
OPERATING SYSTEMS 1 龚玲 lgong@sjtu.edu.cn
OPERATING SYSTEMS 龚玲 lgong@sjtu.edu.cn 1

TODAY'S GOALS o Interrupt o Dual Mode o System Calls vs.APIs o Multiprogramming/Concurrency o http://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77fldcccda38376ba flfae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94
TODAY’S GOALS Interrupt Dual Mode System Calls vs. APIs Multiprogramming/Concurrency http://wenku.baidu.com/course/study/77f1dcccda38376ba f1fae94#665ea0c7aa00b52acfc7ca94
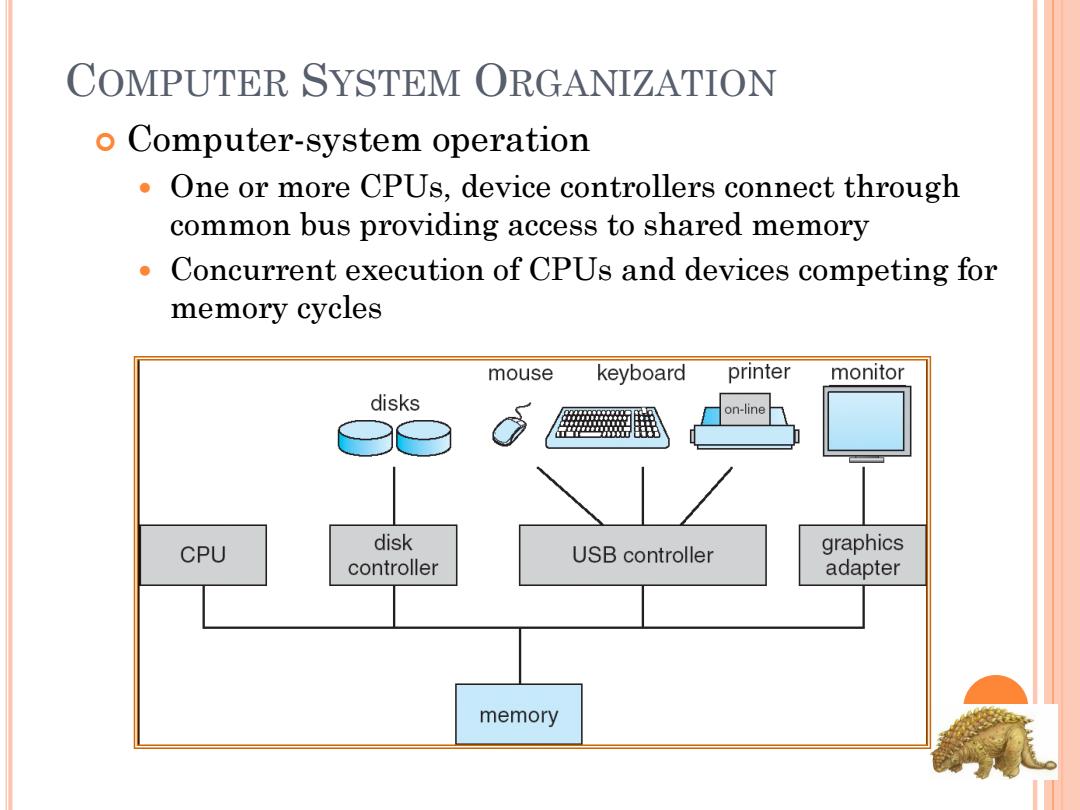
COMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANIZATION o Computer-system operation One or more CPUs,device controllers connect through common bus providing access to shared memory Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles mouse keyboard printer monitor disks on-line CPU disk controller USB controller graphics adapter memory
COMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANIZATION Computer-system operation One or more CPUs, device controllers connect through common bus providing access to shared memory Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles

I/O STRUCTURE 0 After I/O starts,control returns to user program only upon I/O completion. Wait instruction idles the CPU until the next interrupt Wait loop (contention for memory access). At most one I/O request is outstanding at a time,no simultaneous I/O processing. o After I/O starts,control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion. 0 System call-request to the operating system to allow user to wait for I/O completion. Device-status table contains entry for each I/O device indicating its type,address,and state. Operating system indexes into I/O device table to determine device status and to modify table entry to include interrupt
I/O STRUCTURE After I/O starts, control returns to user program only upon I/O completion. Wait instruction idles the CPU until the next interrupt Wait loop (contention for memory access). At most one I/O request is outstanding at a time, no simultaneous I/O processing. After I/O starts, control returns to user program without waiting for I/O completion. System call – request to the operating system to allow user to wait for I/O completion. Device-status table contains entry for each I/O device indicating its type, address, and state. Operating system indexes into I/O device table to determine device status and to modify table entry to include interrupt

TWO I/O METHODS Synchronous Asynchronous user requesting process requesting process user -waiting一 device driver device driver kernel interrupt handler interrupt handler kernel hardware hardware data transfer data transfer- time time (a) (b)
TWO I/O METHODS Synchronous Asynchronous
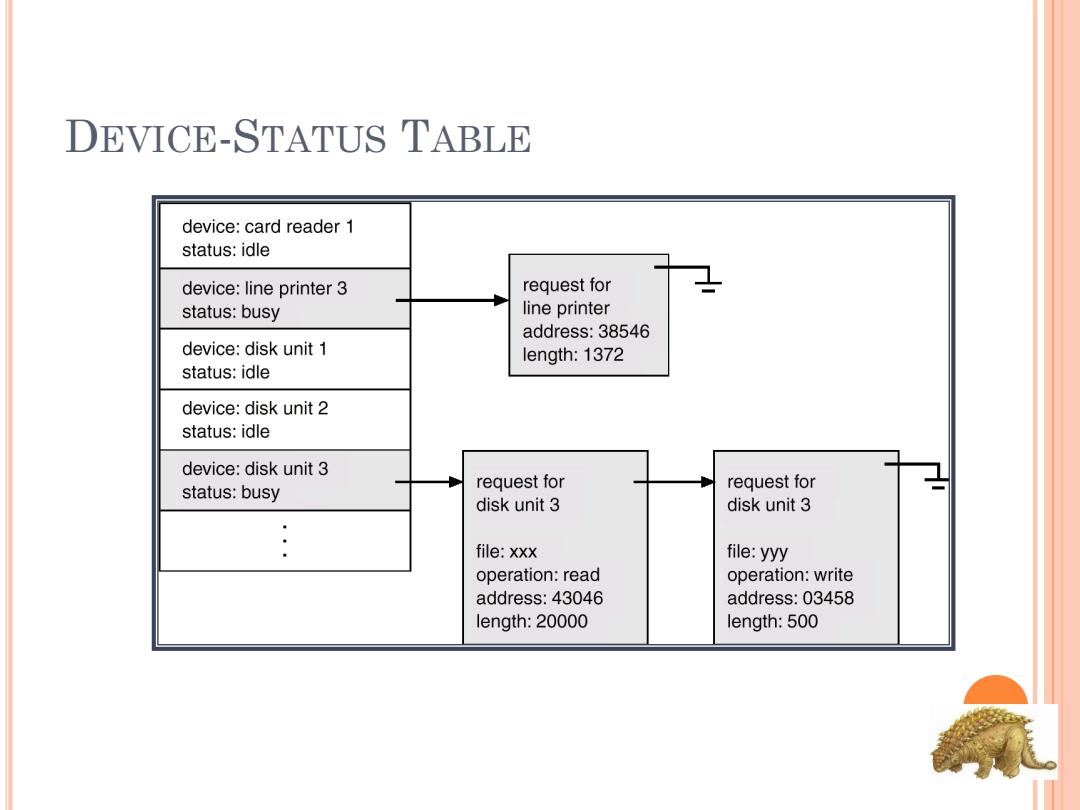
DEVICE-STATUS TABLE device:card reader 1 status:idle device:line printer 3 request for status:busy line printer address:38546 device:disk unit 1 length:1372 status:idle device:disk unit 2 status:idle device:disk unit 3 status:busy request for request for disk unit 3 disk unit 3 file:xxx file:yyy operation:read operation:write address:43046 address:03458 length:20000 length:500
DEVICE-STATUS TABLE
DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS STRUCTURE o Used for high-speed I/O devices able to transmit information at close to memory speeds. o Device controller transfers blocks of data from buffer storage directly to main memory without CPU intervention. o Only one interrupt is generated per block,rather than the one interrupt per byte
DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS STRUCTURE Used for high-speed I/O devices able to transmit information at close to memory speeds. Device controller transfers blocks of data from buffer storage directly to main memory without CPU intervention. Only one interrupt is generated per block, rather than the one interrupt per byte
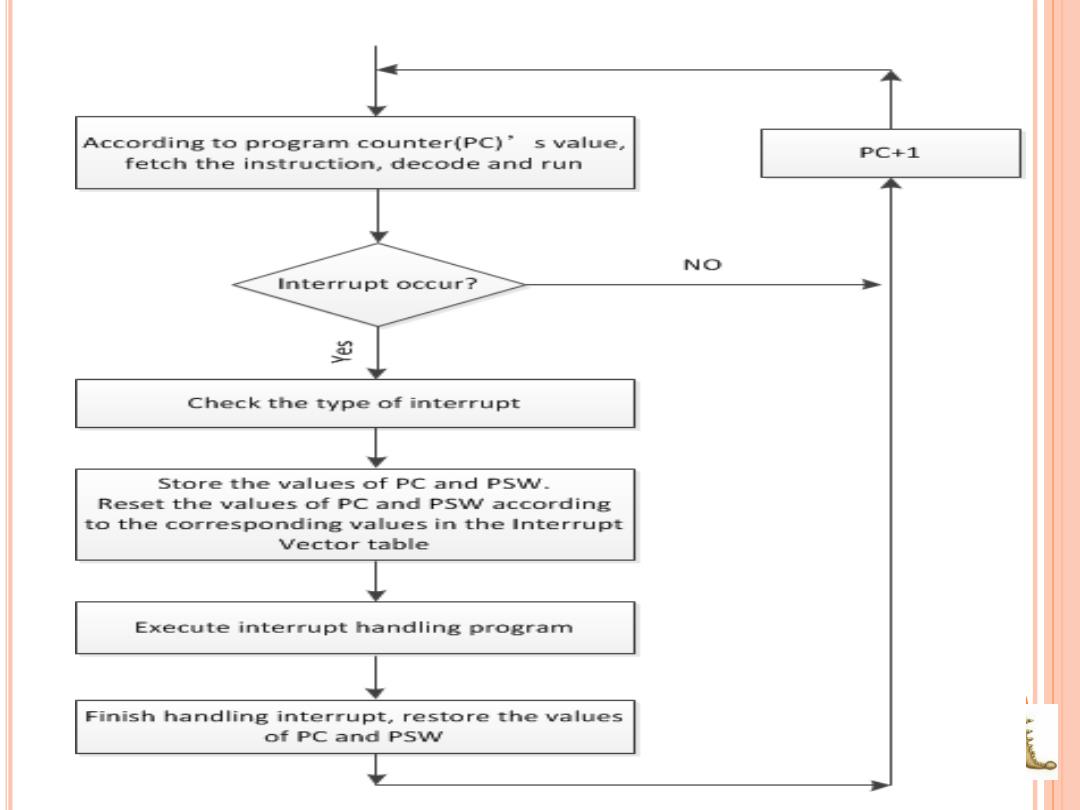
According to program counter(PC)'s value, PC+1 fetch the instruction,decode and run NO Interrupt occur? 单 Check the type of interrupt Store the values of PC and PSW. Reset the values of PC and PSW according to the corresponding values in the Interrupt Vector table Execute interrupt handling program Finish handling interrupt,restore the values of PC and PSW

OPERATING-SYSTEM OPERATIONS o Interrupt driven by hardware 0 Software error or request creates exception or trap Division by zero,request for operating system service o Other process problems include infinite loop,processes modifying each other or the operating system o Dual-mode operation allows Os to protect itself and other system components User mode and kernel mode Mode bit provided by hardware o Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code o Some instructions designated as privileged,only executable in kernel mode o System call changes mode to kernel,return from call resets it to user
OPERATING-SYSTEM OPERATIONS Interrupt driven by hardware Software error or request creates exception or trap Division by zero, request for operating system service Other process problems include infinite loop, processes modifying each other or the operating system Dual-mode operation allows OS to protect itself and other system components User mode and kernel mode Mode bit provided by hardware Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode System call changes mode to kernel, return from call resets it to user

TRANSITION FROM USER TO KERNEL MODE o Timer to prevent infinite loop process hogging resources* Set interrupt after specific period Operating system decrements counter When counter zero generate an interrupt Set up before scheduling process to regain control or terminate program that exceeds allotted time user process user mode user process executing calls system call return from system call (mode bit=1) trap return kernel mode bit =0 mode bit =1 kernel mode execute system call (mode bit=0) If you hog something,you take all of it in a greedy or impolite way
TRANSITION FROM USER TO KERNEL MODE Timer to prevent infinite loop / process hogging resources* Set interrupt after specific period Operating system decrements counter When counter zero generate an interrupt Set up before scheduling process to regain control or terminate program that exceeds allotted time * If you hog something, you take all of it in a greedy or impolite way. 独占