
Chapter 7 Using the genetic code 清革大当
Chapter 7 Using the genetic code

7.1 Introduction 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties 7.4 (There are sporadic alterations of the universal code) 7.5 tRNAs are charged with amino acids by synthetases 7.6 Accuracy depends on proofreading 7.7 Suppressor tRNAs have mutated anticodons that read new codons 7.8 The accuracy of translation 7.9 tRNA may influence the reading frame 情莘大当
7.1 Introduction 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties 7.4 (There are sporadic alterations of the universal code) 7.5 tRNAs are charged with amino acids by synthetases 7.6 Accuracy depends on proofreading 7.7 Suppressor tRNAs have mutated anticodons that read new codons 7.8 The accuracy of translation 7.9 tRNA may influence the reading frame

7.1 Introduction Stop codons are the three triplets (UAA,UAG. UGA)which terminate protein synthesis. 清苇大当
Stop codons are the three triplets (UAA, UAG, UGA) which terminate protein synthesis. 7.1 Introduction

900h啊 7.1 Introduction U 0 UUU Phe UCU UAU UUC UAC Tyr UGU UGC Cys UUA Ser UAA UUG Leu UAG STOPUGA STOP UGG Trp Figure 7.1 All the CUU triplet codons have cuc Leu CAU CAC His CGU cGc CUA CCA CAA CGA Arg CUG cce GIn meaning:61 CAG cGG represent amino Asn AGU AGCI Ser acids,and 3 cause AA Met Lys AGA AGG Arg termination (STOP) 勇 GAU GGU Val Ala GAC GGc GUG Glu GGA Gly CGG 情華大当
Figure 7.1 All the triplet codons have meaning: 61 represent amino acids, and 3 cause termination (STOP). 7.1 Introduction
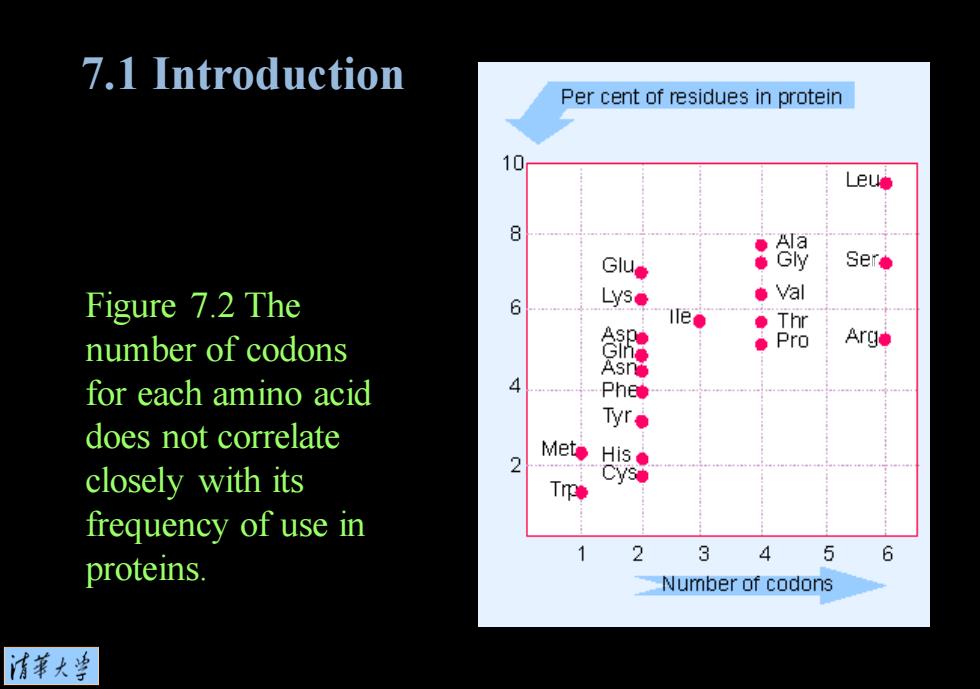
7.1 Introduction Per cent of residues in protein 10 Le墙 8 Ala Gu● Gly Ser◆ Figure 7.2 The ●Val 6 ●Thr number of codons Pro Arge for each amino acid 4 does not correlate Mete closely with its T frequency of use in 2 3 4 5 6 proteins. Number of codons 清苇大当
Figure 7.2 The number of codons for each amino acid does not correlate closely with its frequency of use in proteins. 7.1 Introduction

7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling Wobble hypothesis accounts for the ability of a tRNA to recognize more than one codon by unusual (non-G C non-A T)pairing with the third base of a codon. 情莘大当
Wobble hypothesis accounts for the ability of a tRNA to recognize more than one codon by unusual (non-G C, non-A T) pairing with the third base of a codon. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling
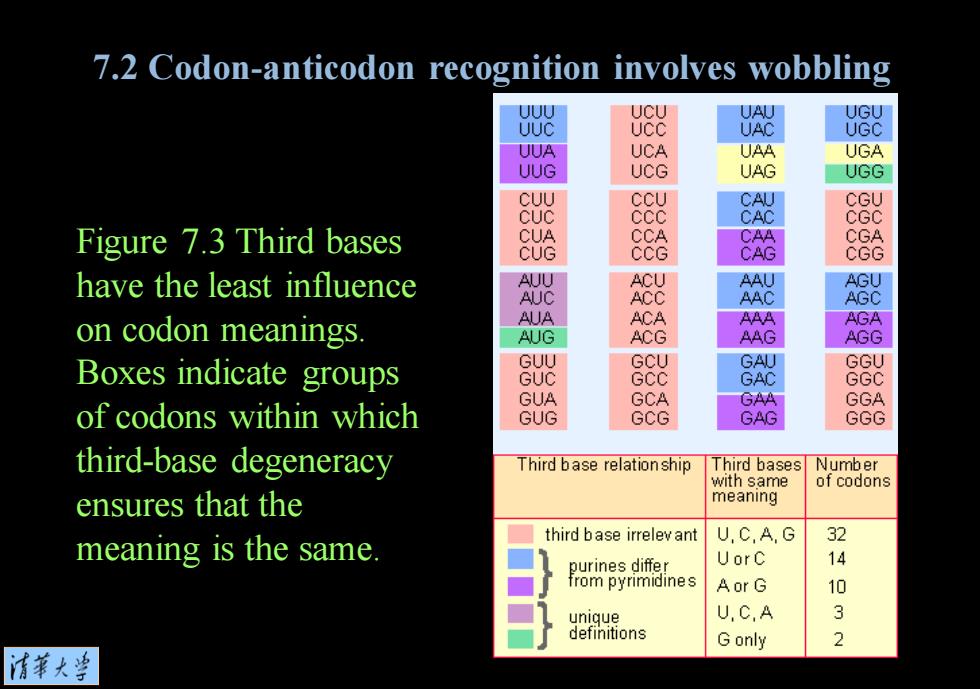
7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling UUU UCU UAU UGU UUC ucc UAC UGC UUA UCA UAA UGA UUG UCG UAG UGG CUU CCU CAU CGU cuC ccc CAC CGC Figure 7.3 Third bases CUA CCA CAA CGA CUG cCG CAG CGG have the least influence AUU ACU AAU AGU AUC ACC AAC AGC on codon meanings AUA ACA AAA AGA AUG ACG AAG AGG Boxes indicate groups GUU GCU GAU GGU GUC Gcc GAC GGC GUA GCA GAA GGA of codons within which GUG GCG GAG GGG third-base degeneracy Third base relation ship Third bases Number with same of codons ensures that the meaning third base irrelev ant U,C,A,G 32 meaning is the same. purines differ UorC 14 from pyrimidines AorG 10 unique U,C,A 3 definitions G only 2 清苇大兰
Figure 7.3 Third bases have the least influence on codon meanings. Boxes indicate groups of codons within which third-base degeneracy ensures that the meaning is the same. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling
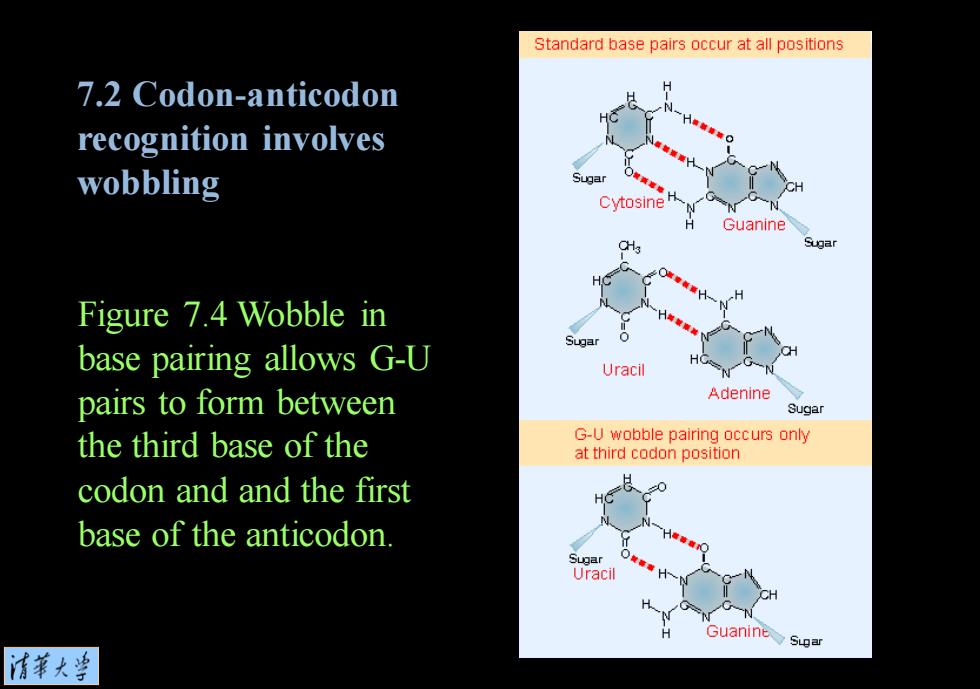
Standard base pairs occur at all positions 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling Cytosine Guanine ugar Figure 7.4 Wobble in base pairing allows G-U Uracil pairs to form between Adenine Sugar the third base of the G-U wobble pairing occurs only at third codon position codon andand the first base of the anticodon. Uracil N Guanine suar 情莘大当
Figure 7.4 Wobble in base pairing allows G-U pairs to form between the third base of the codon and and the first base of the anticodon. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling
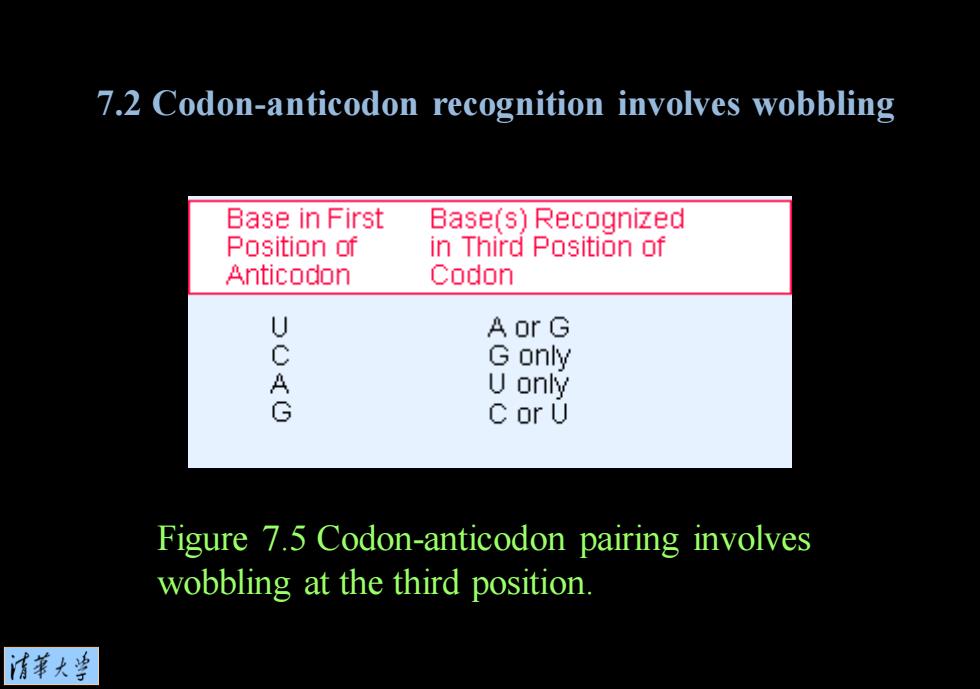
7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling Base in First Base(s)Recognized Position of in Third Position of Anticodon Codon U AorG G only U only G C or U Figure 7.5 Codon-anticodon pairing involves wobbling at the third position. 清苇大当
Figure 7.5 Codon-anticodon pairing involves wobbling at the third position. 7.2 Codon-anticodon recognition involves wobbling
7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties Modification of DNA or RNA includes all changes made to the nucleotides after their initial incorporation into the polynucleotide chain. 情莘大当
Modification of DNA or RNA includes all changes made to the nucleotides after their initial incorporation into the polynucleotide chain. 7.3 tRNA contains modified bases that influence its pairing properties