
Chapter 20:Data Analysis Decision Support Systems Data Warehousing Data Mining Classification Association Rules Clustering Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Chapter 20: Data Analysis Decision Support Systems Data Warehousing Data Mining Classification Association Rules Clustering

Decision Support Systems Decision-support systems are used to make business decisions, often based on data collected by on-line transaction-processing systems. Examples of business decisions: What items to stock? What insurance premium to change? To whom to send advertisements? Examples of data used for making decisions Retail sales transaction details Customer profiles (income,age,gender,etc.) Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Decision Support Systems Decision-support systems are used to make business decisions, often based on data collected by on-line transaction-processing systems. Examples of business decisions: What items to stock? What insurance premium to change? To whom to send advertisements? Examples of data used for making decisions Retail sales transaction details Customer profiles (income, age, gender, etc.)
Decision-Support Systems:Overview Data analysis tasks are simplified by specialized tools and SQL extensions Example tasks For each product category and each region,what were the total sales in the last quarter and how do they compare with the same quarter last year As above,for each product category and each customer category Statistical analysis packages (e.g.,S++)can be interfaced with databases Statistical analysis is a large field,but not covered here Data mining seeks to discover knowledge automatically in the form of statistical rules and patterns from large databases. A data warehouse archives information gathered from multiple sources,and stores it under a unified schema,at a single site. Important for large businesses that generate data from multiple divisions,possibly at multiple sites Data may also be purchased externally Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.4 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Decision-Support Systems: Overview Data analysis tasks are simplified by specialized tools and SQL extensions Example tasks For each product category and each region, what were the total sales in the last quarter and how do they compare with the same quarter last year As above, for each product category and each customer category Statistical analysis packages (e.g., : S++) can be interfaced with databases Statistical analysis is a large field, but not covered here Data mining seeks to discover knowledge automatically in the form of statistical rules and patterns from large databases. A data warehouse archives information gathered from multiple sources, and stores it under a unified schema, at a single site. Important for large businesses that generate data from multiple divisions, possibly at multiple sites Data may also be purchased externally

Data Warehousing Data sources often store only current data,not historical data Corporate decision making requires a unified view of all organizational data,including historical data A data warehouse is a repository (archive)of information gathered from multiple sources,stored under a unified schema,at a single site Greatly simplifies querying,permits study of historical trends Shifts decision support query load away from transaction processing systems Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Warehousing Data sources often store only current data, not historical data Corporate decision making requires a unified view of all organizational data, including historical data A data warehouse is a repository (archive) of information gathered from multiple sources, stored under a unified schema, at a single site Greatly simplifies querying, permits study of historical trends Shifts decision support query load away from transaction processing systems
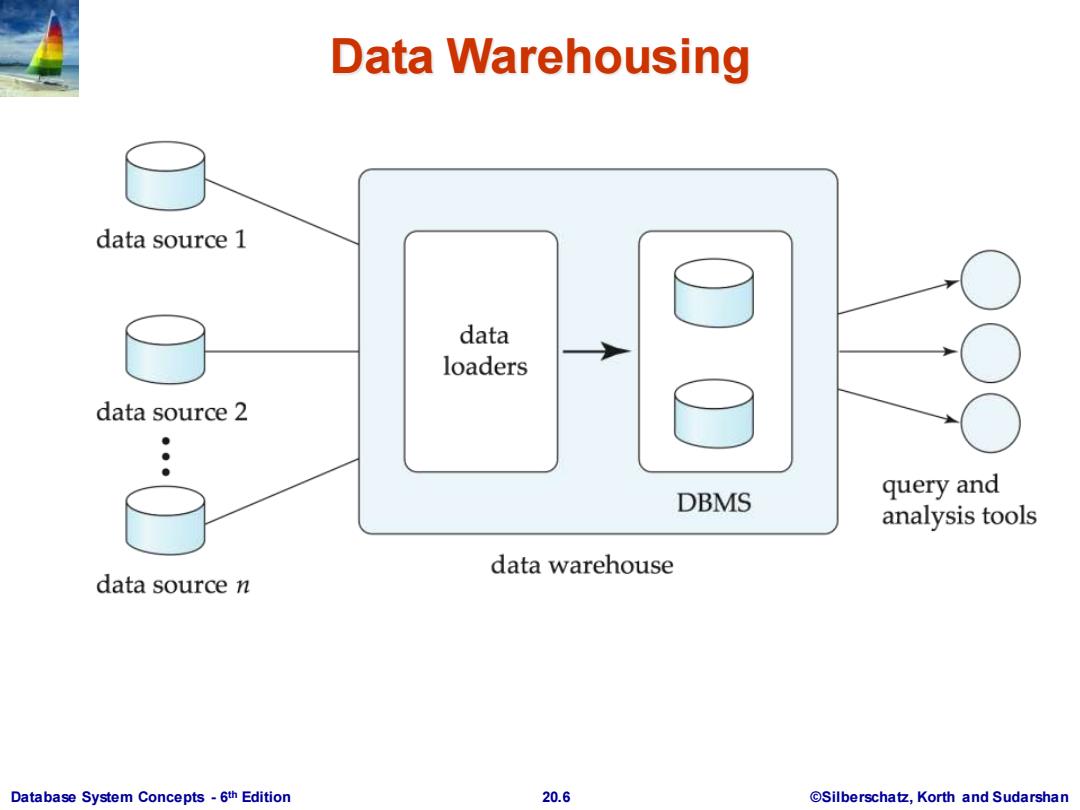
Data Warehousing data source 1 data loaders data source 2 ● DBMS query and analysis tools data warehouse data source n Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Warehousing

Design Issues When and how to gather data Source driven architecture:data sources transmit new information to warehouse,either continuously or periodically (e.g.,at night) Destination driven architecture:warehouse periodically requests new information from data sources Keeping warehouse exactly synchronized with data sources (e.g.,using two-phase commit)is too expensive Usually OK to have slightly out-of-date data at warehouse Data/updates are periodically downloaded form online transaction processing (OLTP)systems. What schema to use Schema integration Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.7 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Design Issues When and how to gather data Source driven architecture: data sources transmit new information to warehouse, either continuously or periodically (e.g., at night) Destination driven architecture: warehouse periodically requests new information from data sources Keeping warehouse exactly synchronized with data sources (e.g., using two-phase commit) is too expensive Usually OK to have slightly out-of-date data at warehouse Data/updates are periodically downloaded form online transaction processing (OLTP) systems. What schema to use Schema integration

More Warehouse Design Issues Data cleansing E.g.,correct mistakes in addresses(misspellings,zip code errors) Merge address lists from different sources and purge duplicates How to propagate updates Warehouse schema may be a(materialized)view of schema from data sources What data to summarize Raw data may be too large to store on-line Aggregate values(totals/subtotals)often suffice Queries on raw data can often be transformed by query optimizer to use aggregate values Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition More Warehouse Design Issues Data cleansing E.g., correct mistakes in addresses (misspellings, zip code errors) Merge address lists from different sources and purge duplicates How to propagate updates Warehouse schema may be a (materialized) view of schema from data sources What data to summarize Raw data may be too large to store on-line Aggregate values (totals/subtotals) often suffice Queries on raw data can often be transformed by query optimizer to use aggregate values

Warehouse Schemas Dimension values are usually encoded using small integers and mapped to full values via dimension tables Resultant schema is called a star schema More complicated schema structures Snowflake schema:multiple levels of dimension tables Constellation:multiple fact tables Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.9 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Warehouse Schemas Dimension values are usually encoded using small integers and mapped to full values via dimension tables Resultant schema is called a star schema More complicated schema structures Snowflake schema: multiple levels of dimension tables Constellation: multiple fact tables
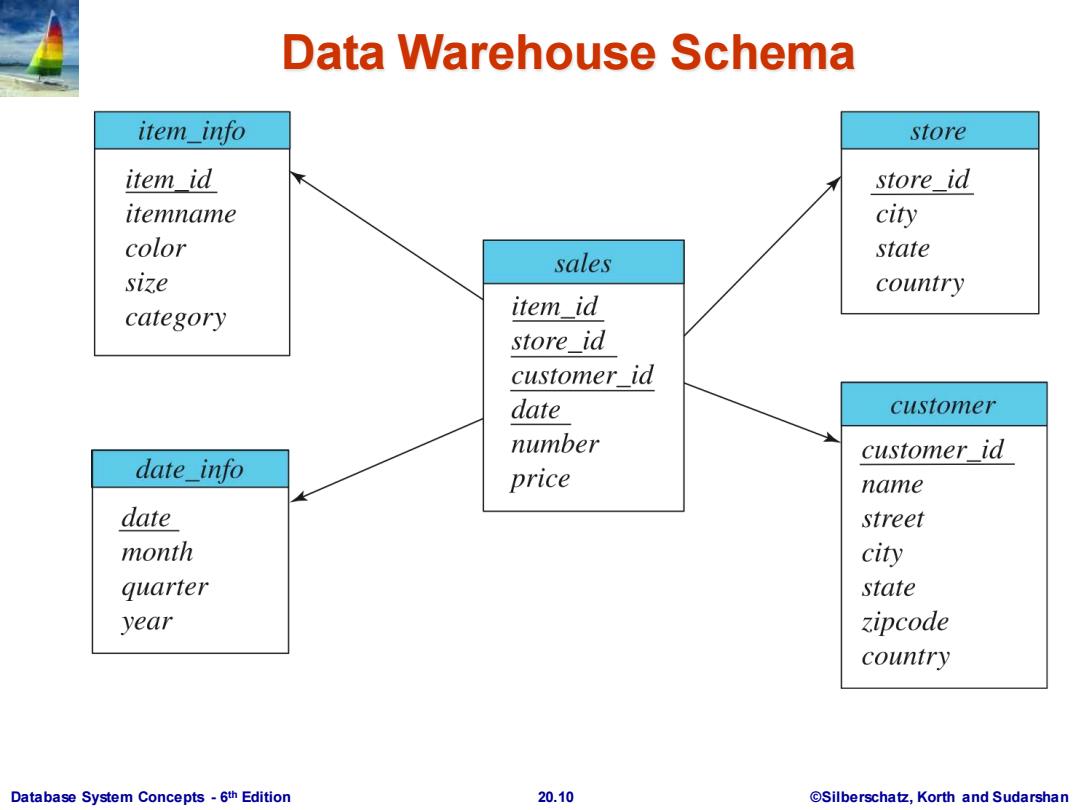
Data Warehouse Schema item_info store item id store_id itemname city color state sales size country category item id store id customer id date customer number date info customer id price name date street month city quarter state year zipcode country Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.10 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Warehouse Schema
Data Mining Data mining is the process of semi-automatically analyzing large databases to find useful patterns Prediction based on past history Predict if a credit card applicant poses a good credit risk,based on some attributes(income,job type,age,..and past history Predict if a pattern of phone calling card usage is likely to be fraudulent Some examples of prediction mechanisms: Classification Given a new item whose class is unknown,predict to which class it belongs Regression formulae Given a set of mappings for an unknown function,predict the function result for a new parameter value Database System Concepts-6th Edition 20.11 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 20.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Data Mining Data mining is the process of semi-automatically analyzing large databases to find useful patterns Prediction based on past history Predict if a credit card applicant poses a good credit risk, based on some attributes (income, job type, age, ..) and past history Predict if a pattern of phone calling card usage is likely to be fraudulent Some examples of prediction mechanisms: Classification Given a new item whose class is unknown, predict to which class it belongs Regression formulae Given a set of mappings for an unknown function, predict the function result for a new parameter value