第十一章糖代谢
第十一章糖代谢

Key Terms ·glycolysis lactic acid fermentation alcoholic fermentation ●gluconeogenesis ●obligate anaerobe facultative anaerobe ●hexokinase ●kinase phosphofructokinase (PFK) thioester intermediate
Key Terms ⚫ glycolysis ⚫ lactic acid fermentation ⚫ alcoholic fermentation ⚫ gluconeogenesis ⚫ obligate anaerobe ⚫ facultative anaerobe ⚫ hexokinase ⚫ kinase ⚫ phosphofructokinase (PFK) ⚫ thioester intermediate

substrate-level phosphorylation ●nutase ●enol phosphate ●pyruvate kinase bifunctional enzyme feedforward stimulation ● committed step pyruvate carboxylase biotin glucose 6-phosphatase ●substrate cycle ·Cori cycle ●ll.Transducing
⚫ substrate-level phosphorylation ⚫ mutase ⚫ enol phosphate ⚫ pyruvate kinase ⚫ bifunctional enzyme ⚫ feedforward stimulation ⚫ committed step ⚫ pyruvate carboxylase ⚫ biotin ⚫ glucose 6-phosphatase ⚫ substrate cycle ⚫ Cori cycle ⚫ II. Transducing

一 糖的生理功能 ·构成组织和细胞的成分(核糖,粘 多糖,细胞膜,神经组织) ·氧化供能 (1克葡萄糖完全氧化可放 出4千卡能量) 。转变成其他物质
一 糖的生理功能 ⚫构成组织和细胞的成分(核糖,粘 多糖,细胞膜,神经组织) ⚫氧化供能(1克葡萄糖完全氧化可放 出4千卡能量) ⚫转变成其他物质

二糖的来源与去路 来源: ·消化道吸收;不同动物有不同的形式 。 非糖物质转变而来:肝脏中的糖异生 去路:小肠吸收→肝:合成糖原 氧化供能 进入血液→☆机体组织细胞 转变成其他物质 ☆机体组织细胞:合成肌糖原 氧化供能 转变成其他物质
二 糖的来源与去路 来源: ⚫ 消化道吸收;不同动物有不同的形式 ⚫ 非糖物质转变而来:肝脏中的糖异生 去路:小肠吸收→肝:合成糖原 氧化供能 进入血液→ ☆机体组织细胞 转变成其他物质 ☆机体组织细胞:合成肌糖原 氧化供能 转变成其他物质

三糖原的合成与分解 ☆糖原的合成 ☆糖原的分解
三 糖原的合成与分解 ☆糖原的合成 ☆糖原的分解
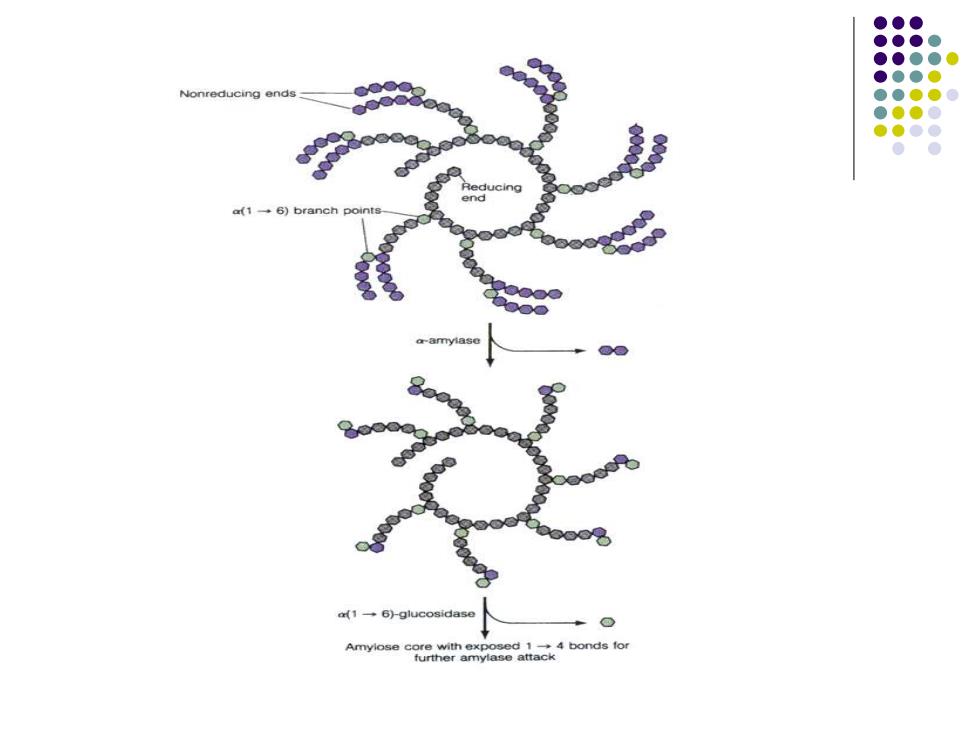
Nonreducing ends -.6)branc a1→6)-glucosidas Amylose core with exposed 1-4 bonds for further amylase attack
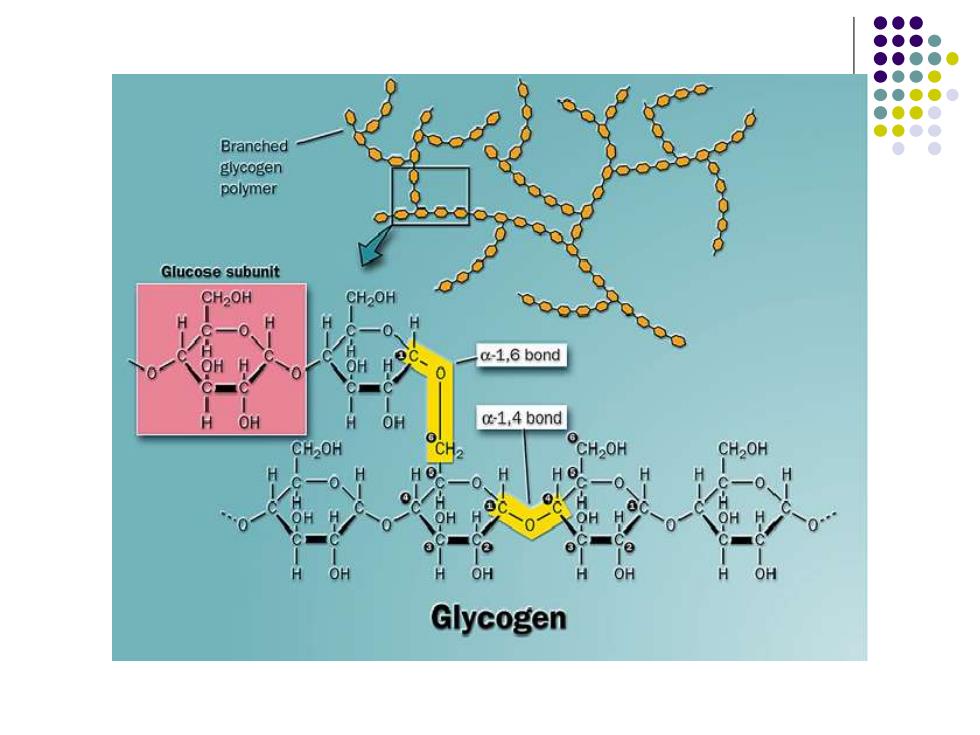
Branched glycogen polymer Glucose subunit CH2OH H Qo.O a-1,6 bond OH OH o-1,4 bond CH2OH H H 2 OH OH OH Glycogen
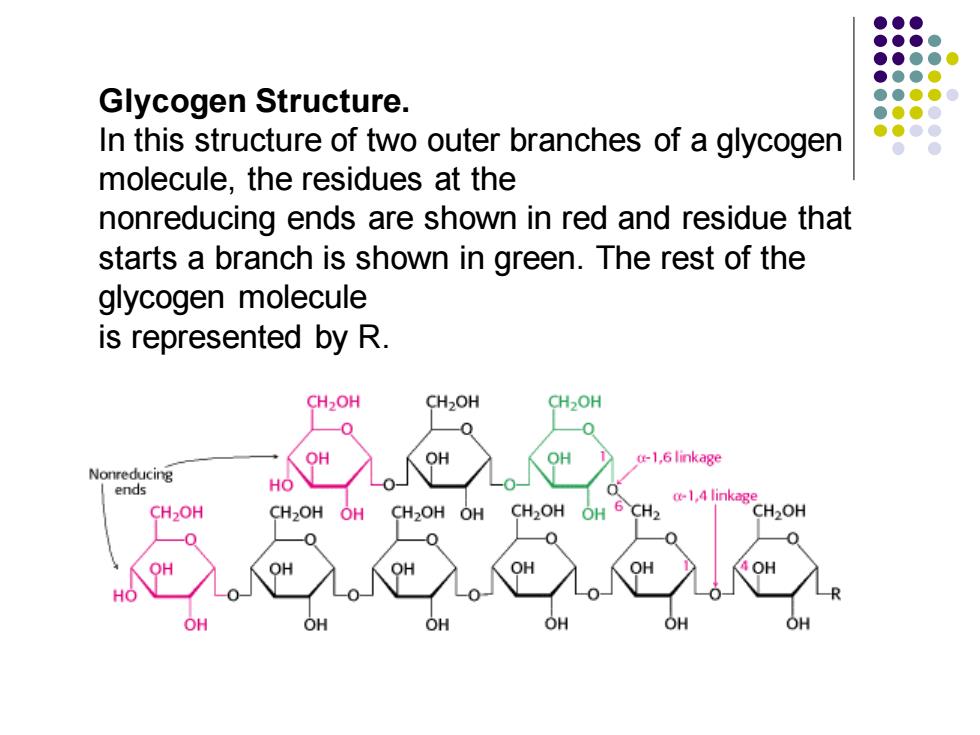
Glycogen Structure. In this structure of two outer branches of a glycogen molecule,the residues at the nonreducing ends are shown in red and residue that starts a branch is shown in green.The rest of the glycogen molecule is represented by R. CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH 0 0 OH OH OH c-1,6 linkage Nonreducing ends HO CH2OH CH2OH OH CH2OH OH CH2OH OH 6 CH2 1 linkagCH2OH 0 OH HO
Glycogen Structure. In this structure of two outer branches of a glycogen molecule, the residues at the nonreducing ends are shown in red and residue that starts a branch is shown in green. The rest of the glycogen molecule is represented by R
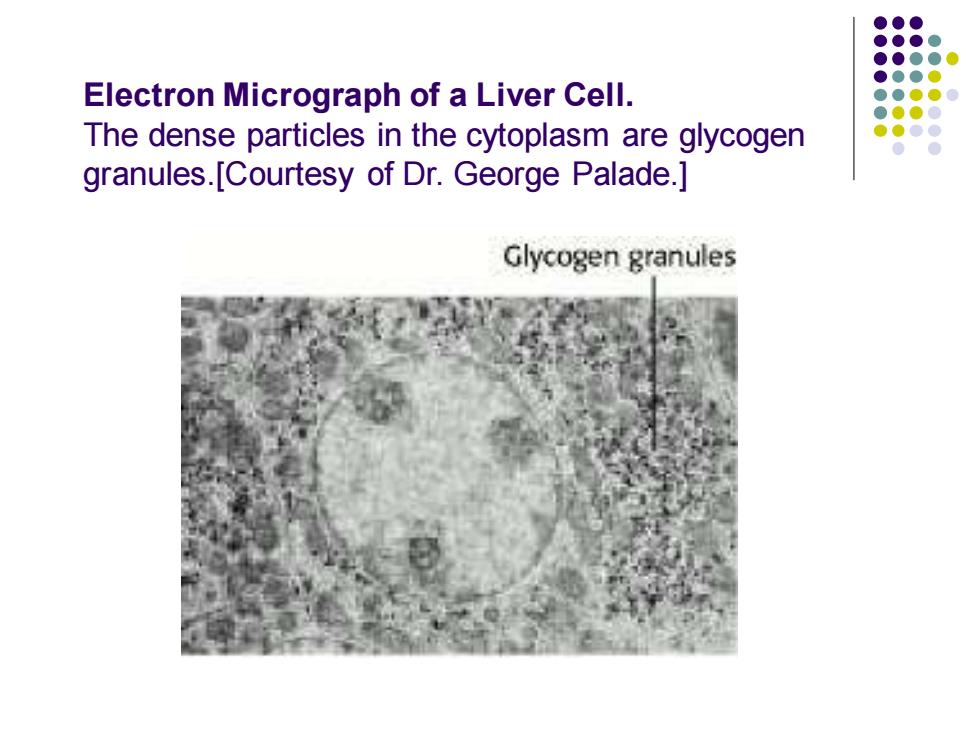
Electron Micrograph of a Liver Cell. The dense particles in the cytoplasm are glycogen granules.[Courtesy of Dr.George Palade.] Glycogen granules
Electron Micrograph of a Liver Cell. The dense particles in the cytoplasm are glycogen granules.[Courtesy of Dr. George Palade.]