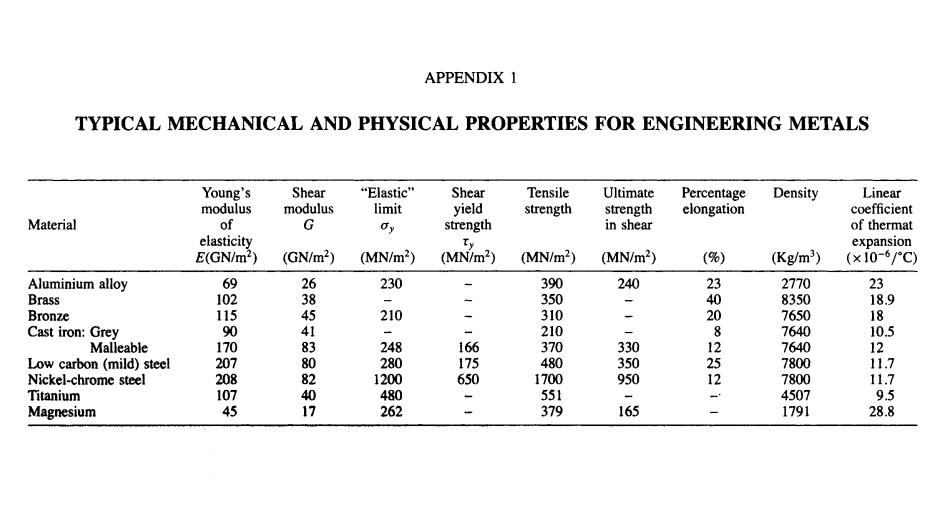
APPENDIX 1 TYPICAL MECHANICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR ENGINEERING METALS Young's Shear “Elastic” Shear Tensile Ultimate Percentage Density Linear modulus modulus limit yield strength strength elongation coefficient Material of G Oy strength in shear of thermat elasticity Ty expansion E(GN/m2) (GN/m2) (MN/m2) (MN/m2) (MN/m2) (MN/m2) (%) (Kg/m3) (×10-6/C) Aluminium alloy 69 2 230 390 240 23 2770 23 Brass 102 二 350 4 8350 18.9 Bronze 115 210 310 - 20 7650 18 Cast iron:Grey 0 4 210 7640 10.5 Malleable 170 248 166 370 330 81215 7640 12 Low carbon (mild)steel 207 280 175 480 350 7800 11.7 Nickel-chrome steel 208 1200 650 1700 950 2 7800 11.7 Titanium 107 40 480 551 4507 9.5 Magnesium 5 1 262 379 165 1791 28.8
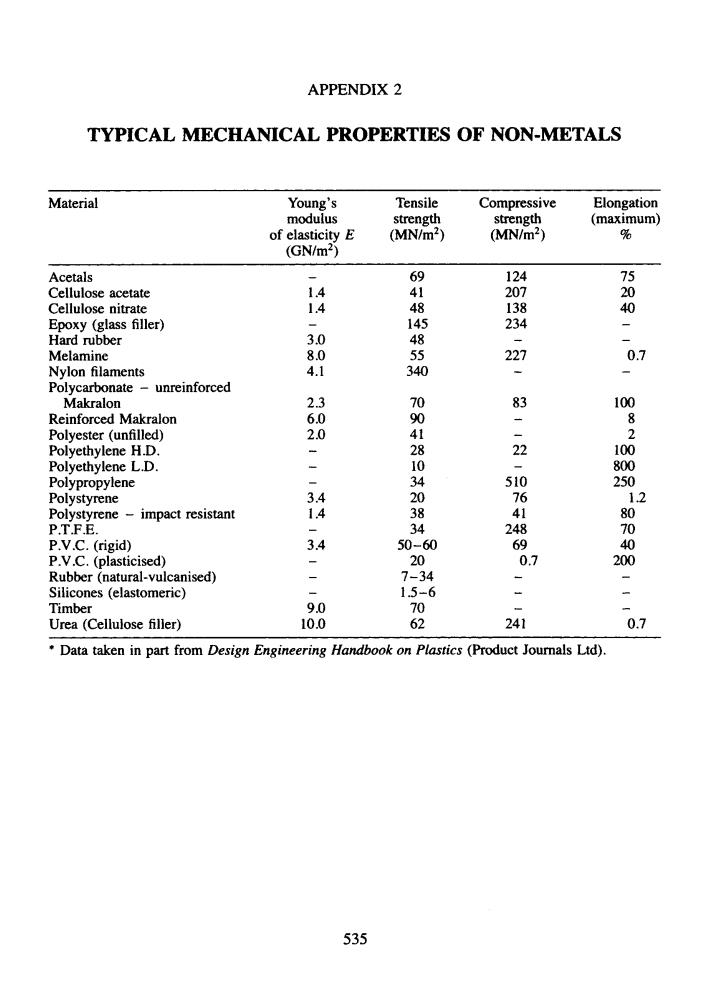
APPENDIX 2 TYPICAL MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NON-METALS Material Young's Tensile Compressive Elongation modulus strength strength (maximum) of elasticity E (MN/m2) (MN/m2) % (GN/m2) Acetals 69 124 75 Cellulose acetate 1.4 41 207 20 Cellulose nitrate 1.4 48 138 40 Epoxy(glass filler) 145 234 Hard rubber 3.0 4 Melamine 8.0 55 227 0.7 Nylon filaments 4.1 340 Polycarbonate -unreinforced Makralon 2.3 70 83 100 Reinforced Makralon 6.0 90 8 Polyester (unfilled) 2.0 41 二 2 Polyethylene H.D. 28 22 100 Polyethylene L.D. Polypropylene 10 800 34 510 250 Polystyrene 3.4 20 76 12 Polystyrene-impact resistant 1.4 38 41 80 P.T.F.E. 34 248 70 P.V.C.(rigid) 3.4 50-60 69 40 P.V.C.(plasticised) 20 0.7 200 Rubber(natural-vulcanised) 二 7-34 Silicones (elastomeric) 1.5-6 二 Timber 9.0 70 Urea (Cellulose filler) 10.0 62 241 0.7 Data taken in part from Design Engineering Handbook on Plastics(Product Journals Ltd). 535
APPENDIX 2 TYPICAL MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NON-METALS Material Young’s Tensile Compressive Elongation modulus strength strength (maximum) (GN/m2) of elasticity E (MN/m2) (MN/m2) 8 Acetals - 69 124 75 Cellulose acetate 1.4 41 207 20 Cellulose nitrate 1.4 48 138 40 Hard rubber 3 .O 48 Melamine 8 .O 55 227 0.7 Polycarbonate - unreinforced Reinforced Makralon 6 .O 90 - Epoxy (glass filler) - 145 234 - Nylon filaments 4.1 340 - - Makralon 2.3 70 83 100 8 2 Polyethylene L.D. - 10 - 800 Polypropylene - 34 5 10 250 - - Polyester (unfilled) 2 .o 41 - Polyethylene H.D. - 28 22 100 Polystyrene 3.4 20 76 1.2 Polystyrene - impact resistant 1.4 38 41 80 P.V.C. (rigid) 3.4 50-60 69 40 P.V.C. (plasticised) - 20 0.7 200 Rubber (natural-vulcanised) - 7-34 - - Silicones (elastomeric) - 1.5-6 - - P .T .F .E. - 34 248 70 Timber 9 .O 70 - - Urea (Cellulose filler) 10.0 62 24 1 0.7 * Data taken in part from Design Engineering Handbook on Plastics (Product Journals Ltd). 535
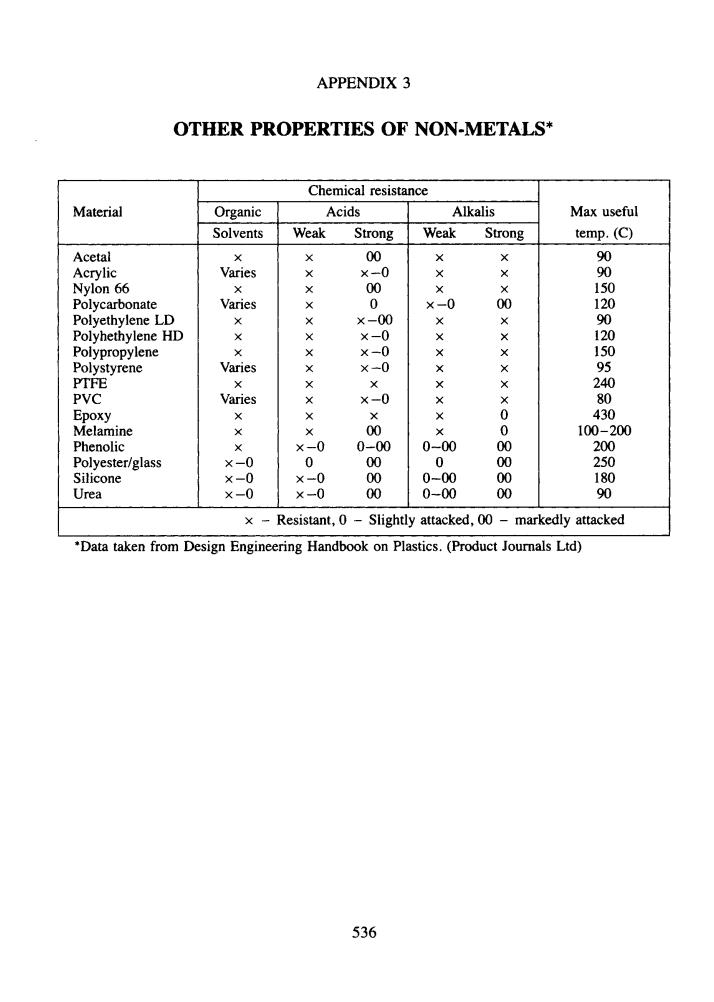
APPENDIX 3 OTHER PROPERTIES OF NON-METALS* Chemical resistance Material Organic Acids Alkalis Max useful Solvents Weak Strong Weak Strong temp.(C) Acetal X X 00 × × 90 Acrylic Varies × ×-0 × + 90 Nylon 66 × + 00 + + 150 Polycarbonate Varies X 0 ×-0 00 120 Polyethylene LD X ×-00 + 90 Polyhethylene HD × X ×-0 × 120 Polypropylene X × ×-0 + 150 Polystyrene Varies X ×-0 + X 95 PTFE + + × 240 PVC Varies × ×-0 x × 80 Epoxy × × x 0 430 Melamine X 4 00 0 100-200 Phenolic X ×-0 0-00 0-00 00 200 Polyester/glass ×-0 0 00 0 00 250 Silicone ×-0 ×-0 00 0-00 00 180 Urea ×-0 ×-0 00 0-00 00 90 Resistant,0-Slightly attacked,00 markedly attacked "Data taken from Design Engineering Handbook on Plastics.(Product Journals Ltd) 536
APPENDIX 3 Material Acetal Acrylic Nylon 66 Polycarbonate Polyethylene LD Polyhethylene HD Polypropylene Polystyrene PTFE PVC EPOXY Melamine Phenolic Pol yestedglass Silicone Urea OTHER PROPERTIES OF NON-METALS* Chemical resistance Organic Acids Alkalis Max useful Solvents Weak Strong Weak Strong temp. (C) X X 00 X X 90 Varies X x -0 X X 90 X X 00 X X 150 Varies X 0 x -0 00 1 20 X X X -00 X X 90 X X x -0 X X 1 20 X X x -0 X X 150 Varies X x -0 X X 95 X X X X X 240 Varies X x -0 X X 80 X X X X 0 430 X X 00 X 0 100-200 X x-0 0-00 0-00 00 200 x -0 0 00 0 00 250 x -0 x -0 00 0-00 00 180 x -0 x -0 00 0-00 00 90 x - Resistant, 0 - Slightly attacked, 00 - markedly attacked I 1 *Data taken from Design Engineering Handbook on Plastics. (Product Journals Ltd) 536