
Pulpal Disease and Periapical Disease
Pulpal Disease and Disease and Disease and Disease and Disease and Disease and Disease and Disease and Periapical Disease Periapical Disease Periapical Disease Periapical Disease Periapical Disease Periapical Disease Periapical Disease Periapical Disease
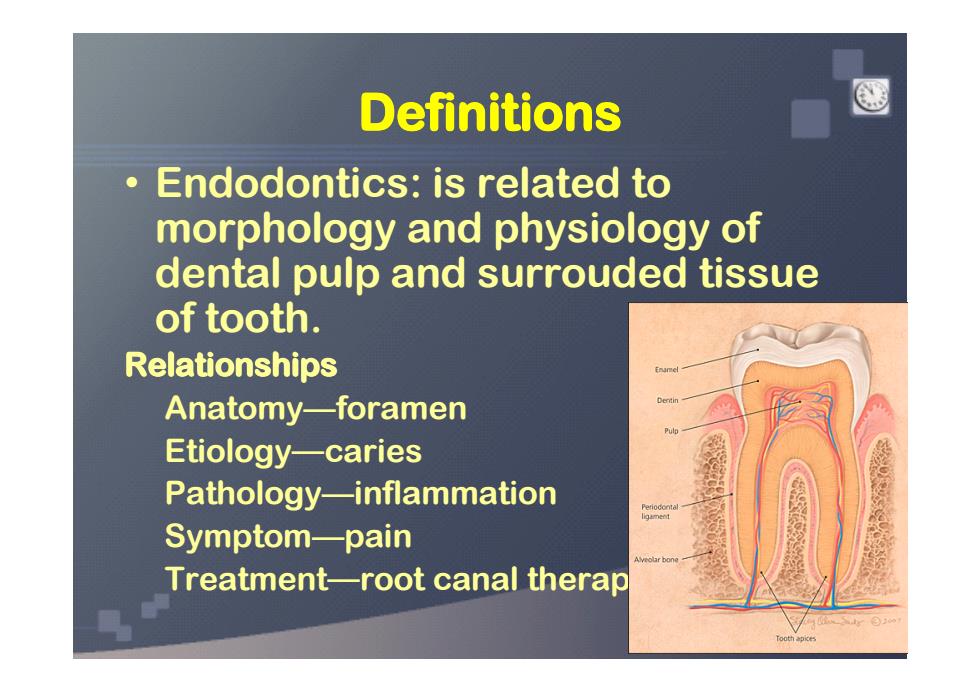
Definitions Endodontics:is related to morphology and physiology of dental pulp and surrouded tissue of tooth. Relationships Anatomy-foramen Etiology-caries Pathology-inflammation Symptom-pain Treatment-root canal therap
Definitions Definitions Definitions Definitions • Endodontics: is related to morphology and physiology of dental pulp and surrouded tissue of tooth. Relationships Relationships Relationships Relationships Anatomy—foramen Etiology—caries Pathology—inflammation Symptom—pain Treatment—root canal therapy

Contents Histology and Physiology Etiology Diagnostic Procedures
• Histology and Physiology • Etiology • Diagnostic Procedures Content Content Content Content Content Content Content Contents
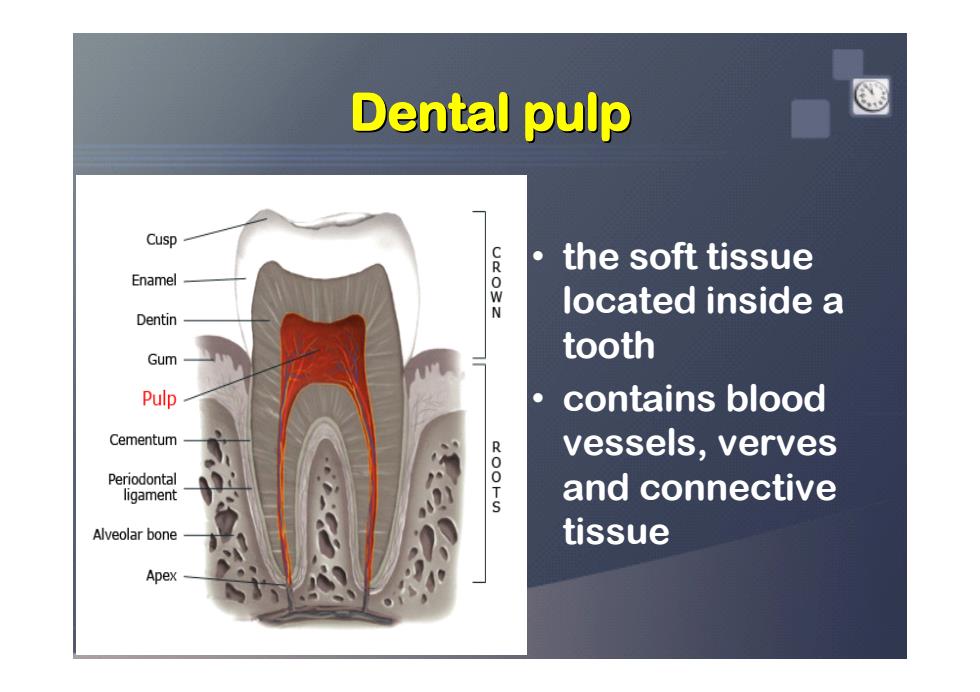
Dental pulp Cusp the soft tissue Enamel located inside a Dentin Gum tooth Pulp contains blood Cementum vessels,verves Periodontal ligament oO-u and connective Alveolar bone tissue Apex
Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp • the soft tissue located inside a tooth • contains blood vessels, verves and connective tissue
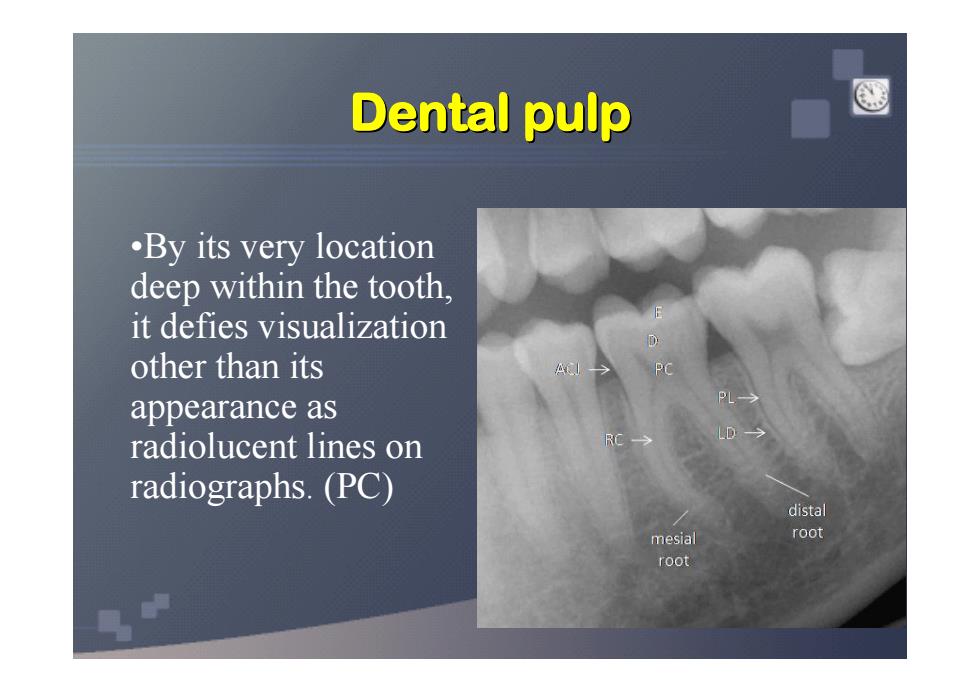
Dental pulp .By its very location deep within the tooth. it defies visualization other than its appearance as radiolucent lines on radiographs.(PC) distal mesial root root
Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp •By its very location deep within the tooth, it defies visualization other than its appearance as radiolucent lines on radiographs. (PC)
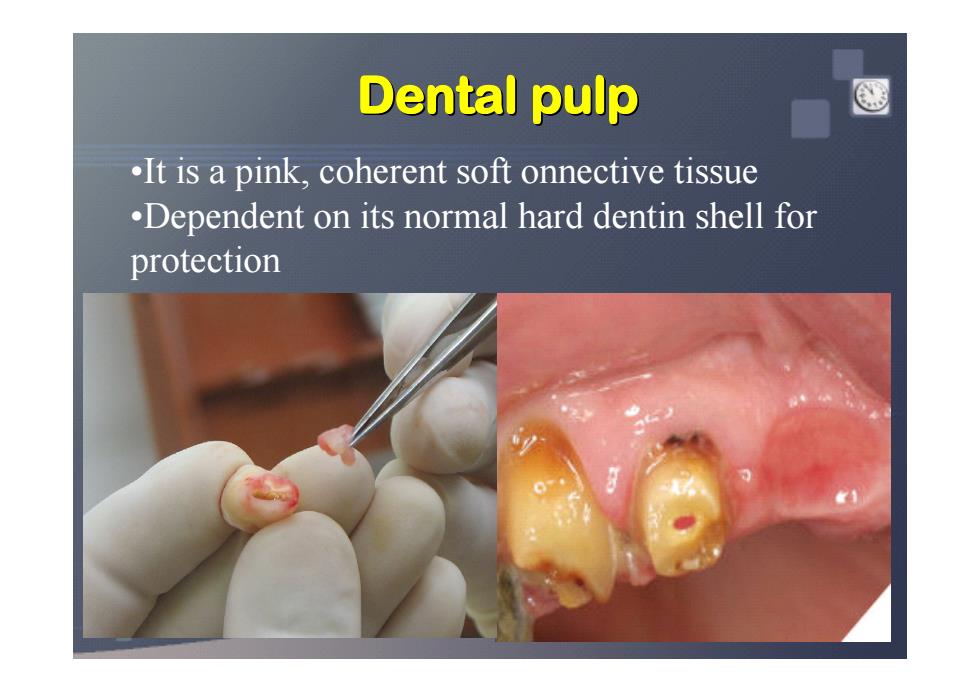
Dental pulp .It is a pink,coherent soft onnective tissue .Dependent on its normal hard dentin shell for protection
•It is a pink, coherent soft onnective tissue •Dependent on its normal hard dentin shell for protection Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp
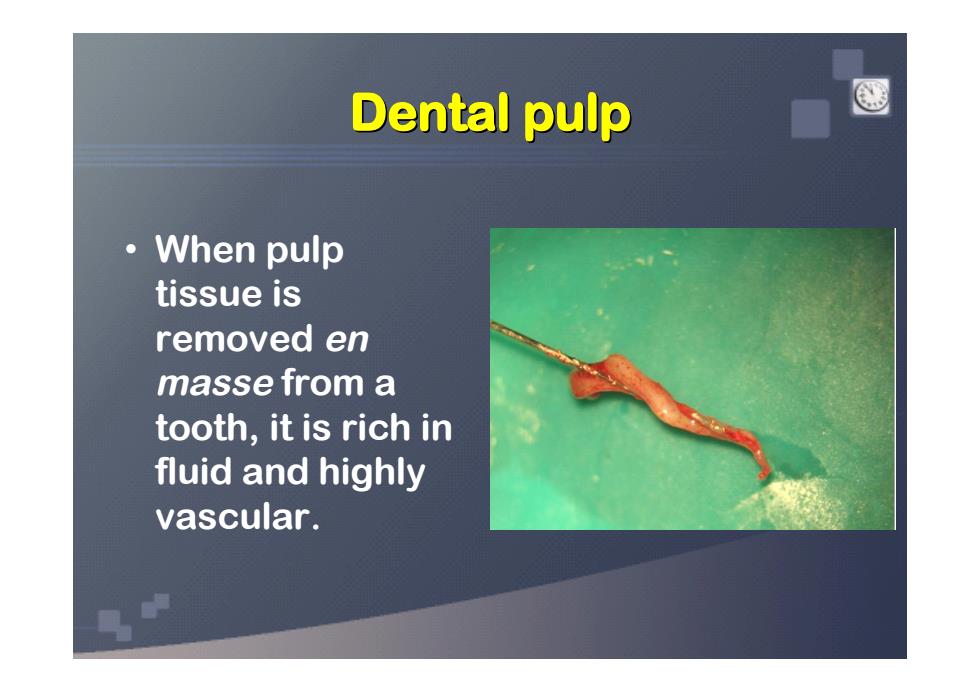
Dental pulp When pulp tissue is removed en masse from a tooth,it is rich in fluid and highly vascular
• When pulp tissue is removed en masse from a tooth, it is rich in fluid and highly vascular. Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp Dental pulp
Histophysiology of the dental pulp The dental pulp is one kind of loose connective tissue,and the respond to changes in environment should be the same as any other loose connective tissue.However, several factors make it unique and thus alter its ability to respond to irritation
Histophysiology of the dental Histophysiology of the dental Histophysiology of the dental Histophysiology of the dental pulp The dental pulp is one kind of loose connective tissue, and the respond to changes in environment should be the same as any other loose connective tissue. However, several factors make it unique and thus alter its ability to respond to irritation
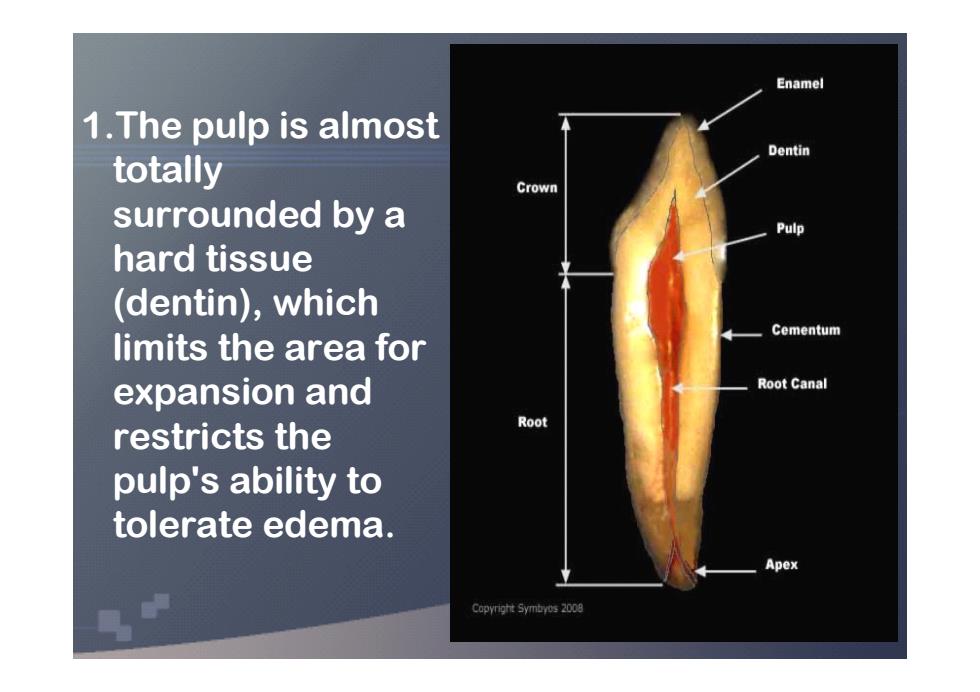
Enamel 1.The pulp is almost Dentin totally Crown surrounded by a Pulp hard tissue (dentin),which Cementum limits the area for expansion and Root Canal Root restricts the pulp's ability to tolerate edema. Apex Copyright Symbyos 2008
1.The pulp is almost totally surrounded by a hard tissue (dentin), which limits the area for expansion and restricts the pulp's ability to tolerate edema
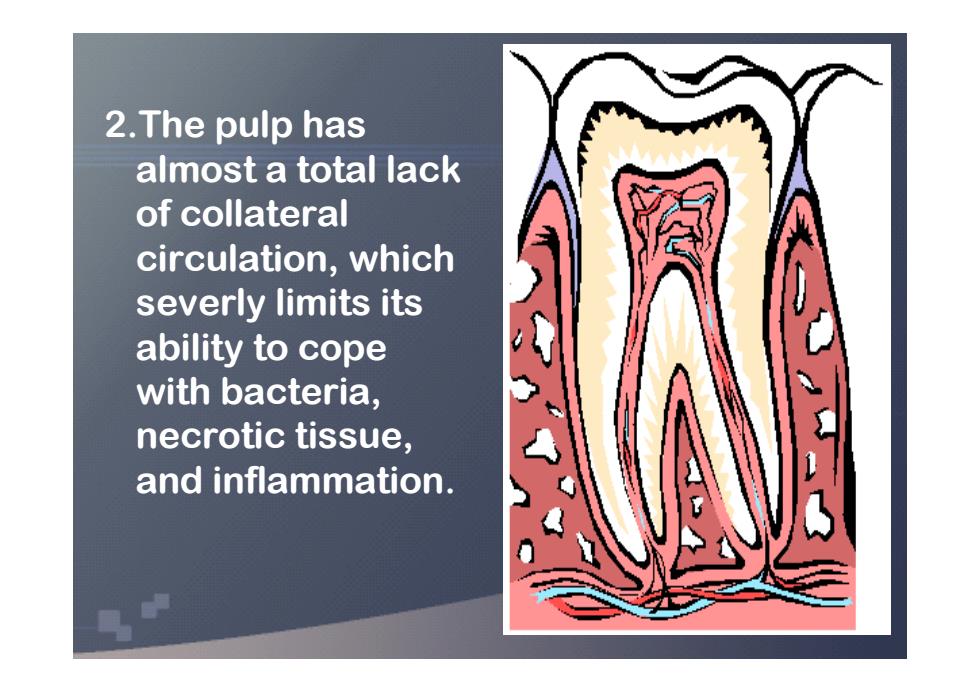
2.The pulp has almost a total lack of collateral circulation,which severly limits its ability to cope with bacteria, necrotic tissue, and inflammation
2.The pulp has almost a total lack of collateral circulation, which severly limits its ability to cope with bacteria, necrotic tissue, and inflammation