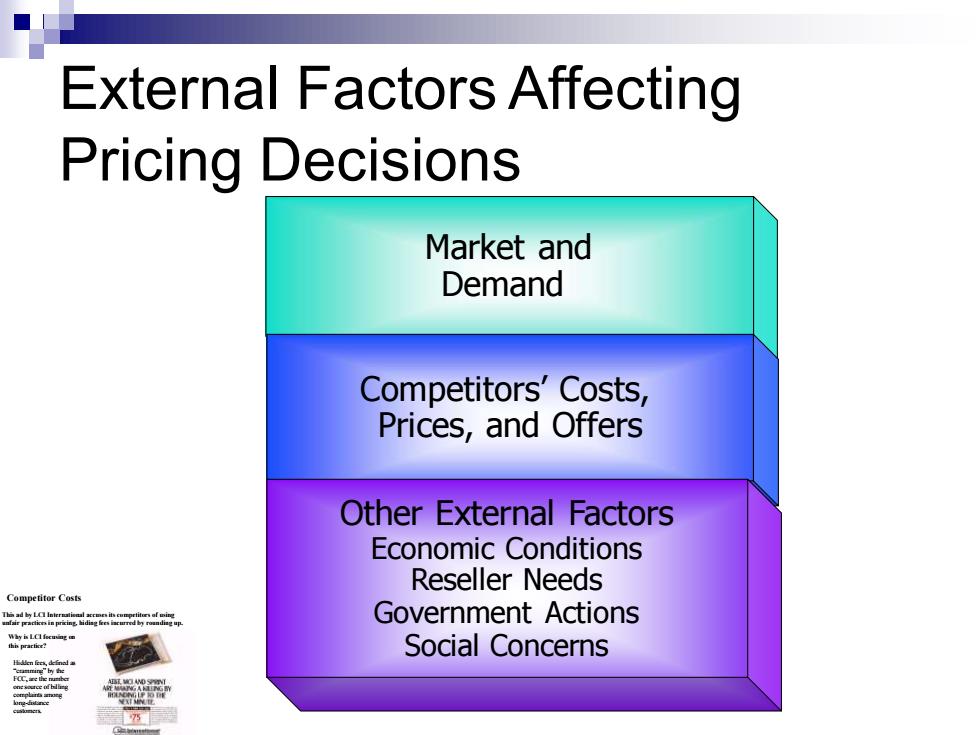
External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions Market and Demand Competitors'Costs, Prices,and Offers Other External Factors Economic Conditions Reseller Needs Competitor Costs Government Actions Social Concerns
Market and Demand Competitors’ Costs, Prices, and Offers Other External Factors Economic Conditions Reseller Needs Government Actions Social Concerns External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions Competitor Costs This ad by LCI International accuses its competitors of using unfair practices in pricing, hiding fees incurred by rounding up. Hidden fees, defined as “cramming” by the FCC, are the number one source of billing complaints among long-distance customers. Why is LCI focusing on this practice?