冠 上海充通大¥ t-f+口 LECTURE 11 Gear train 轮系与传动比 5t1 手柄 2 ·LD灯 5花
1 Gear train 轮系与传动比 LECTURE 11
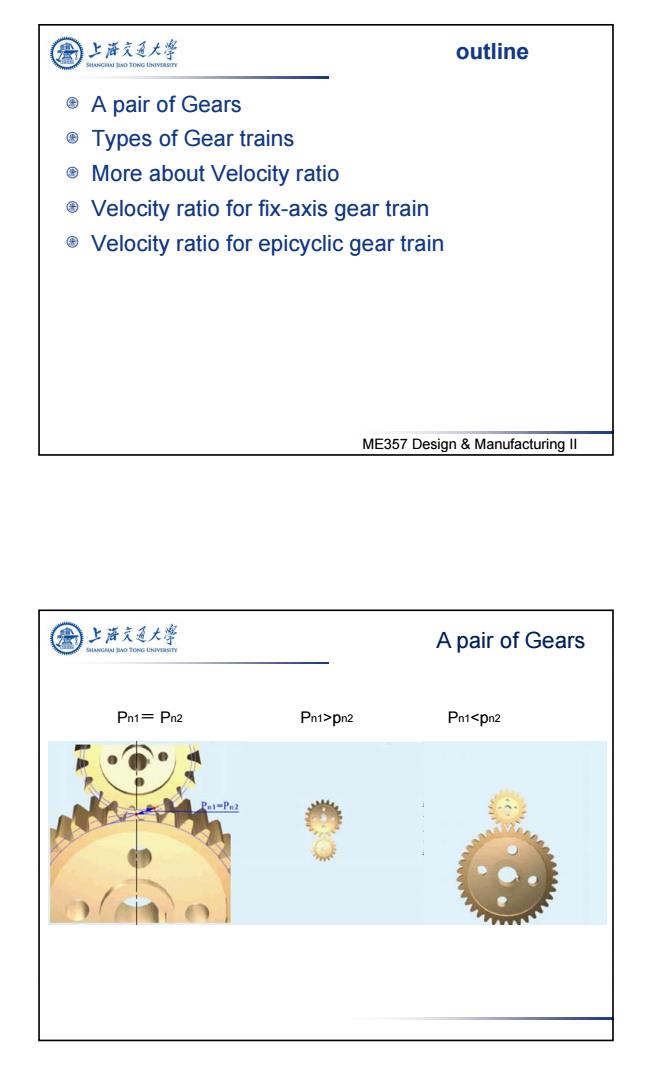
上海充通大 outline JNO TONG LN A pair of Gears ©Types of Gear trains More about Velocity ratio Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Velocity ratio for epicyclic gear train ME357 Design Manufacturing ll 上海充通大粤 A pair of Gears Pn1=Pn2 Pn1>pn2 Pn1<pn2 nl=Pn2
2 ME357 Design & Manufacturing II outline A pair of Gears Types of Gear trains More about Velocity ratio Velocity ratio for fix-axis gear train Velocity ratio for epicyclic gear train Pn1= Pn2 Pn1>pn2 Pn1<pn2 A pair of Gears
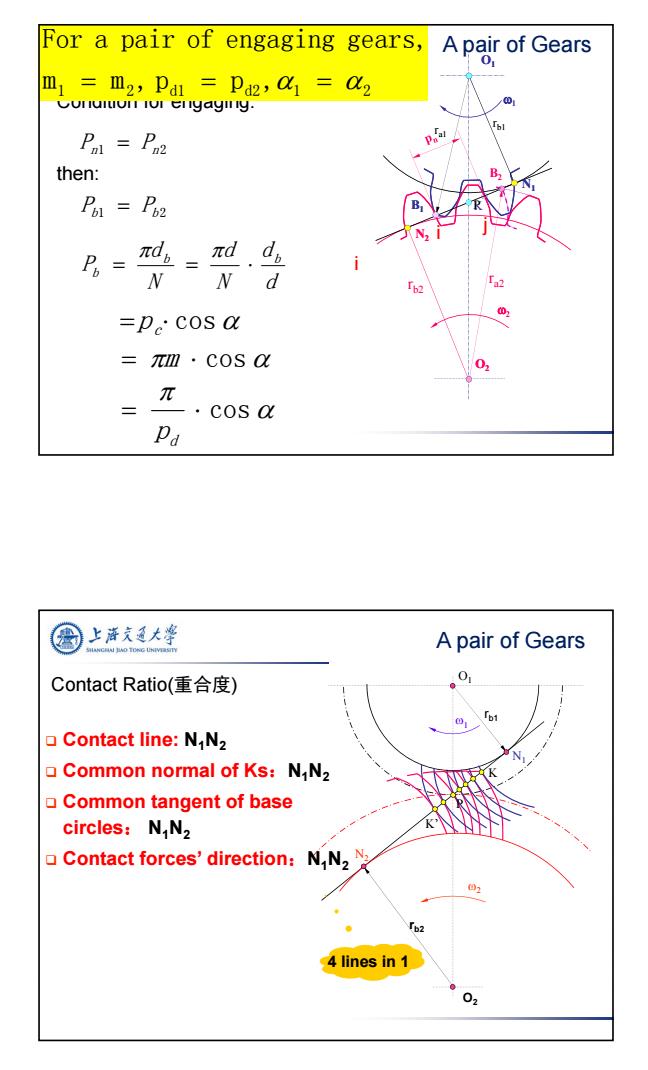
For a pair of engaging gears, A pair of Gears 01 m1=m2,Pal Pd2,1=d2 Conulton iol engaying. Pat =Pn2 then: P1=P2 πdh= nd dp d a2 02 =p cos a =πm·COS O: π cos a Pa 上游文通大 A pair of Gears Contact Ratio(重合度) 0 口Contact line:NN2 Common normal of Ks:N N2 Common tangent of base circles:N N2 Contact forces'direction:N,N2 4 lines in 1 02
3 O1 O2 1 2 N2 N1 B2 B1 K ra2 ra1 rb1 rb2 O1 O2 N2 N1 B1 P i i j Condition for engaging: Pn1 Pn 2 Pb1 Pb 2 then: d d N d N d P b b b p c cos m cos cos pd 1 2 d1 d2 1 2 m m , p p , For a pair of engaging gears, A pair of Gears Contact Ratio(重合度) rb2 O2 1 2 N2 O1 rb1 P N1 K K’ 4 lines in 1 Contact line: N1N2 Common normal of Ks:N1N2 Common tangent of base circles: N1N2 Contact forces’ direction:N1N2 A pair of Gears
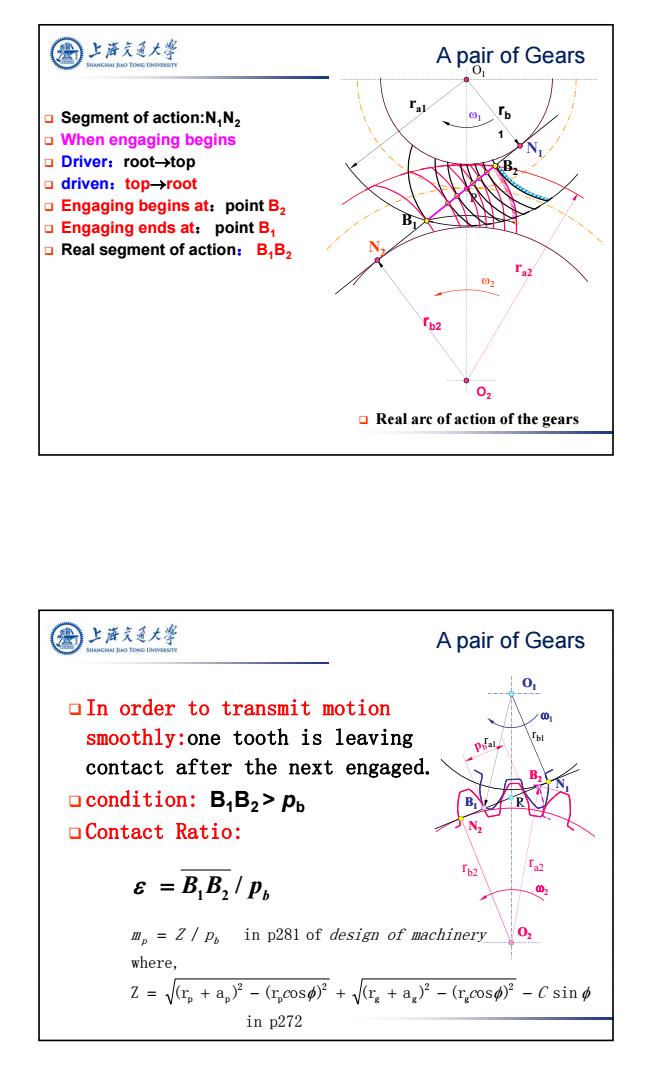
上海充通大学 A pair of Gears 01 Segment of action:N,N2 When engaging begins Driver:root→top 口 driven:top→root 口 Engaging begins at:point B2 Engaging ends at:point B Real segment of action:B,B2 「a2 02 02 Real arc of action of the gears 上海充通大粤 A pair of Gears In order to transmit motion smoothly:one tooth is leaving contact after the next engaged. 口condition:B,B2>Pb Contact Ratio: 8=B,B21P6 皿p=Z/P6 in p281 of design of machinery 01 where, Z=+ap)-(rcos)++ag)2-(rgcos)2-C sin in p272
4 Segment of action:N1N2 When engaging begins Driver:roottop driven:toproot Engaging begins at:point B2 Engaging ends at: point B1 Real segment of action: B1B2 Real arc of action of the gears rb2 O2 1 2 N2 O1 rb 1 P N1 ra1 ra2 B1 B2 A pair of Gears In order to transmit motion smoothly:one tooth is leaving contact after the next engaged. condition: B1B2 > pb Contact Ratio: O1 O2 1 2 N2 N1 B2 B1 K ra2 ra1 rb1 rb2 O1 O2 N2 N1 B1 B2 P B B pb / 1 2 in p272 Z (r a ) (r os ) (r a ) (r os ) sin where, / in p281 of 2 g 2 g g 2 p 2 p p c c C m p Z p b design of machinery A pair of Gears
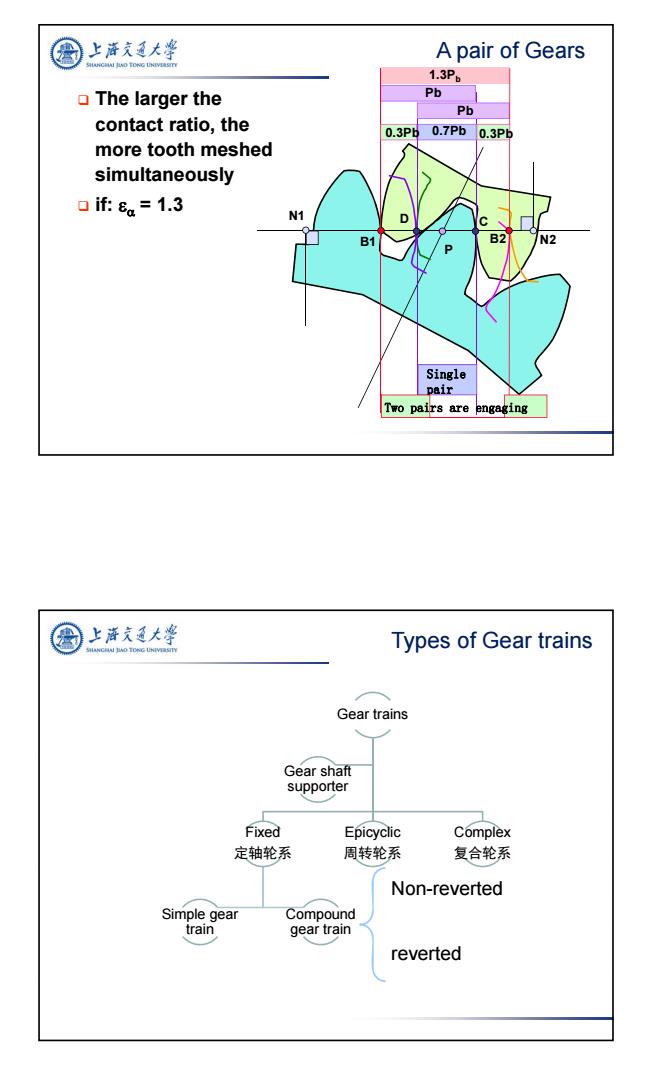
上海充通大学 A pair of Gears 1.3P。 The larger the Pb Pb contact ratio,the 0.3P6 0.7Pb0.3Pb more tooth meshed simultaneously 口if:8。=1.3 N1 B1 N2 Single pair Two pairs are engaging 上游充通大 Types of Gear trains Gear trains Gear shaft supporter Fixed Epicyclic Complex 定轴轮系 周转轮系 复合轮系 Non-reverted Simple gear Compound train gear train reverted
5 The larger the contact ratio, the more tooth meshed simultaneously if: = 1.3 N2 P N1 B1 B2 Pb Pb 1.3Pb 0.3Pb 0.7Pb 0.3Pb D C Single pair Two pairs are engaging A pair of Gears Types of Gear trains Gear trains Fixed 定轴轮系 Compound gear train Simple gear train Epicyclic 周转轮系 Complex 复合轮系 Gear shaft supporter Non-reverted reverted
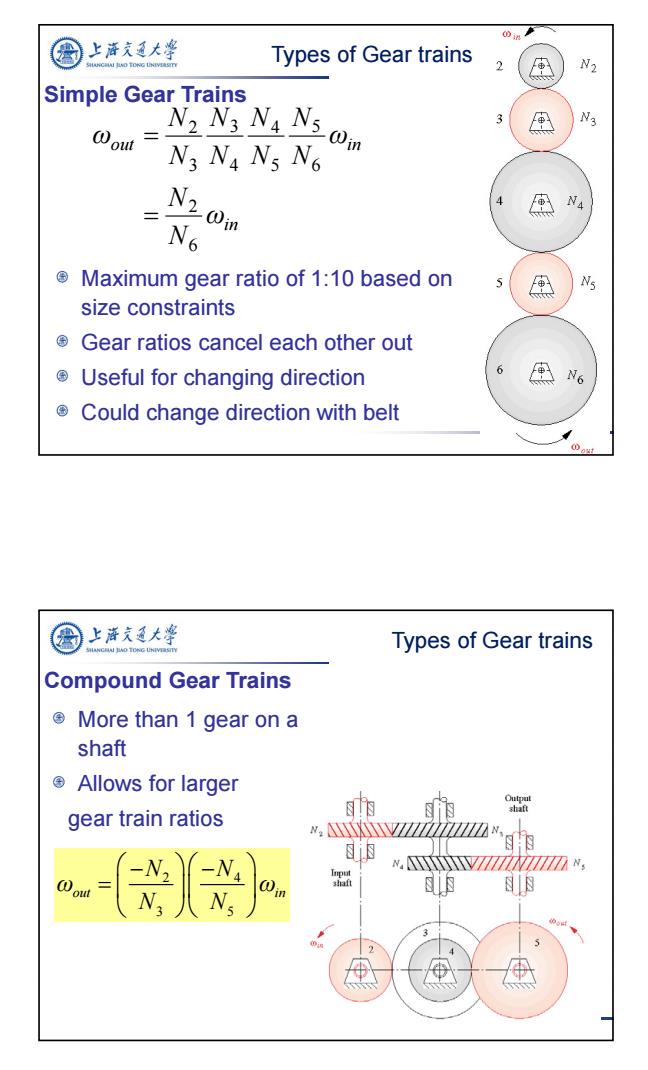
上济充道大峰 A BNO TONG LN时 Types of Gear trains N2 out NIN NAN5 Om Simple Gear Trains N3 Na Ns N6 N2Om N4 N6 ® Maximum gear ratio of 1:10 based on size constraints Gear ratios cancel each other out ® Useful for changing direction 6 N6 Could change direction with belt 上海充通大粤 Types of Gear trains Compound Gear Trains ©More than1 gear on a shaft ©Allows for larger N Output shaft gear train ratios .YZiW“g▣ * N.V77777W777777N, -Q shaft N
6 Simple Gear Trains Maximum gear ratio of 1:10 based on size constraints Gear ratios cancel each other out Useful for changing direction Could change direction with belt in out in ω N N ω N N N N N N N N ω 6 2 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 Types of Gear trains Compound Gear Trains More than 1 gear on a shaft Allows for larger gear train ratios 2 4 3 5 out in N N ω ω N N Types of Gear trains
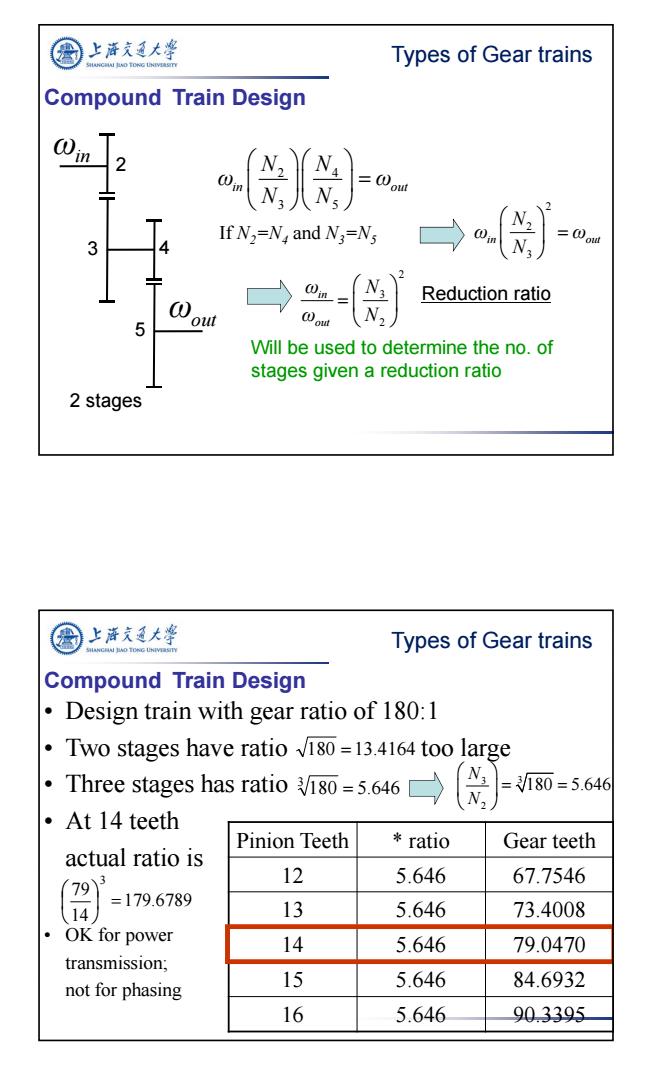
上海充通大学 Types of Gear trains Compound Train Design 2 是) @ou N If N2=N,and N3=Ns 3 Reduction ratio out →品) 5 Will be used to determine the no.of stages given a reduction ratio 2 stages 上海充通大粤 Types of Gear trains Compound Train Design Design train with gear ratio of 180:1 ·Two stages have ratio√8o-l3.4164 too large Three stages has ratio 180=5.646 →贷)=56 ·At14 teeth Pinion Teeth ratio Gear teeth actual ratio is 9 12 5.646 67.7546 =179.6789 13 5.646 73.4008 OK for power 14 5.646 79.0470 transmission; not for phasing 15 5.646 84.6932 16 5.646 90.3395
7 Compound Train Design ωin ωout 2 3 4 5 2 4 3 5 in out N N ω ω N N If N2=N4 and N3=N5 2 2 3 in out N ω ω N 2 3 2 in out ω N ω N Reduction ratio 2 stages Will be used to determine the no. of stages given a reduction ratio Types of Gear trains • Design train with gear ratio of 180:1 • Two stages have ratio too large • Three stages has ratio • At 14 teeth actual ratio is • OK for power transmission; not for phasing 180 13.4164 180 5.646 3 Pinion Teeth * ratio Gear teeth 12 5.646 67.7546 13 5.646 73.4008 14 5.646 79.0470 15 5.646 84.6932 16 5.646 90.3395 179.6789 14 79 3 3 3 2 180 5.646 N N Compound Train Design Types of Gear trains
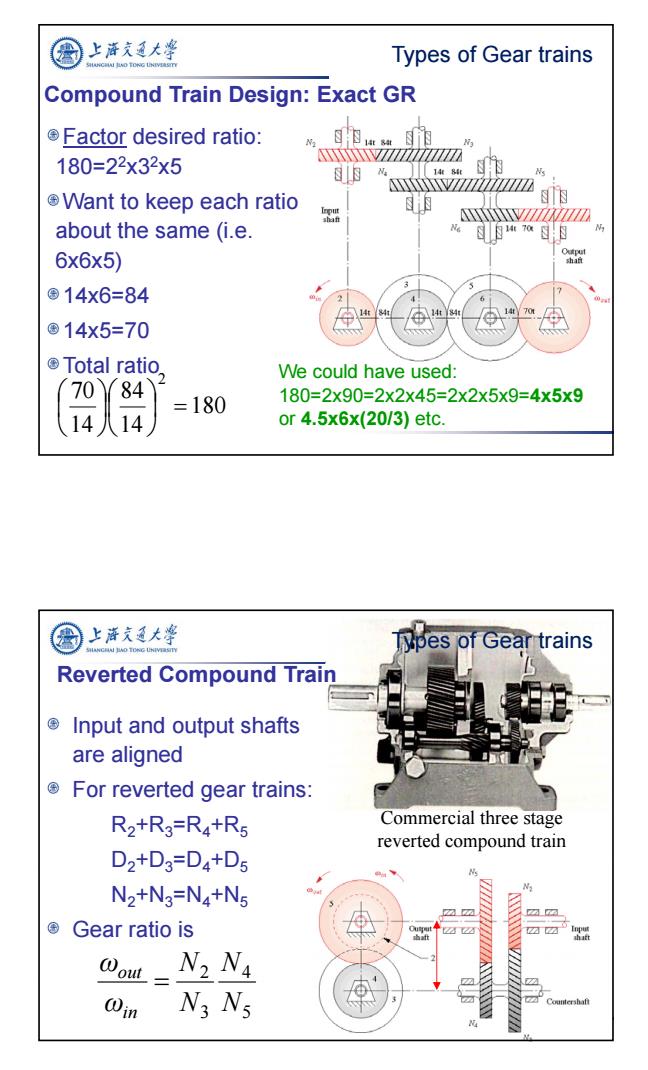
上海充通大学 Types of Gear trains Compound Train Design:Exact GR Factor desired ratio: 180=22x32x5 XXZZZZZZZZ7Z Want to keep each ratio ii的 品 NXXXXXXXZZZ77ZZ about the same (i.e. 6x6x5) ©14x6=84 114t h14t8 ©14x5=70 ©Total ratio, We could have used: 70 84 =180 180=2x90=2x2x45=2x2x5x9=4x5x9 14 or 4.5x6x(20/3)etc. 上海充通大粤 Types of Gear trains Reverted Compound Train Input and output shafts are aligned For reverted gear trains: R2+R3=R4+R5 Commercial three stage reverted compound train D2+D3=D4+D5 N2+N3=N4+N5 ©Gear ratio is N2N4 @Din N3 Ns
8 Compound Train Design: Exact GR Factor desired ratio: 180=22x32x5 Want to keep each ratio about the same (i.e. 6x6x5) 14x6=84 14x5=70 Total ratio 180 14 84 14 70 2 We could have used: 180=2x90=2x2x45=2x2x5x9=4x5x9 or 4.5x6x(20/3) etc. Types of Gear trains Reverted Compound Train Input and output shafts are aligned For reverted gear trains: R2+R3=R4+R5 D2+D3=D4+D5 N2+N3=N4+N5 Gear ratio is Commercial three stage reverted compound train 5 4 3 2 N N N N ω ω in out Types of Gear trains

上海充通大学 Types of Gear trains Design a reverted compound gear train for a gear ratio of 18:1 =18 18=3x6→N3=6N2,N5=3N4 N, N2+N3=N4+N =constant N2+6N2=N4+3N4=C -3 7N2=4N4=C >Take C=28,then N,=4,N=7 >This is too small for a gear!Choose C=28x4=112(say) 亿ad N2=16,N3=96, 。 N4=28,N5=84 Counterhaft 上游克通大 Planetary or Epicyclic Gears Conventional gearset has one DOF If you remove the ground at gear 3,it has two DOF 3 Output 0=0 Input #1 Input #1 Arm Arm. Output Planet gear Input #2 Pinion Gear Sun gear (a)Conventional gearset (b)Ranetary or epicyclic gearset
9 3 5 2 4 18 N N N N Design a reverted compound gear train for a gear ratio of 18:1 18=3x6 N3=6N2, N5=3N4 N2+N3=N4+N5=constant N2+6N2=N4+3N4=C 7N2=4N4=C Take C=28, then N2=4, N4=7 This is too small for a gear! Choose C=28x4=112 (say) • N2=16, N3=96, • N4=28, N5=84 3 2 6 N N 5 4 3 N N Types of Gear trains Planetary or Epicyclic Gears Conventional gearset has one DOF If you remove the ground at gear 3, it has two DOF

上海充通大学 Types of Gear trains Planet Ring gear Output 80t Ring gear Sun gear Planet 20t 3 Arm Sun 40t 02 Input #1 Input #2 Bearing 上游文通大 Types of Gear trains 4M111000//6A planetary train differential train 行星轮系 差动轮系
10 Types of Gear trains planetary train 行星轮系 differential train 差动轮系 Types of Gear trains