
Chapter 26:Advanced Transaction Processing Transaction-Processing Monitors Transactional Workflows High-Performance Transaction Systems Main memory databases Real-Time Transaction Systems Long-Duration Transactions Transaction management in multidatabase systems Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Chapter 26: Advanced Transaction Processing Transaction-Processing Monitors Transactional Workflows High-Performance Transaction Systems Main memory databases Real-Time Transaction Systems Long-Duration Transactions Transaction management in multidatabase systems
Transaction Processing Monitors TP monitors initially developed as multithreaded servers to support large numbers of terminals from a single process. Provide infrastructure for building and administering complex transaction processing systems with a large number of clients and multiple servers. Provide services such as: Presentation facilities to simplify creating user interfaces Persistent queuing of client requests and server responses Routing of client messages to servers Coordination of two-phase commit when transactions access multiple servers. Some commercial TP monitors:CICS from IBM,Pathway from Tandem, Top End from NCR,and Encina from Transarc Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Transaction Processing Monitors TP monitors initially developed as multithreaded servers to support large numbers of terminals from a single process. Provide infrastructure for building and administering complex transaction processing systems with a large number of clients and multiple servers. Provide services such as: Presentation facilities to simplify creating user interfaces Persistent queuing of client requests and server responses Routing of client messages to servers Coordination of two-phase commit when transactions access multiple servers. Some commercial TP monitors: CICS from IBM, Pathway from Tandem, Top End from NCR, and Encina from Transarc
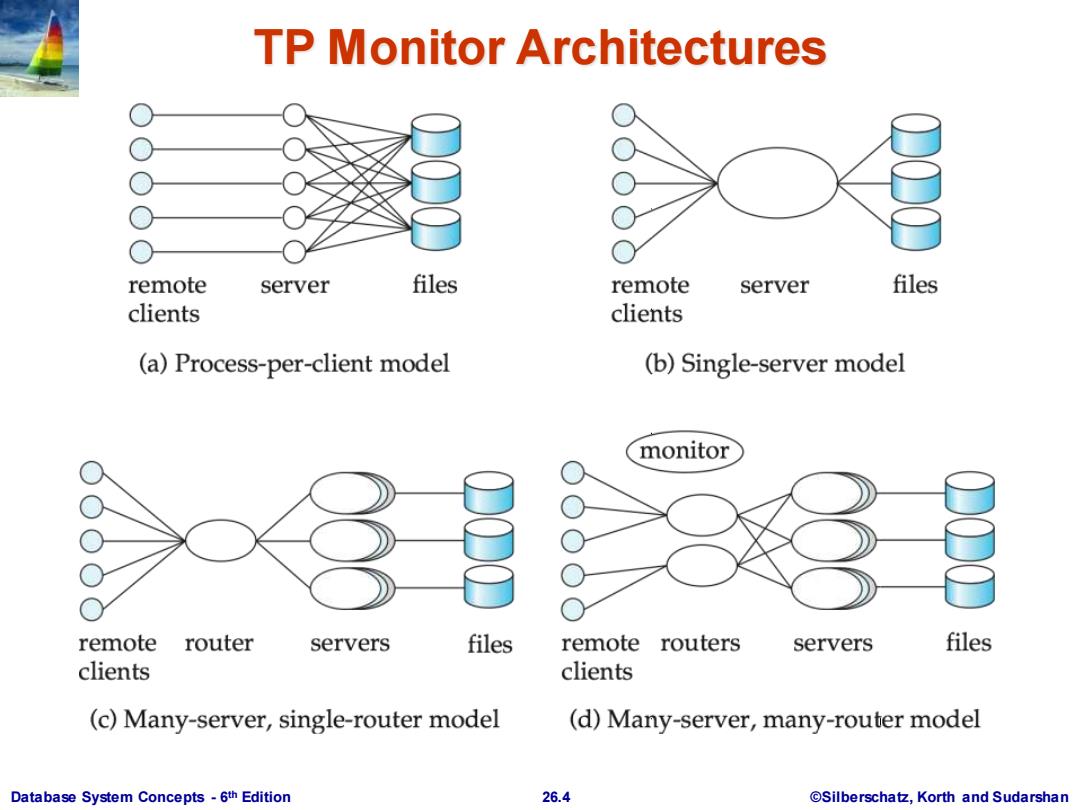
TP Monitor Architectures remote server files remote server files clients clients (a)Process-per-client model (b)Single-server model monitor remote router servers files remote routers servers files clients clients (c)Many-server,single-router model (d)Many-server,many-router model Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.4 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition TP Monitor Architectures
TP Monitor Architectures (Cont.) Process per client model -instead of individual login session per terminal,server process communicates with the terminal,handles authentication,and executes actions. Memory requirements are high Multitasking-high CPU overhead for context switching between processes Single process model -all remote terminals connect to a single server process. Used in client-server environments Server process is multi-threaded;low cost for thread switching No protection between applications Not suited for parallel or distributed databases Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition TP Monitor Architectures (Cont.) Process per client model - instead of individual login session per terminal, server process communicates with the terminal, handles authentication, and executes actions. Memory requirements are high Multitasking- high CPU overhead for context switching between processes Single process model - all remote terminals connect to a single server process. Used in client-server environments Server process is multi-threaded; low cost for thread switching No protection between applications Not suited for parallel or distributed databases
TP Monitor Architectures (Cont.) Many-server single-router model-multiple application server processes access a common database;clients communicate with the application through a single communication process that routes requests. Independent server processes for multiple applications Multithread server process Run on parallel or distributed database Many server many-router model-multiple processes communicate with clients. Client communication processes interact with router processes that route their requests to the appropriate server. Controller process starts up and supervises other processes. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition TP Monitor Architectures (Cont.) Many-server single-router model - multiple application server processes access a common database; clients communicate with the application through a single communication process that routes requests. Independent server processes for multiple applications Multithread server process Run on parallel or distributed database Many server many-router model - multiple processes communicate with clients. Client communication processes interact with router processes that route their requests to the appropriate server. Controller process starts up and supervises other processes
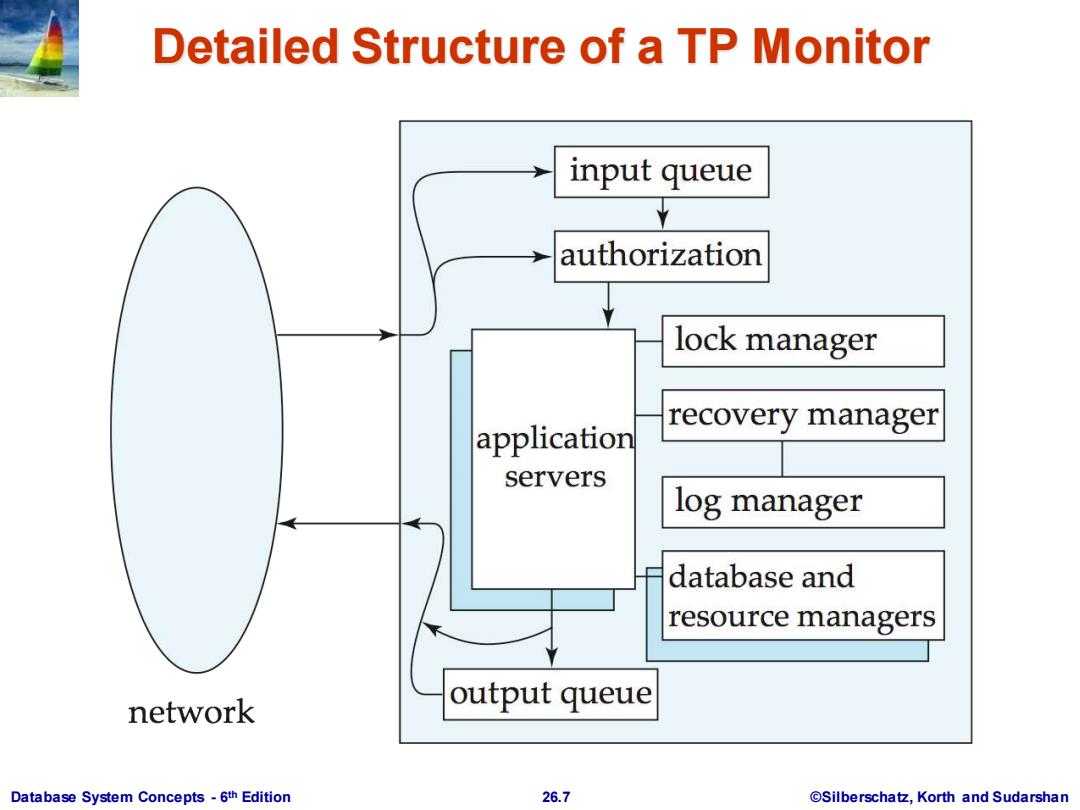
Detailed Structure of a TP Monitor input queue authorization lock manager application recovery manager servers log manager database and resource managers network output queue Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.7 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Detailed Structure of a TP Monitor

Detailed Structure of a TP Monitor Queue manager handles incoming messages Some queue managers provide persistent or durable message queueing contents of queue are safe even if systems fails. Durable queueing of outgoing messages is important application server writes message to durable queue as part of a transaction once the transaction commits,the TP monitor guarantees message is eventually delivered,regardless of crashes. ACID properties are thus provided even for messages sent outside the database Many TP monitors provide locking,logging and recovery services, to enable application servers to implement ACID properties by themselves. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Detailed Structure of a TP Monitor Queue manager handles incoming messages Some queue managers provide persistent or durable message queueing contents of queue are safe even if systems fails. Durable queueing of outgoing messages is important application server writes message to durable queue as part of a transaction once the transaction commits, the TP monitor guarantees message is eventually delivered, regardless of crashes. ACID properties are thus provided even for messages sent outside the database Many TP monitors provide locking, logging and recovery services, to enable application servers to implement ACID properties by themselves
Application Coordination Using TP Monitors A TP monitor treats each subsystem as a resource manager that provides transactional access to some set of resources. The interface between the TP monitor and the resource manager is defined by a set of transaction primitives The resource manager interface is defined by the X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing standard. TP monitor systems provide a transactional remote procedure call (transactional RPC)interface to their service Transactional RPC provides calls to enclose a series of RPC calls within a transaction. Updates performed by an RPC are carried out within the scope of the transaction,and can be rolled back if there is any failure. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.9 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Application Coordination Using TP Monitors A TP monitor treats each subsystem as a resource manager that provides transactional access to some set of resources. The interface between the TP monitor and the resource manager is defined by a set of transaction primitives The resource manager interface is defined by the X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing standard. TP monitor systems provide a transactional remote procedure call (transactional RPC) interface to their service Transactional RPC provides calls to enclose a series of RPC calls within a transaction. Updates performed by an RPC are carried out within the scope of the transaction, and can be rolled back if there is any failure

☒无法显示该图片。 Workflow Systems Database System Concepts,6th Ed. Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use
Database System Concepts, 6th Ed. ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Workflow Systems

Transactional Workflows Workflows are activities that involve the coordinated execution of multiple tasks performed by different processing entities. With the growth of networks,and the existence of multiple autonomous database systems,workflows provide a convenient way of carrying out tasks that involve multiple systems. Example of a workflow delivery of an email message,which goes through several mails systems to reach destination. Each mailer performs a tasks:forwarding of the mail to the next mailer. If a mailer cannot deliver mail,failure must be handled semantically (delivery failure message). Workflows usually involve humans:e.g.loan processing,or purchase order processing. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 26.11 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 26.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Transactional Workflows Workflows are activities that involve the coordinated execution of multiple tasks performed by different processing entities. With the growth of networks, and the existence of multiple autonomous database systems, workflows provide a convenient way of carrying out tasks that involve multiple systems. Example of a workflow delivery of an email message, which goes through several mails systems to reach destination. Each mailer performs a tasks: forwarding of the mail to the next mailer. If a mailer cannot deliver mail, failure must be handled semantically (delivery failure message). Workflows usually involve humans: e.g. loan processing, or purchase order processing