
营养生理学主要营养物质代谢的调控Jing,Hao (景浩)College of Food Science and Nutritional EngineeringChina Agricultural UniversityDec 15, 18, 2009
营养生理学 主要营养物质代谢的调控 Jing, Hao (景浩) College of Food Science and Nutritional Engineering China Agricultural University Dec 15, 18, 2009
EndocrineThe endocrine system is an integrated systemof small organs which involve the releaseof extracellular signalingmoleculesknown as hormonesEndocrinologyis the study of hormones, their receptors and theintracellular signalling pathways they invoke
Endocrine The endocrine system is an integrated system of small organs which involve the release of extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Endocrinology is the study of hormones, their receptors and the intracellular signalling pathways they invoke

"Diffuse" endocrine systemScattered throughout the bodyIn addition to the classical endocrine organs, manyothercellsinthebodysecretehormones.Myocytes in the atria of the heartepithelial cells in stomach/small intestineIf hormone~all secreted chemical messengersThen all cells ~ part of the endocrine system
“Diffuse" endocrine system Scattered throughout the body In addition to the classical endocrine organs, many other cells in the body secrete hormones. Myocytes in the atria of the heart epithelial cells in stomach/small intestine If hormoneall secreted chemical messengers Then all cells ~ part of the endocrine system

· All physiologic events are influencedby the endocrine messanges·All "large" physiologic effects are mediated bymultiple hormones acting in concert:Normal growth: growth hormone, thyroidhormones, insulin-like growth factor-1,glucocorticoids and several other hormones.There are many hormones knownwhile others remain to be discovered
• All physiologic events are influenced by the endocrine messanges • All "large" physiologic effects are mediated by multiple hormones acting in concert: Normal growth: growth hormone, thyroid hormones, insulin-like growth factor-1, glucocorticoids and several other hormones • There are many hormones known while others remain to be discovered

The endocrine system is a collection of glandsthat secrete chemical messages we callhormones.These signals are passed through the blood toarrive at a target organ, which has cellspossessing the appropriate receptor.Exocrineglands(not part of the endocrine system) secreteproducts that are passed outside the body.Sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestiveglands are examples of exocrine glands
The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete chemical messages we call hormones. These signals are passed through the blood to arrive at a target organ, which has cells possessing the appropriate receptor. Exocrine glands (not part of the endocrine system) secrete products that are passed outside the body. Sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestive glands are examples of exocrine glands
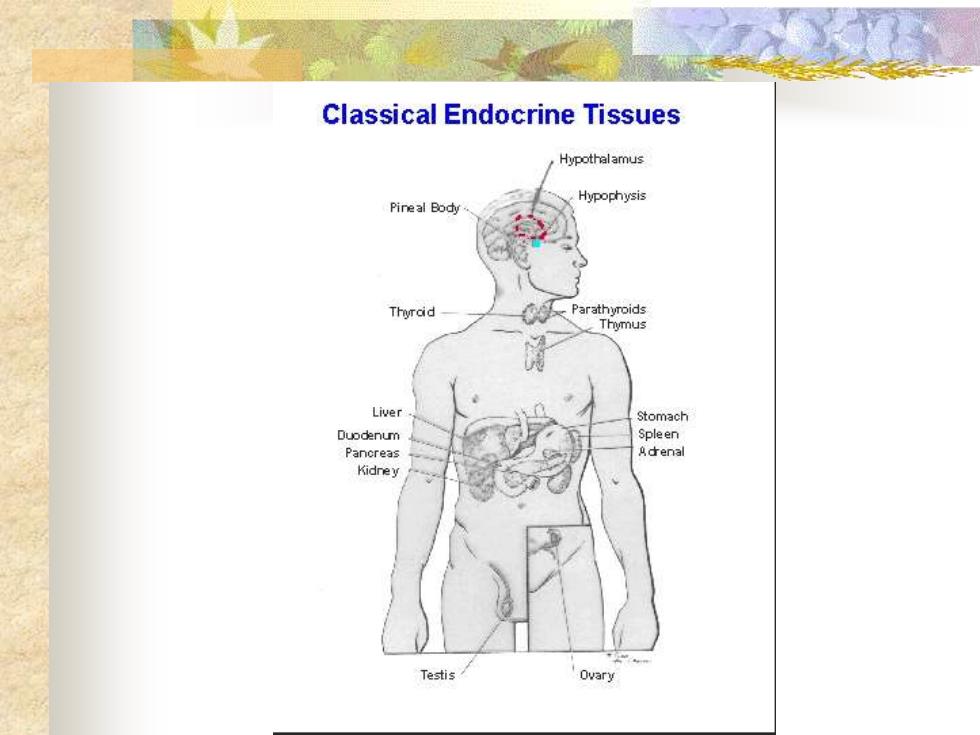
Classical Endocrine TissuesHypothalamusPineal BodyParathuroidThyraiciuerStomachDuodenumSpleenAdrenalPancreasKidreOua

Introduction to the Endocrine SystemThe term ‘hormone'(from the Greek verb ‘hormoa', to excite)1905, E.H. Starling, first defined‘the chemical messengers which,speedingfromcellto cell alongthe blood stream,may coordinatethe activities and growth of different parts of thebody
Introduction to the Endocrine System The term ‘hormone’ (from the Greek verb ‘hormoa’, to excite) 1905, E.H. Starling, first defined ‘the chemical messengers which, speeding from cell to cell along the blood stream, may coordinate the activities and growth of different parts of the body’
Forms of Intercellular CommunicationEndocrine: secretion of a hormone by one cellwith transmission via the blood, or intercellularfluid to a second, target, cell.1.Endocrine/Telecrine远距分泌:viatheblood2.Paracrine旁分泌:viaintercellularfluid,胃肠激素3.Autocrine自分泌:bythesamecell.前列腺素4.Neurocrine神经分泌:neuron,神经肽5. Pheromonal: secretion by one organism andsensation andresponse bya second
Forms of Intercellular Communication Endocrine: secretion of a hormone by one cell with transmission via the blood, or intercellular fluid to a second, target, cell. 1. Endocrine/Telecrine远距分泌: via the blood 2. Paracrine旁分泌: via intercellular fluid,胃肠激素 3. Autocrine自分泌: by the same cell,前列腺素 4. Neurocrine神经分泌: neuron,神经肽 5. Pheromonal: secretion by one organism and sensation and response by a second
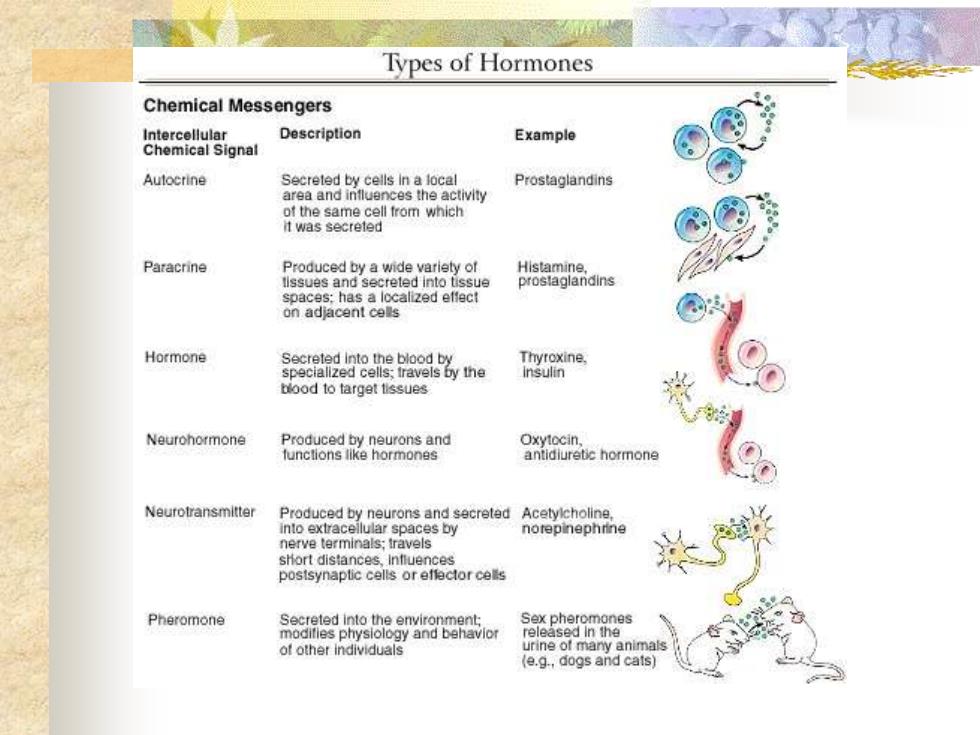
Types of HormonesChemical MessengersDescriptionIntercellularExampleChemical SignalAutocrineSecreted by cells InalocalProstaglandinsareaandintluencestheactivityofthesamecell tromwhichitwassecretedParacrineHistaminProducedbyawidevarietyofprostaglandinslissuesandseratadintotspaces:hasalocalizedetleconadjacentcellsHormoneSecreted intothebloodtThyroxine,cializedcells.fraveinsulinblood to target tissuesOxytocirNeurohormoneProducedbyneuronsandantidiuretic hormonefunclionslikehormonesNeurotransmitterProduced by neurons and secreted Acetyicholinenloextracnotepinephrinlarspacesbynerveterminals:travelsshort.distanceslntluencespostsynaptic cells oreflectorcelsPheromoneSexpheroSecreted intothe emvironmentronesmoditiesphysiologyandbehavioreleasedintheurineofmaanimaot other individuals(e.g.,dogs and cats)

Characteristics of hormoneA hormone is a chemical messenger that is:. Secreted into body fluids (usually the blood)by specialized cells, e.g endocrine ornerve cells·Effective in minute amounts· Detected only by "target" cells possessingspecial protein receptors on cell membranes.Often regulated by a second antagonistic hormone
Characteristics of hormone A hormone is a chemical messenger that is: • Secreted into body fluids (usually the blood) by specialized cells, e.g endocrine or nerve cells • Effective in minute amounts • Detected only by "target" cells possessing special protein receptors on cell membranes • Often regulated by a second antagonistic hormone