
Chapter 19:Distributed Databases Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Databases Distributed Data Storage Distributed Transactions Commit Protocols Concurrency Control in Distributed Databases Availability Distributed Query Processing Heterogeneous Distributed Databases Directory Systems Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Chapter 19: Distributed Databases Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Databases Distributed Data Storage Distributed Transactions Commit Protocols Concurrency Control in Distributed Databases Availability Distributed Query Processing Heterogeneous Distributed Databases Directory Systems
Distributed Database System A distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical component Database systems that run on each site are independent of each other Transactions may access data at one or more sites Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Distributed Database System A distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical component Database systems that run on each site are independent of each other Transactions may access data at one or more sites
Homogeneous Distributed Databases In a homogeneous distributed database All sites have identical software Are aware of each other and agree to cooperate in processing user requests. Each site surrenders part of its autonomy in terms of right to change schemas or software Appears to user as a single system In a heterogeneous distributed database Different sites may use different schemas and software Difference in schema is a major problem for query processing Difference in software is a major problem for transaction processing Sites may not be aware of each other and may provide only limited facilities for cooperation in transaction processing Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.4 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Homogeneous Distributed Databases In a homogeneous distributed database All sites have identical software Are aware of each other and agree to cooperate in processing user requests. Each site surrenders part of its autonomy in terms of right to change schemas or software Appears to user as a single system In a heterogeneous distributed database Different sites may use different schemas and software Difference in schema is a major problem for query processing Difference in software is a major problem for transaction processing Sites may not be aware of each other and may provide only limited facilities for cooperation in transaction processing

Distributed Data Storage Assume relational data model Replication System maintains multiple copies of data,stored in different sites, for faster retrieval and fault tolerance. Fragmentation Relation is partitioned into several fragments stored in distinct sites Replication and fragmentation can be combined Relation is partitioned into several fragments:system maintains several identical replicas of each such fragment. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Distributed Data Storage Assume relational data model Replication System maintains multiple copies of data, stored in different sites, for faster retrieval and fault tolerance. Fragmentation Relation is partitioned into several fragments stored in distinct sites Replication and fragmentation can be combined Relation is partitioned into several fragments: system maintains several identical replicas of each such fragment

Data Replication A relation or fragment of a relation is replicated if it is stored redundantly in two or more sites. Full replication of a relation is the case where the relation is stored at all sites. Fully redundant databases are those in which every site contains a copy of the entire database. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Replication A relation or fragment of a relation is replicated if it is stored redundantly in two or more sites. Full replication of a relation is the case where the relation is stored at all sites. Fully redundant databases are those in which every site contains a copy of the entire database
Data Replication (Cont.) Advantages of Replication Availability:failure of site containing relation r does not result in unavailability of ris replicas exist. Parallelism:queries on r may be processed by several nodes in parallel. Reduced data transfer:relation r is available locally at each site containing a replica of r. Disadvantages of Replication Increased cost of updates:each replica of relation r must be updated. Increased complexity of concurrency control:concurrent updates to distinct replicas may lead to inconsistent data unless special concurrency control mechanisms are implemented. One solution:choose one copy as primary copy and apply concurrency control operations on primary copy Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.7 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Replication (Cont.) Advantages of Replication Availability: failure of site containing relation r does not result in unavailability of r is replicas exist. Parallelism: queries on r may be processed by several nodes in parallel. Reduced data transfer: relation r is available locally at each site containing a replica of r. Disadvantages of Replication Increased cost of updates: each replica of relation r must be updated. Increased complexity of concurrency control: concurrent updates to distinct replicas may lead to inconsistent data unless special concurrency control mechanisms are implemented. One solution: choose one copy as primary copy and apply concurrency control operations on primary copy
Data Fragmentation Division of relation r into fragments n,r2,...rn which contain sufficient information to reconstruct relation r. Horizontal fragmentation:each tuple of r is assigned to one or more fragments Vertical fragmentation:the schema for relation r is split into several smaller schemas All schemas must contain a common candidate key(or superkey)to ensure lossless join property. A special attribute,the tuple-id attribute may be added to each schema to serve as a candidate key. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Fragmentation Division of relation r into fragments r1 , r2 , …, rn which contain sufficient information to reconstruct relation r. Horizontal fragmentation: each tuple of r is assigned to one or more fragments Vertical fragmentation: the schema for relation r is split into several smaller schemas All schemas must contain a common candidate key (or superkey) to ensure lossless join property. A special attribute, the tuple-id attribute may be added to each schema to serve as a candidate key
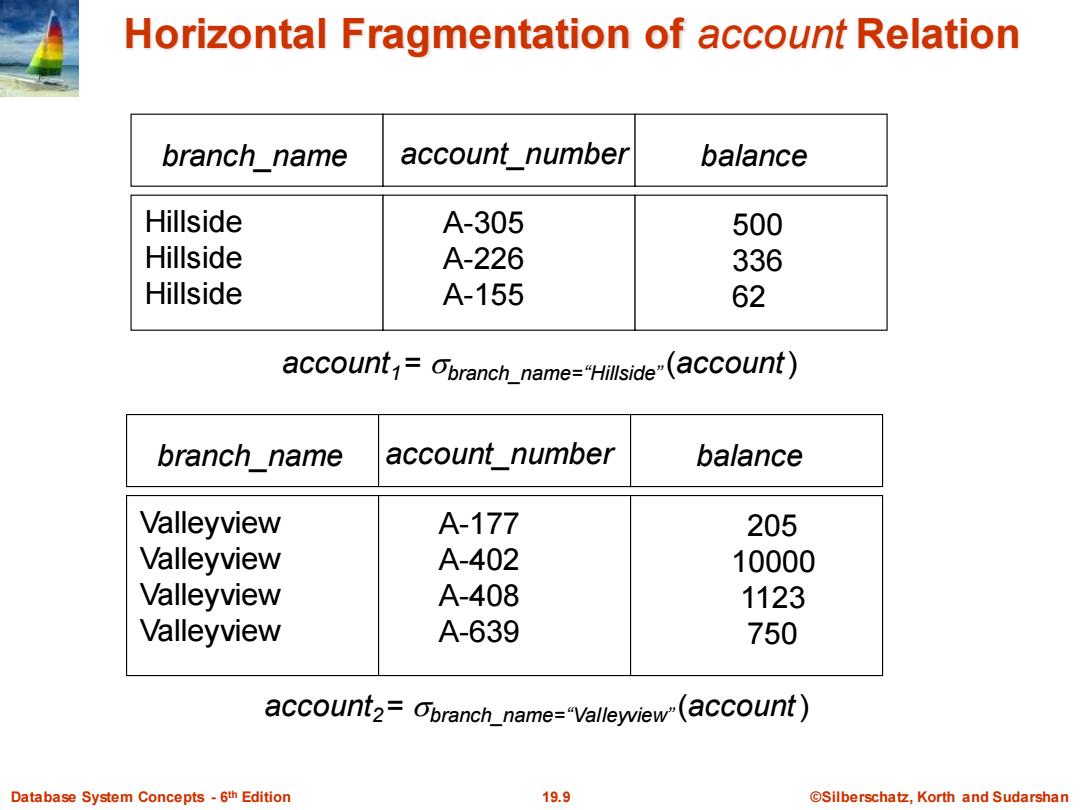
Horizontal Fragmentation of account Relation branch name account number balance Hillside A-305 500 Hillside A-226 336 Hillside A-155 62 account=Oranch_name="Hillside"(account) branch_name account number balance Valleyview A-177 205 Valleyview A-402 10000 Valleyview A-408 1123 Valleyview A-639 750 account2=Obranch_name="Vallewiew(account) Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.9 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Horizontal Fragmentation of account Relation branch_name account_number balance Hillside Hillside Hillside A-305 A-226 A-155 500 336 62 account1 = branch_name=“Hillside” (account ) branch_name account_number balance Valleyview Valleyview Valleyview Valleyview A-177 A-402 A-408 A-639 205 10000 1123 750 account2 = branch_name=“Valleyview” (account )
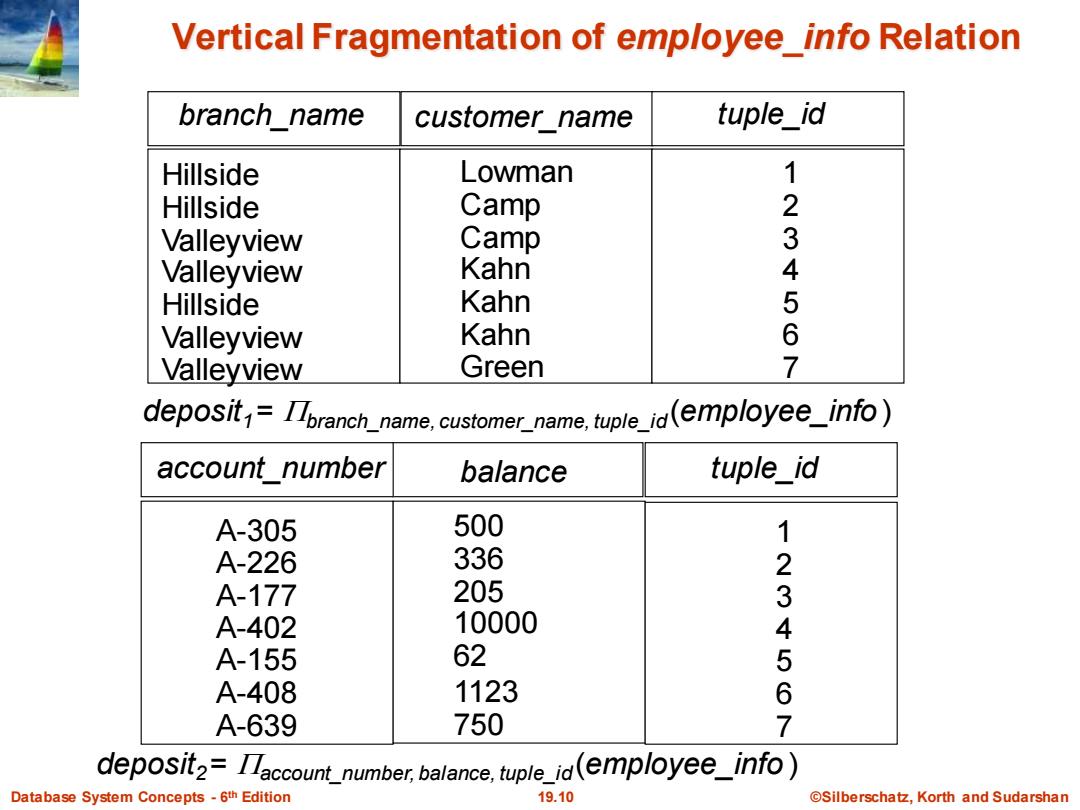
Vertical Fragmentation of employee info Relation branch_name customer name tuple id Hillside Lowman 1 Hillside Camp 2 Valleyview Camp 3 Valleyview Kahn 4 Hillside Kahn 5 Valleyview Kahn 6 Valleyview Green 7 deposit=Ipranch name.customer name,tuple_id(employee_info) account number balance tuple id A-305 500 1 A-226 336 2 A-177 205 3 A-402 10000 4 A-155 62 5 A-408 1123 6 A-639 750 7 deposit2=Iaccount number.balance.tuple_id(employee_info) Database System Concepts -6th Edition 19.10 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Vertical Fragmentation of employee_info Relation branch_name customer_name tuple_id Hillside Hillside Valleyview Valleyview Hillside Valleyview Valleyview Lowman Camp Camp Kahn Kahn Kahn Green deposit1 = branch_name, customer_name, tuple_id (employee_info ) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 account_number balance tuple_id 500 336 205 10000 62 1123 750 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 A-305 A-226 A-177 A-402 A-155 A-408 A-639 deposit2 = account_number, balance, tuple_id (employee_info )
Advantages of Fragmentation Horizontal: allows parallel processing on fragments of a relation allows a relation to be split so that tuples are located where they are most frequently accessed Vertical: allows tuples to be split so that each part of the tuple is stored where it is most frequently accessed tuple-id attribute allows efficient joining of vertical fragments allows parallel processing on a relation Vertical and horizontal fragmentation can be mixed. Fragments may be successively fragmented to an arbitrary depth. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 19.11 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 19.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Advantages of Fragmentation Horizontal: allows parallel processing on fragments of a relation allows a relation to be split so that tuples are located where they are most frequently accessed Vertical: allows tuples to be split so that each part of the tuple is stored where it is most frequently accessed tuple-id attribute allows efficient joining of vertical fragments allows parallel processing on a relation Vertical and horizontal fragmentation can be mixed. Fragments may be successively fragmented to an arbitrary depth