
MOUIE A0010601.mov 神经细胞分泌
神经细胞分泌
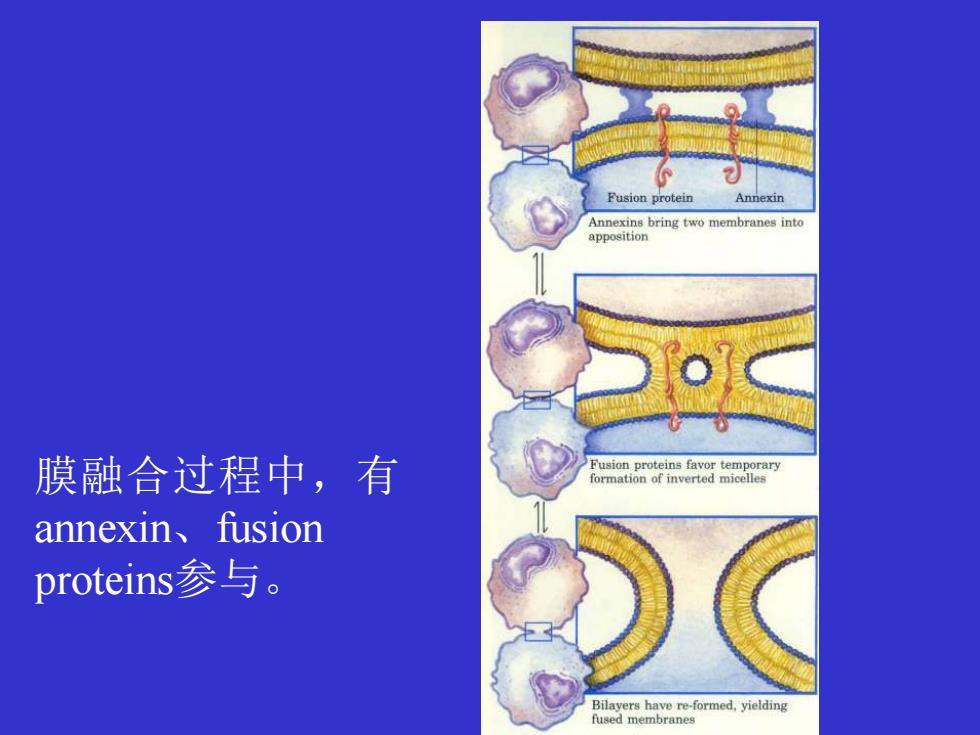
Fusion protein Annexin Annexins bring two membranes into apposition 膜融合过程中,有 annexin、fusion proteins参与
膜融合过程中,有 annexin、fusion proteins参与

三、过膜运输 (一)小分子物质的跨膜运输 被动,主动
三、过膜运输 (一)小分子物质的跨膜运输 被动, 主动

1 被动运输(passive transport) 方式: *简单扩散(Simple diffusion) *协助扩散(facilitated diffusion)
1 被动运输(passive transport) 方式: *简单扩散(Simple diffusion) *协助扩散(facilitated diffusion)

简单扩散 通过膜脂瞬间通道(直径8nm)进行。 适于脂溶性物质或极性小分子(HO,CO2
简单扩散 通过膜脂瞬间通道(直径8nm)进行。 适于脂溶性物质或极性小分子(H2O, CO2, O2)

协助扩散 借助载体(carrier ) 缬氨霉素是钾离子载体。 借助通道蛋白(channel protein)
协助扩散 借助载体(carrier ) 缬氨霉素是钾离子载体。 借助通道蛋白(channel protein)
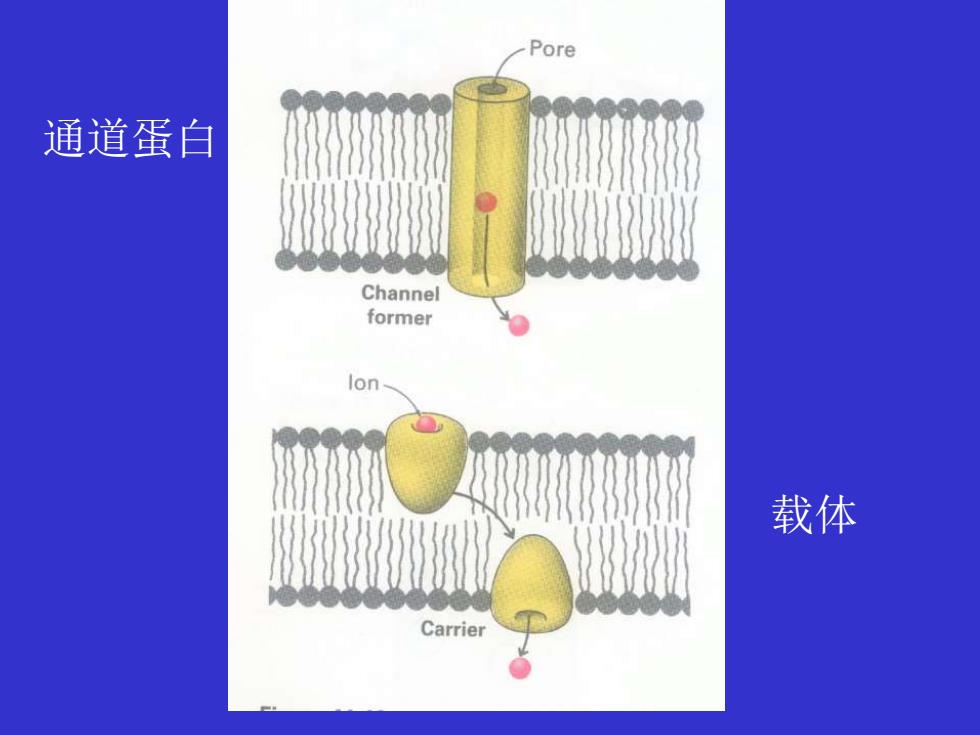
Pore 通道蛋白 Channel former lon 载体 Carrier
通道蛋白 载体

红细胞葡萄糖运输借助通道蛋白(被动运输) 葡萄糖渗透酶 Glucose in blood [S]out≈5mM Glucose permease Intracellular glucose-> Energy-yielding [S]in <5 mM metabolism
红细胞葡萄糖运输借助通道蛋白(被动运输) 葡萄糖渗透酶

Cytoplasm Proteins Nuclear envelope Nuclear pore complex Nucleus Less than 65,000 daltons in molecular mass Nuclear Import(Passive)

被动运输主要特点: 顺浓度梯度: 运输速率既依赖于跨膜物质浓度差,又与物 质分子大小、电荷、脂溶性有关: 为自发过程,不需要提供能量
被动运输主要特点: 顺浓度梯度; 运输速率既依赖于跨膜物质浓度差,又与物 质分子大小、电荷、脂溶性有关; 为自发过程,不需要提供能量