
Chapter 20 Initiation of transcription 清苇大当
Chapter 20 Initiation of transcription

20.1 Introduction 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters 20.6 The startpoint for RNA polymerase II 20.7 TBP is a universal factor 20.8 TBP binds DNA in an unusual way 20.9 The basal apparatus assembles at the promoter 20.10 Initiation is followed by promoter clearance 20.11 A connection between transcription and repair 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bidirectional elements that assist initiation 20.15 Independent domains bind DNA and activate transcription 20.16 The two hybrid assay detects protein-protein interactions 20.17 Interaction of upstream factors with the basal apparatus 清苇大兰
20.1 Introduction 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters 20.6 The startpoint for RNA polymerase II 20.7 TBP is a universal factor 20.8 TBP binds DNA in an unusual way 20.9 The basal apparatus assembles at the promoter 20.10 Initiation is followed by promoter clearance 20.11 A connection between transcription and repair 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bidirectional elements that assist initiation 20.15 Independent domains bind DNA and activate transcription 20.16 The two hybrid assay detects protein-protein interactions 20.17 Interaction of upstream factors with the basal apparatus

20.1 Introduction Enhancer element is a cis-acting sequence that increases the utilization of (some)eukaryotic promoters,and can function in either orientation and in any location (upstream or downstream) relative to the promoter. 情莘大当
Enhancer element is a cis-acting sequence that increases the utilization of (some) eukaryotic promoters, and can function in either orientation and in any location (upstream or downstream) relative to the promoter. 20.1 Introduction
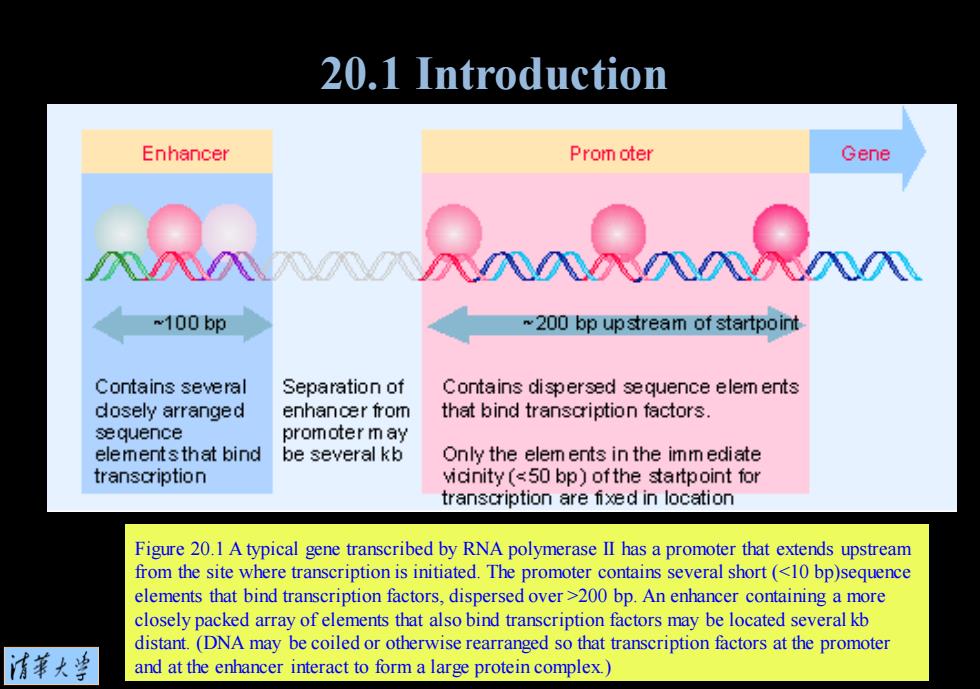
20.1 Introduction Enhancer Prom oter Gene ~100bp ~200 bp upstream of startpoint Contains several Separation of Contains dispersed sequence elem ents dosely arranged enhancer from that bind transcription factors. sequence promoter m ay elements that bind be several kb Only the elem ents in the imm ediate transcription vicnity (200 bp.An enhancer containing a more closely packed array of elements that also bind transcription factors may be located several kb distant.(DNA may be coiled or otherwise rearranged so that transcription factors at the promoter 清菜大当 and at the enhancer interact to form a large protein complex.)
Figure 20.1 A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated. The promoter contains several short (200 bp. An enhancer containing a more closely packed array of elements that also bind transcription factors may be located several kb distant. (DNA may be coiled or otherwise rearranged so that transcription factors at the promoter and at the enhancer interact to form a large protein complex.) 20.1 Introduction
20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits Amanitin (more fully a-amanitin)is a bicyclic octapeptide derived from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides;it inhibits transcription by certain eukaryotic RNA polymerases, especially RNA polymerase II. 情華大当
Amanitin (more fully a-amanitin)is a bicyclic octapeptide derived from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides; it inhibits transcription by certain eukaryotic RNA polymerases, especially RNA polymerase II. 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits
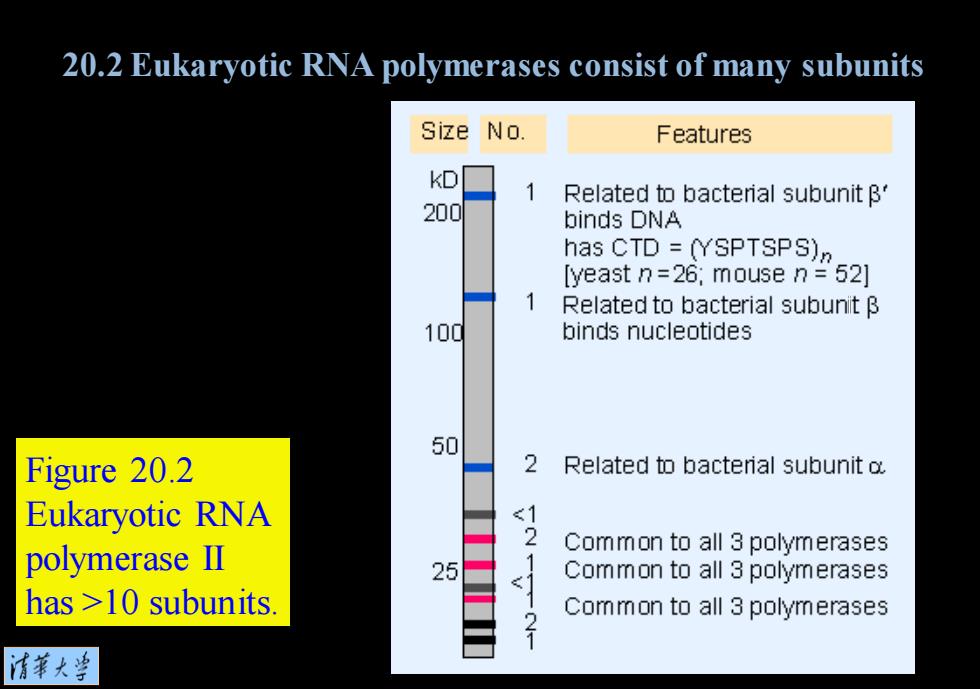
20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits Size No. Features kD 1 Related to bacterial subunit B' 200 binds DNA has CTD =(YSPTSPS) [yeast n=26;mouse n =52] 1 Related to bacterial subunit B 100 binds nucleotides 50 Figure 20.2 2 Related to bacterial subunito Eukaryotic RNA 10 subunits. 2 Common to all 3 polymerases 清苇大当
Figure 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II has >10 subunits. 20.2 Eukaryotic RNA polymerases consist of many subunits
20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting Cotransfection is the simultaneous transfection of two markers. 清菜大当
Cotransfection is the simultaneous transfection of two markers. 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting
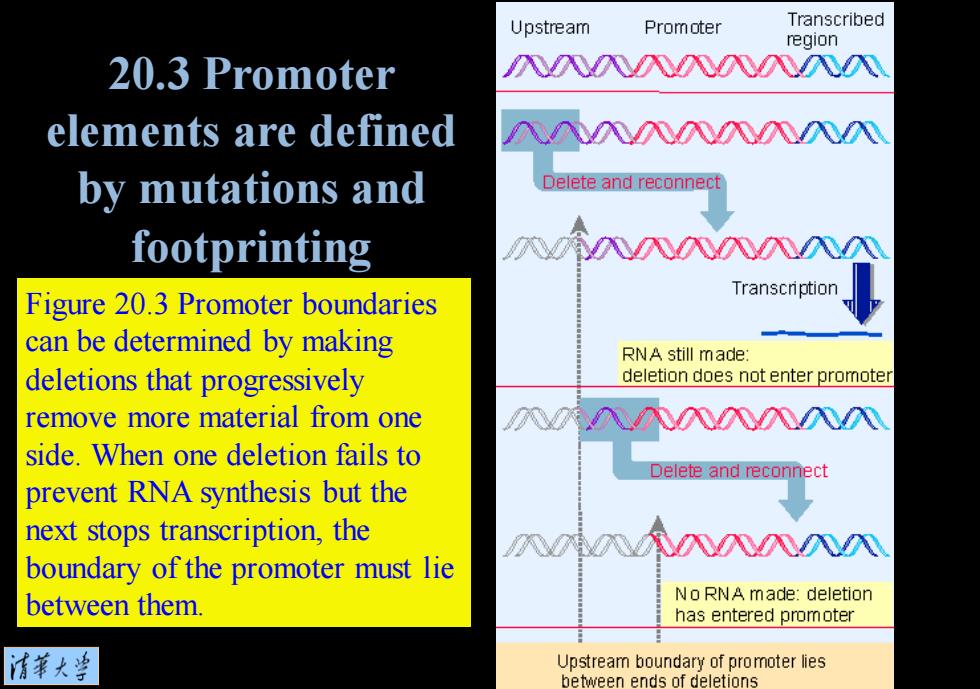
Upstream Promoter Transcribed region 20.3 Promoter 八入入八八NN elements are defined N八八八八N by mutations and Delete and reconnect footprinting NN八N入NNN Figure 20.3 Promoter boundaries Transcription can be determined by making RNA still made: deletions that progressively deletion does not enter promoter remove more material from one N入八八入入八八 side.When one deletion fails to Delete and reconnect prevent RNA synthesis but the next stops transcription,the NiN八入NN boundary of the promoter must lie between them. No RNA made:deletion has entered promoter 清第大当 Upstream boundary of promoter lies between ends of deletions
Figure 20.3 Promoter boundaries can be determined by making deletions that progressively remove more material from one side. When one deletion fails to prevent RNA synthesis but the next stops transcription, the boundary of the promoter must lie between them. 20.3 Promoter elements are defined by mutations and footprinting
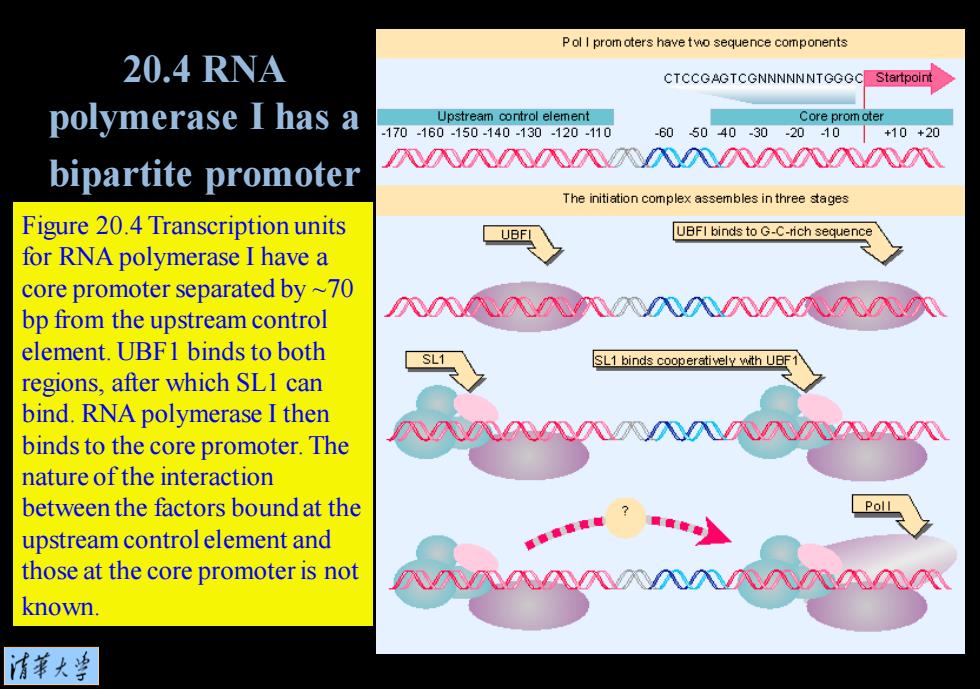
P ol I prom oters have two sequence components 20.4 RNA CTCCGAGTCGNNNNNNTGGGC Startpoint polymerase I has a Upstream control element Core prom oter -170160-150-140.130120.110 -605040-30-2010+10+20 bipartite promoter 入NM八NNN八N八八八八八 The initiation complex assembles in three stages Figure 20.4 Transcription units UBFI UBFI binds to G-C-rich sequence for RNA polymerase I have a core promoter separated by ~70 bp from the upstream control 八八代NN八八八入心 element.UBF1 binds to both SL1 SL1 binds cooperatively with UBF1 regions,after which SLI can bind.RNA polymerase I then binds to the core promoter.The N入NN入八入 nature of the interaction between the factors bound at the Poll upstream control element and those at the core promoter is not N八NNN入NNN known 情華大当
Figure 20.4 Transcription units for RNA polymerase I have a core promoter separated by ~70 bp from the upstream control element. UBF1 binds to both regions, after which SL1 can bind. RNA polymerase I then binds to the core promoter. The nature of the interaction between the factors bound at the upstream control element and those at the core promoter is not known. 20.4 RNA polymerase I has a bipartite promoter
20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters Preinitiation complex in eukaryotic transcription describes the assembly of transcription factors at the promoter before RNA polymerase binds. 清菜大当
Preinitiation complex in eukaryotic transcription describes the assembly of transcription factors at the promoter before RNA polymerase binds. 20.5 RNA polymerase III uses both downstream and upstream promoters