
CHAPTER 10:FILE-SYSTEM INTERFACE
CHAPTER 10: FILE-SYSTEM INTERFACE

CHAPTER 10:FILE-SYSTEM INTERFACE o File Concept o Access Methods o Directory Structure o File-System Mounting o File Sharing o Protection
CHAPTER 10: FILE-SYSTEM INTERFACE File Concept Access Methods Directory Structure File-System Mounting File Sharing Protection

OBJECTIVES o To explain the function of file systems o To describe the interfaces to file systems o To discuss file-system design tradeoffs, including access methods,file sharing,file locking,and directory structures o To explore file-system protection
OBJECTIVES To explain the function of file systems To describe the interfaces to file systems To discuss file-system design tradeoffs, including access methods, file sharing, file locking, and directory structures To explore file-system protection
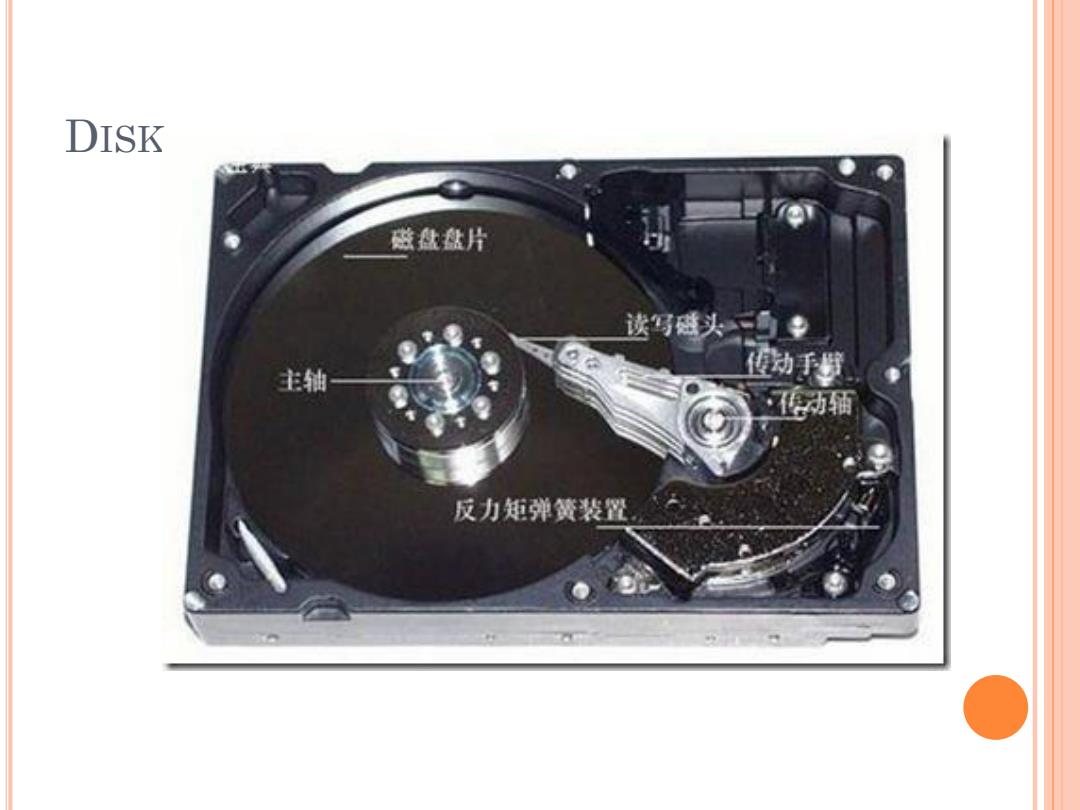

DISK 磁盘盘片 读写磁头· o+ 主轴 动手 动缅 反力矩弹簧装置
DISK
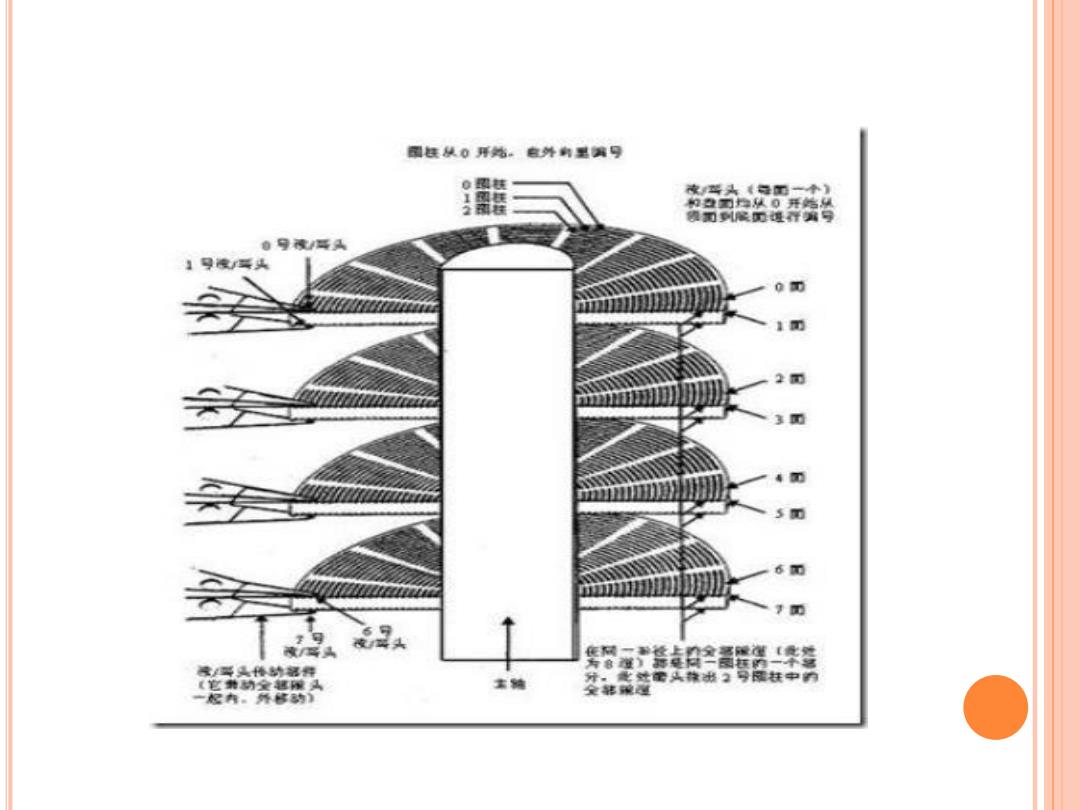
留赶从0开站。自外角里舞号 0 凌些头《号小》 的2面扫从0并始从 预司到展厅进产写 自号液写具 】号液/写头 o 1前 2 3面 s m 6 m 禁空爱然华签 液/可头体特幅件 (它物特金越雅头 宝轴 分,处管路出2号候赶中内 一起内。外解特) 金韩延
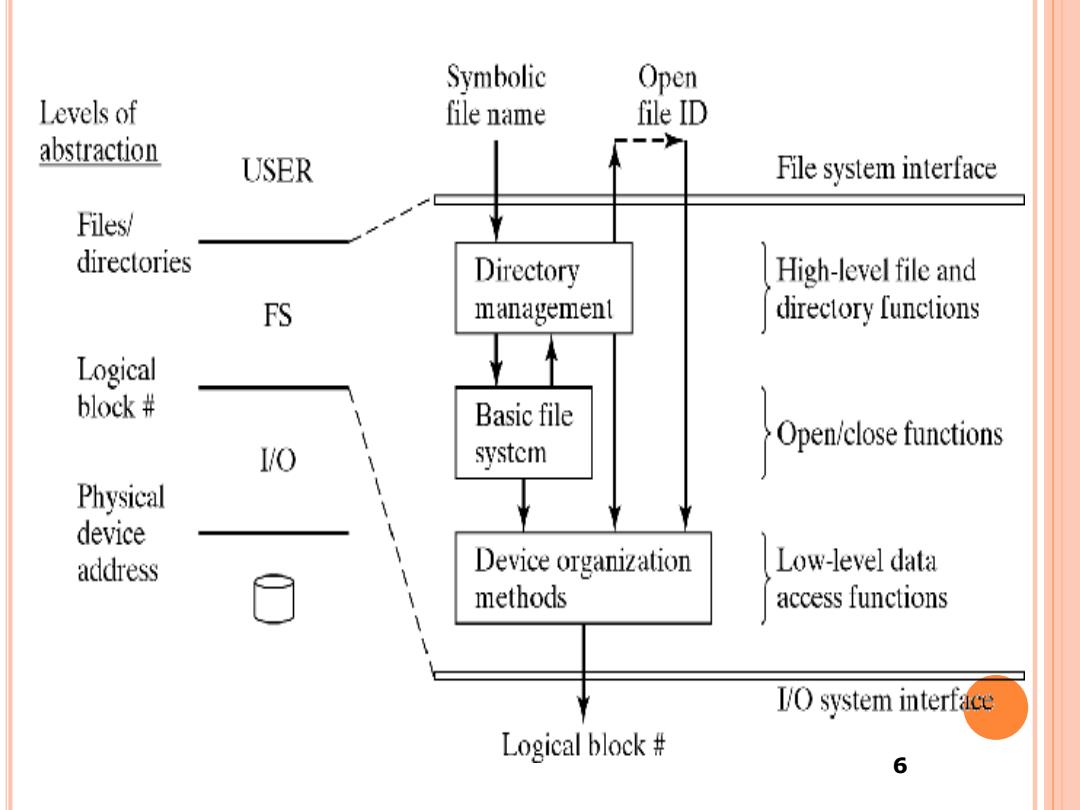
Symbolic Open Levels of file name file ID abstraction USER File system interface Files/ directories Directory High-level file and FS management directory functions Logcal block# Basic file system Open/close functions Physical device address Device organization Low-level data methods access functions 1O system interface Logical block# 6
6
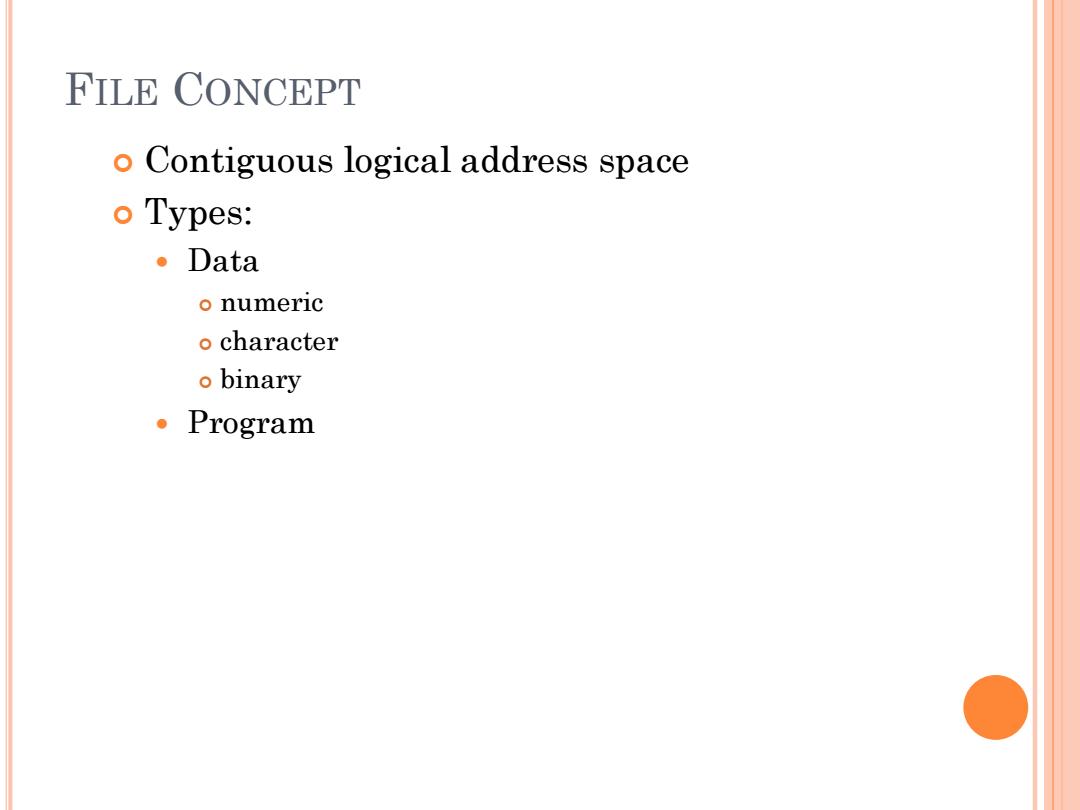
FILE CONCEPT o Contiguous logical address space o Types: ·Data o numeric o character o binary ·Program
FILE CONCEPT Contiguous logical address space Types: Data numeric character binary Program
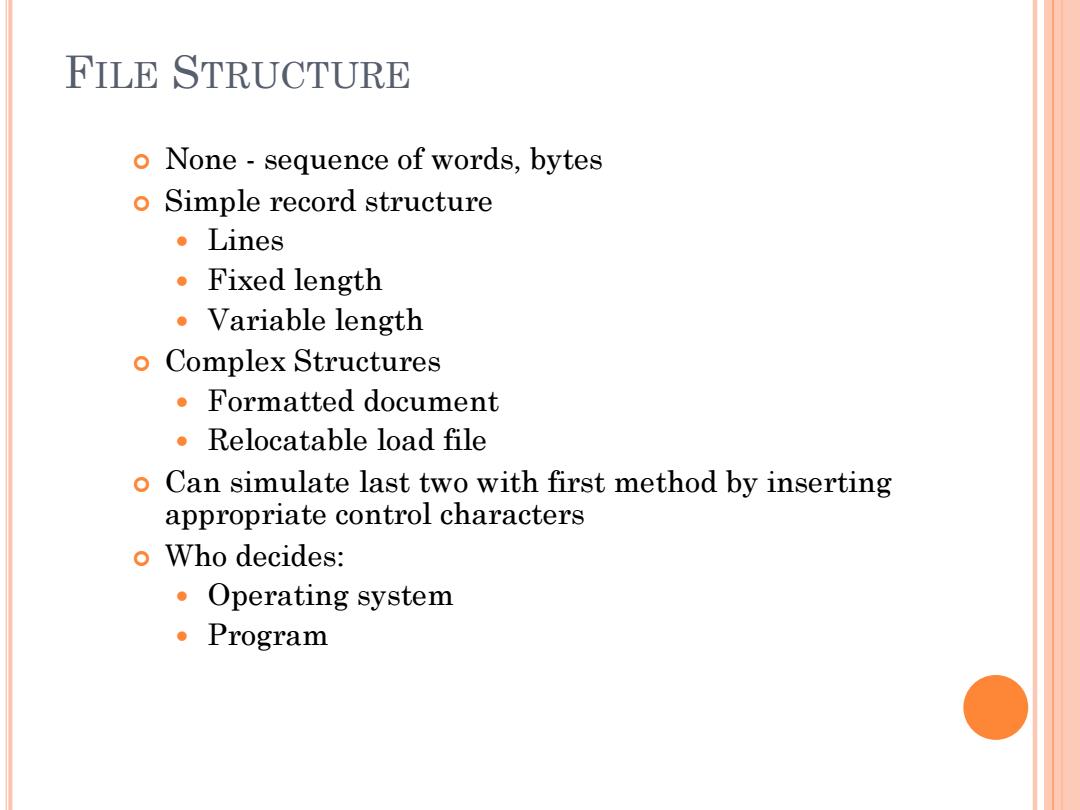
FILE STRUCTURE o None-sequence of words,bytes o Simple record structure 。Lines 。Fixed length ·Variable length o Complex Structures ·Formatted document Relocatable load file o Can simulate last two with first method by inserting appropriate control characters o Who decides: ·Operating system Program
FILE STRUCTURE None - sequence of words, bytes Simple record structure Lines Fixed length Variable length Complex Structures Formatted document Relocatable load file Can simulate last two with first method by inserting appropriate control characters Who decides: Operating system Program
FILE ATTRIBUTES o Name-only information kept in human-readable form o Identifier-unique tag(number)identifies file within file system o Type-needed for systems that support different types o Location-pointer to file location on device o Size-current file size o Protection-controls who can do reading,writing, executing o Time,date,and user identification-data for protection,security,and usage monitoring o Information about files are kept in the directory structure, which is maintained on the disk
FILE ATTRIBUTES Name – only information kept in human-readable form Identifier – unique tag (number) identifies file within file system Type – needed for systems that support different types Location – pointer to file location on device Size – current file size Protection – controls who can do reading, writing, executing Time, date, and user identification – data for protection, security, and usage monitoring Information about files are kept in the directory structure, which is maintained on the disk

FILE OPERATIONS o File is an abstract data type o Create o Write o Read o Reposition within file o Delete o Truncate o Open(F:)-search the directory structure on disk for entry F;,and move the content of entry to memory o Close (F)-move the content of entry F;in memory to directory structure on disk
FILE OPERATIONS File is an abstract data type Create Write Read Reposition within file Delete Truncate Open(Fi ) – search the directory structure on disk for entry Fi , and move the content of entry to memory Close (Fi ) – move the content of entry Fi in memory to directory structure on disk