
L8 Explanation&the Methodology You may or may not need to work on Language Focus or Vocabulary for Causality in this handout.All exercises are obligatory. Lesson 8 Reading and Writing Explanation and the Methodology 1. Your Mini-talk II.The Text Types:Explanation Explanations are concerned with explaining how processes happen."To this end they imply sequences of causes and effects"(Wignell,Martin Eggins,1993). 4 types of explanations: sequential explanation factorial explanation consequential explanation conditional explanation Schematic structure in explanation writing: 1)specifying the Phenomenon (effect/cause/issue) 2)the Explanation stage the implication sequence causes/effects/sequence of events conditions-effects 3)Extension/Implication/Significance/Recapitulation Important in explanation writing: Presence of Causality Logic and Thoroughness Implicit Causality---absence of conjunctions Multi-modal Reports and Explanations 1.The Sequential explanation is typically constructed as a series of events. Logical relations between events are temporal,either succeeding each other in time or happening at the same time. 2.The Factorial explanation explains how an effect involves multiple factors 3.The Consequential explanation explains how a single factor leads to multiple consequences. 4.The Conditional explanation deals with how effects are contingent on variable factors. 5.Differentiating types of explanation Ex.8-1 Read the following texts,and determine which type of explanation they respectively are.Make sure that you identify factor-consequence relations in the particular type of explanation. Text 1 Predator and Prey 1/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 1 / 10 You may or may not need to work on Language Focus or Vocabulary for Causality in this handout. All exercises are obligatory. Lesson 8 Reading and Writing Explanation and the Methodology I. Your Mini-talk II. The Text Types: Explanation Explanations are concerned with explaining how processes happen. “To this end they imply sequences of causes and effects” (Wignell, Martin & Eggins, 1993). 4 types of explanations: sequential explanation factorial explanation consequential explanation conditional explanation Schematic structure in explanation writing: 1) specifying the Phenomenon (effect/cause/issue) 2) the Explanation stage / the implication sequence causes / effects / sequence of events / conditions-effects 3) Extension / Implication / Significance / Recapitulation Important in explanation writing: Presence of Causality Logic and Thoroughness Implicit Causality --- absence of conjunctions Multi-modal Reports and Explanations 1. The Sequential explanation is typically constructed as a series of events. Logical relations between events are temporal, either succeeding each other in time or happening at the same time. 2. The Factorial explanation explains how an effect involves multiple factors. 3. The Consequential explanation explains how a single factor leads to multiple consequences. 4. The Conditional explanation deals with how effects are contingent on variable factors. 5. Differentiating types of explanation Ex. 8-1 Read the following texts, and determine which type of explanation they respectively are. Make sure that you identify factor-consequence relations in the particular type of explanation. Text 1 Predator and Prey

L8 Explanation&the Methodology Population size of one species can be affected by the size of the population of another species.This is true in the case of a predator species and the prey species on which it feeds.Over time,several outcomes are possible: If the predators are absent,the prey population will increase exponentially but will eventually crash'when its numbers become too high to be supported by the food resources in the habitat. If the prey population is too small,the predator population will starve and die. In some cases,cycles of boom-and-bust'can be seen in both populations,with the peak in the predator population occurring after the peak in the prey population. Why? (Kinnear Martin,2004) Text 2 The Mulga Tree How can plant life grow so well in such dry,hot and infertile places?The mulga tree likes long droughts-if it is too wet,mulga trees will not grow. The shape of the mulga tree is the key to its surviving dry times.The branches of the mulga fan out from the bottom-like a huge half-moon.The branching leaves and stem catch the rain and it trickles down to the soil.This traps more rainfall than if the tree grew straight up.The mulga catches more water than a gum tree.The water is stored in the soil to be used by the tree during the next drought. Even the mulga's leaves help it survive the drought.They are a silvery grey color. The sun's rays bounce off the leaves helping the plant to stay cool.Also the mulga tree makes its own food by dropping thousands of leaves. (Scott Robinson,1993) Text 3 What Causes and Transmits Sounds? Figure 15.1 shows a vibrating object producing sound waves.As the object moves to the right it pushes or compresses the air particles next to it.The compressed air particles then push on the particles to their right and compress them.As each air particle pushes on the next one to its right the compression travels through the air. When the vibrating object moves back to its left the air particles next to it are no longer being pushed.They spread out or are stretched apart.As a compression travels through the air it is followed by the stretching apart of air particles.Because the vibrating object continually moves back and forth a series of compressions and stretchings of air particles is sent out from the object. (Martin Rose,2008) Text 4 The Vietnam War The Vietnam War,which is the main topic of this chapter,also had a major impact on the twentieth century national history of the USA and was one of the defining events of the Cold War. 2/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 2 / 10 Population size of one species can be affected by the size of the population of another species. This is true in the case of a predator species and the prey species on which it feeds. Over time, several outcomes are possible: If the predators are absent, the prey population will increase exponentially but will eventually ‘crash’ when its numbers become too high to be supported by the food resources in the habitat. If the prey population is too small, the predator population will starve and die. In some cases, cycles of ‘boom-and-bust’ can be seen in both populations, with the peak in the predator population occurring after the peak in the prey population. Why? (Kinnear & Martin, 2004) Text 2 The Mulga Tree How can plant life grow so well in such dry, hot and infertile places? The mulga tree likes long droughts – if it is too wet, mulga trees will not grow. The shape of the mulga tree is the key to its surviving dry times. The branches of the mulga fan out from the bottom – like a huge half-moon. The branching leaves and stem catch the rain and it trickles down to the soil. This traps more rainfall than if the tree grew straight up. The mulga catches more water than a gum tree. The water is stored in the soil to be used by the tree during the next drought. Even the mulga’s leaves help it survive the drought. They are a silvery grey color. The sun’s rays bounce off the leaves helping the plant to stay cool. Also the mulga tree makes its own food by dropping thousands of leaves. (Scott & Robinson, 1993) Text 3 What Causes and Transmits Sounds? Figure 15.1 shows a vibrating object producing sound waves. As the object moves to the right it pushes or compresses the air particles next to it. The compressed air particles then push on the particles to their right and compress them. As each air particle pushes on the next one to its right the compression travels through the air. When the vibrating object moves back to its left the air particles next to it are no longer being pushed. They spread out or are stretched apart. As a compression travels through the air it is followed by the stretching apart of air particles. Because the vibrating object continually moves back and forth a series of compressions and stretchings of air particles is sent out from the object. (Martin & Rose, 2008) Text 4 The Vietnam War The Vietnam War, which is the main topic of this chapter, also had a major impact on the twentieth century national history of the USA and was one of the defining events of the Cold War

L8 Explanation&the Methodology Professor David Kennedy of Stanford University has argued that the cost and trauma of the Vietnam War produced a 'crisis of confidence'in the USA.Until the Vietnam War,Americans had generally felt confident in their ability to mould events through the exercise of their ingenuity,energy and vast economic resources.Vietnam proved to be a problem that they couldn't manage. The Vietnam conflict gave rise to social division and distrust of government in the US.It ended the political career of President Lyndon Johnson and his dreams of major social reform.It also produced,in the case of Richard Nixon's presidency,a siege mentality that contributed directly to the infamous Watergate Scandal (1973-74)and the resignation,in disgrace,of Nixon.Because of the Vietnam War, as part of the wider conflict in Indochina,a generation of Americans identified with anti -conscription and anti-war protest movements.Many of the social and political effects evident in the US were also present in Australia (Dennett Dixon,2003) Ex.8-2 Determine which type of explanation would most probably apply if your assignment is to write on the following topics. 1.What are the causes of increased obesity in the U.S.? 2.What would be the possible effects of the rising costs of college education? 3.What would possibly cause Americans having large credit card debt? 4.What impact does cyber bullying have on teenagers? 5.What would cause college students unable to manage their time well? 6. What is the relationship between grazing and soil protection? 7.How effective is the use of alternate punishments and praises in education? Ex.8-3 (Teamwork)Analyze the text type(s)in the Discussion of the article Pedestrians,Vehicles and Cell Phones. Pedestrians,Vehicles and Cell Phones Neider,M.B.,McCarley,J.S.,Crowell,J.A., Kaczmarski,H.,and Kramer,A.F.(2010) Accident Analysis &Prevention,42,589-594 4.Discussion Field studies (e.g,[Hatfield and Murphy,2007]and [Nasar et al.,2008]) have observed that pedestrians make more unsafe street crossings when conversing on a cell phone than when undistracted.Our findings provide partial experimental confirmation of these observations.Participants were less likely to successfully cross the street in our task when they were conversing on a cell phone than when they were listening to music on an iPod.Furthermore,engaging in a cell phone conversation while crossing the street led to higher time out rates in our virtual street-crossing task than did listening to music or performing the task distracted.Additionally,participants took more time to initiate a crossing when conversing on a cell phone,and walked more slowly during crossing.The last result is consistent with data from field studies of pedestrian street crossing that 3/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 3 / 10 Professor David Kennedy of Stanford University has argued that the cost and trauma of the Vietnam War produced a ‘crisis of confidence’ in the USA. Until the Vietnam War, Americans had generally felt confident in their ability to mould events through the exercise of their ingenuity, energy and vast economic resources. Vietnam proved to be a problem that they couldn’t manage. The Vietnam conflict gave rise to social division and distrust of government in the US. It ended the political career of President Lyndon Johnson and his dreams of major social reform. It also produced, in the case of Richard Nixon’s presidency, a siege mentality that contributed directly to the infamous Watergate Scandal (1973‐74) and the resignation, in disgrace, of Nixon. Because of the Vietnam War, as part of the wider conflict in Indochina, a generation of Americans identified with anti‐conscription and anti‐war protest movements. Many of the social and political effects evident in the US were also present in Australia. (Dennett & Dixon, 2003) Ex. 8-2 Determine which type of explanation would most probably apply if your assignment is to write on the following topics. 1. What are the causes of increased obesity in the U.S.? 2. What would be the possible effects of the rising costs of college education? 3. What would possibly cause Americans having large credit card debt? 4. What impact does cyber bullying have on teenagers? 5. What would cause college students unable to manage their time well? 6. What is the relationship between grazing and soil protection? 7. How effective is the use of alternate punishments and praises in education? Ex. 8-3 (Teamwork) Analyze the text type(s) in the Discussion of the article Pedestrians, Vehicles and Cell Phones. Pedestrians, Vehicles and Cell Phones Neider, M.B., McCarley, J.S., Crowell, J.A., Kaczmarski, H., and Kramer, A.F.(2010) Accident Analysis &Prevention, 42, 589-594 4. Discussion Field studies (e.g., [Hatfield and Murphy, 2007] and [Nasar et al., 2008]) have observed that pedestrians make more unsafe street crossings when conversing on a cell phone than when undistracted. Our findings provide partial experimental confirmation of these observations. Participants were less likely to successfully cross the street in our task when they were conversing on a cell phone than when they were listening to music on an iPod. Furthermore, engaging in a cell phone conversation while crossing the street led to higher time out rates in our virtual street-crossing task than did listening to music or performing the task distracted. Additionally, participants took more time to initiate a crossing when conversing on a cell phone, and walked more slowly during crossing. The last result is consistent with data from field studies of pedestrian street crossing that

L8 Explanation the Methodology have observed slower walking during cell phone conversations(e.g.,[Hatfield and Murphy,2007]and [Nasar et al.,2008]). [The remainder of the Discussion section has been omitted.] III.Language Focus:Evaluative language According to Hyland's 2004 study of 160 book reviews from eight disciplines---Cell Biology,Electrical Engineering,Mechanical Engineering,Physics, Marketing,Applied Linguistics,Philosophy,and Sociology,some evaluative terms cut across several disciplines,while others have preferred status in one or two.Here is a summary of his findings of frequently used evaluative words: Adjectives in all disciplines:useful,important,interesting ·Nouns in the“soft”fields:clarity,accessibility Adjectives in the hard sciences:detailed,up-to-date On a more specific level,philosophers and applied linguists often described books as detailed,while philosophers and marketing specialists praised books for being insightful and significant.Books in Engineering were commended for being comprehensive and practical.Of course,not all evaluation is positive.For all fields the most common negative adjective was difficult.In the softer fields,books were criticized for being inconsistent,restricted,and misleading (Swales Feak,2014). IV.Reading and Writing the Methodology 1.Methods and Material Read the following passages on methods and material to answer the questions below. 1)What makes Methodology writing important? 2)How much detailed should the Methodology be?And in what order should it be written? 3)How much writing on materials should there be in the Methodology? 4)What is the structure of Methodology used in your research field? 1.1 Methods How the research was accomplished A description of methods used is key to evaluating the significance of the research accomplished.If faulty procedures are used,obviously the results are questionable.You want therefore to convince your readers that you have used a sound methodology; In case of a new method or an unusual application of an older method,the description and justification may be as important as or more important than the results obtained. A"rule"of the scientific method states that the results based on the method must be reproducible,thus the method used must be described in sufficient detail. First give the preconditions necessary for applying the method.Describe preparations,if any,for performing the method.For example,describe the criteria for selecting specimens or subjects and how you assigned them to either the experimental 4/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 4 / 10 have observed slower walking during cell phone conversations (e.g., [Hatfield and Murphy, 2007] and [Nasar et al., 2008]). [The remainder of the Discussion section has been omitted.] III. Language Focus: Evaluative language According to Hyland’s 2004 study of 160 book reviews from eight disciplines---Cell Biology, Electrical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Physics, Marketing, Applied Linguistics, Philosophy, and Sociology, some evaluative terms cut across several disciplines, while others have preferred status in one or two. Here is a summary of his findings of frequently used evaluative words: Adjectives in all disciplines: useful, important, interesting Nouns in the “soft” fields: clarity, accessibility Adjectives in the hard sciences: detailed, up-to-date On a more specific level, philosophers and applied linguists often described books as detailed, while philosophers and marketing specialists praised books for being insightful and significant. Books in Engineering were commended for being comprehensive and practical. Of course, not all evaluation is positive. For all fields the most common negative adjective was dif icult. In the softer fields, books were criticized for being inconsistent, restricted, and misleading (Swales & Feak, 2014). IV. Reading and Writing the Methodology 1. Methods and Material Read the following passages on methods and material to answer the questions below. 1) What makes Methodology writing important? 2) How much detailed should the Methodology be? And in what order should it be written? 3) How much writing on materials should there be in the Methodology? 4) What is the structure of Methodology used in your research field? 1.1 Methods = How the research was accomplished A description of methods used is key to evaluating the significance of the research accomplished. If faulty procedures are used, obviously the results are questionable. You want therefore to convince your readers that you have used a sound methodology; In case of a new method or an unusual application of an older method, the description and justification may be as important as or more important than the results obtained. A “rule” of the scientific method states that the results based on the method must be reproducible, thus the method used must be described in sufficient detail. First give the preconditions necessary for applying the method. Describe preparations, if any, for performing the method. For example, describe the criteria for selecting specimens or subjects and how you assigned them to either the experimental

L8 Explanation&the Methodology or control groups.You should also describe any preliminary investigations which lead you to select the method you eventually employed. Describe next in the chronological order the procedure employed.Group similar steps of a procedure together.In case of a new procedure,describe it in greater detail than a well-known procedure in your field.Describe the procedure only in general terms and refer to the original work if it has been elaborated in a previous RP in a readily available publication.Since the Results will follow the procedure in the Methodology,both should be organized similarly to clearly show the relationship between. 1.2 Material Resources used during the research The material is often combined with methods,thus it is necessary to state with each step of your procedure the material required.Materials are any physical or abstract items used in applying the method.The term "resource"may be preferred to "material".For example,in conducting their research,some investigators may rely upon a group of people as their resource for information.Materials/resources can be equipment,natural or man-made substances,computer or mathematical models, questionnaires,artifacts,biological specimens,or human subjects.Well-known material in your field need to be briefly identified only;unique or unconventional resources must be described and justified in detail. 2.Components of the Methodology Section Ex.8-4 Below is the Methodology in a RP entitled Changes in the chemistry of groundwater in the chalk of the London Basin.Read it to see what each sentence is about.Be prepared to share your analysis the structure with the class. 5/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 5 / 10 or control groups. You should also describe any preliminary investigations which lead you to select the method you eventually employed. Describe next in the chronological order the procedure employed. Group similar steps of a procedure together. In case of a new procedure, describe it in greater detail than a well-known procedure in your field. Describe the procedure only in general terms and refer to the original work if it has been elaborated in a previous RP in a readily available publication. Since the Results will follow the procedure in the Methodology, both should be organized similarly to clearly show the relationship between. 1.2 Material = Resources used during the research The material is often combined with methods, thus it is necessary to state with each step of your procedure the material required. Materials are any physical or abstract items used in applying the method. The term “resource” may be preferred to “material”. For example, in conducting their research, some investigators may rely upon a group of people as their resource for information. Materials/resources can be equipment, natural or man-made substances, computer or mathematical models, questionnaires, artifacts, biological specimens, or human subjects. Well-known material in your field need to be briefly identified only; unique or unconventional resources must be described and justified in detail. 2. Components of the Methodology Section Ex. 8-4 Below is the Methodology in a RP entitled Changes in the chemistry of groundwater in the chalk of the London Basin. Read it to see what each sentence is about. Be prepared to share your analysis the structure with the class
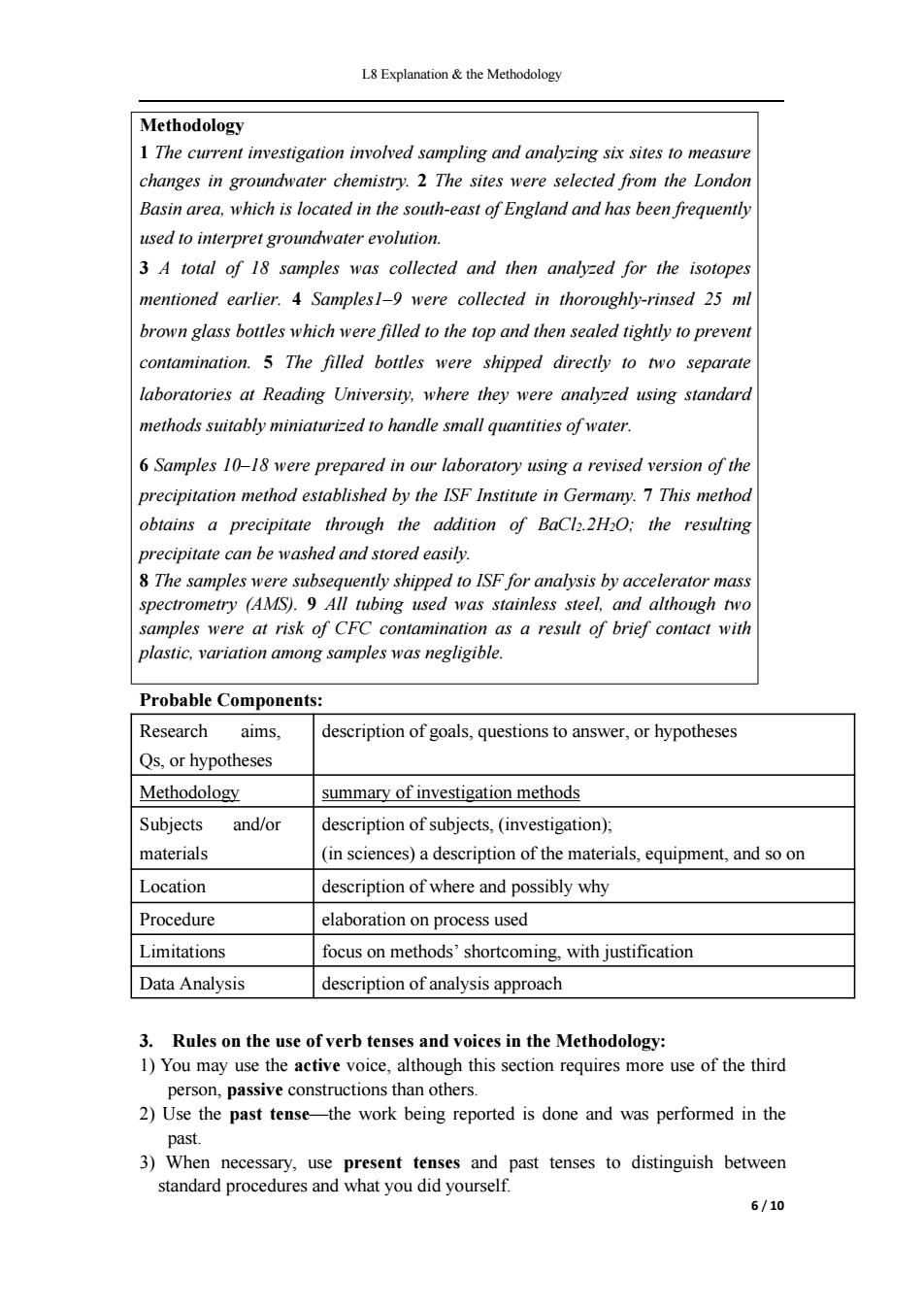
L8 Explanation&the Methodology Methodology 1 The current investigation involved sampling and analyzing six sites to measure changes in groundwater chemistry.2 The sites were selected from the London Basin area,which is located in the south-east of England and has been frequently used to interpret groundwater evolution. 3 A total of 18 samples was collected and then analyzed for the isotopes mentioned earlier.4 Samples1-9 were collected in thoroughly-rinsed 25 ml brown glass bottles which were filled to the top and then sealed tightly to prevent contamination.5 The filled bottles were shipped directly to two separate laboratories at Reading University,where they were analyzed using standard methods suitably miniaturized to handle small quantities of water. 6 Samples 10-18 were prepared in our laboratory using a revised version of the precipitation method established by the ISF Institute in Germany.7 This method obtains a precipitate through the addition of BaCl2.2H2O:the resulting precipitate can be washed and stored easily. 8 The samples were subsequently shipped to ISF for analysis by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS).9 All tubing used was stainless steel,and although two samples were at risk of CFC contamination as a result of brief contact with plastic,variation among samples was negligible. Probable Components: Research aims. description of goals,questions to answer,or hypotheses Qs,or hypotheses Methodology summary of investigation methods Subjects and/or description of subjects,(investigation); materials (in sciences)a description of the materials,equipment,and so on Location description of where and possibly why Procedure elaboration on process used Limitations focus on methods'shortcoming,with justification Data Analysis description of analysis approach 3.Rules on the use of verb tenses and voices in the Methodology: 1)You may use the active voice,although this section requires more use of the third person,passive constructions than others. 2)Use the past tense-the work being reported is done and was performed in the past. 3)When necessary,use present tenses and past tenses to distinguish between standard procedures and what you did yourself. 6/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 6 / 10 Methodology 1 The current investigation involved sampling and analyzing six sites to measure changes in groundwater chemistry. 2 The sites were selected from the London Basin area, which is located in the south-east of England and has been frequently used to interpret groundwater evolution. 3 A total of 18 samples was collected and then analyzed for the isotopes mentioned earlier. 4 Samples1–9 were collected in thoroughly-rinsed 25 ml brown glass bottles which were filled to the top and then sealed tightly to prevent contamination. 5 The filled bottles were shipped directly to two separate laboratories at Reading University, where they were analyzed using standard methods suitably miniaturized to handle small quantities of water. 6 Samples 10–18 were prepared in our laboratory using a revised version of the precipitation method established by the ISF Institute in Germany. 7 This method obtains a precipitate through the addition of BaCl2.2H2O; the resulting precipitate can be washed and stored easily. 8 The samples were subsequently shipped to ISF for analysis by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS). 9 All tubing used was stainless steel, and although two samples were at risk of CFC contamination as a result of brief contact with plastic, variation among samples was negligible. Probable Components: Research aims, Qs, or hypotheses description of goals, questions to answer, or hypotheses Methodology summary of investigation methods Subjects and/or materials description of subjects, (investigation); (in sciences) a description of the materials, equipment, and so on Location description of where and possibly why Procedure elaboration on process used Limitations focus on methods’ shortcoming, with justification Data Analysis description of analysis approach 3. Rules on the use of verb tenses and voices in the Methodology: 1) You may use the active voice, although this section requires more use of the third person, passive constructions than others. 2) Use the past tense—the work being reported is done and was performed in the past. 3) When necessary, use present tenses and past tenses to distinguish between standard procedures and what you did yourself

L8 Explanation&the Methodology e.g.Samples of gas analysis were collected using the method described by Brown (1999),which uses a pneumatic air sampling pump. Ex.8-5 Teamwork Planning: The Methodology basically describes and justifies the procedure in which you conducted your research.Be aware of the text types when you read and write the Methodology. In the Methodology of your article collection,isolate procedural indicators/transitions,verbs,references to material,and see how the authors vary in vocabulary in these cases.Have your ideas on how the issues in writing are related to procedural recount(in Lesson 9).Be ready to share them with the class. Assignment: 1.Team research:See Ex.8-5. 2.Individual work(analysis on writing): Label in bold letters and in brackets [the steps in lightning formation. Determine which type/types of explanation has/have been adopted in the extract below. Add procedural transitions and factor-consequence transitions in bold letters and in parenthesis ()wherever you think they could have occurred. Are there hidden types of report and argumentation?The reader-friendly passage below may be more complicated in structure than it seems.Label in bold letters and in brackets [elements/stages of every different text type you find. Develop a display to best illustrate organization of the ideas in the passage. 。 The assignment will be DUE by the 11th week classroom morning(SJTU calendar). Follow the template below. Entitle your virtual copy "Student ID NAME W11 Analysis.docx"and attach it as an assignment Canvas(M**Text Types Analysis). How well you accomplish this assignment depends on how thoroughly you have analyzed the passage and on how effectively you have designed the display. To further explore,you may also visit the following to see examples of nominalization.http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/p/index.php?title=Lightning. See Charge Seperation/Electrostatic Induction Theory .Scientific reasoning depends on simple cause/effect relations,not contextually sensitive interpretations of just how one thing affects another.Cause in the clause is also an important resource in scientific explanations for packaging information as cause and effect. Template for the Analysis Assignment Explanation Analysis Week 11 7/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 7 / 10 e.g. Samples of gas analysis were collected using the method described by Brown (1999), which uses a pneumatic air sampling pump. Ex. 8-5 Teamwork Planning: The Methodology basically describes and justifies the procedure in which you conducted your research. Be aware of the text types when you read and write the Methodology. • In the Methodology of your article collection, isolate procedural indicators/transitions, verbs, references to material, and see how the authors vary in vocabulary in these cases. Have your ideas on how the issues in writing are related to procedural recount (in Lesson 9). Be ready to share them with the class. Assignment: 1. Team research: See Ex. 8-5. 2. Individual work (analysis on writing): • Label in bold letters and in brackets [ ] the steps in lightning formation. Determine which type/types of explanation has/have been adopted in the extract below. • Add procedural transitions and factor-consequence transitions in bold letters and in parenthesis ( ) wherever you think they could have occurred. • Are there hidden types of report and argumentation? The reader-friendly passage below may be more complicated in structure than it seems. Label in bold letters and in brackets [ ] elements/stages of every different text type you find. • Develop a display to best illustrate organization of the ideas in the passage. • The assignment will be DUE by the 11 th week classroom morning (SJTU calendar). • Follow the template below. • Entitle your virtual copy “Student ID + NAME + W11 Analysis.docx” and attach it as an assignment @ Canvas (M** Text Types Analysis). How well you accomplish this assignment depends on how thoroughly you have analyzed the passage and on how effectively you have designed the display. To further explore, you may also visit the following to see examples of nominalization. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/p/index.php?title=Lightning. See Charge Seperation/Electrostatic Induction Theory •Scientific reasoning depends on simple cause/ef ect relations, not contextually sensitive interpretations of just how one thing af ects another. Cause in the clause is also an important resource in scientific explanations for packaging information as cause and ef ect.Template for the Analysis Assignment Explanation Analysis Week 11

L8 Explanation the Methodology EAP Class Number: Name: Student ID Text Types adopted: Add procedural indicators transitions,factor-consequence transitions,steps and text type labels in the passage below. Warm air rise in hot clouds and encounters cold air,charging the particles in the cloud making them both positive and negative charges,and this is called static electricity. When enough positive and negative charges occur,they build up too much energy and explode in a flash of light that we call lightening. This flash of light helps balance out the number of negative and positive charges in atmosphere. Sometimes the flash of light is movement within the cloud and sometimes it is lightening movement between the atmosphere and the ground. The movement between the atmosphere and the ground is the reason that tall objects on earth like trees are struck by lightning. Light travels faster than sound,and because of this,we see the flash of lighting before we hear the clap of thunder.There is a direct relationship between thunder and lightning;they are not separate phenomena. Thunder and lightning lasts only as long as is necessary to get all the electrical charges in the atmosphere back in balance. Put your display below 3.You are supposed to deal with language issues in the Lesson 9 students'handout before Lesson 9,and bring your previous Methodology writing to the L9 classroom. References: Dennett,B Dixon,S.2003.Key Features of Modern History [2nd Edition]. Melbourne:Oxford University Press. Kinnear,J.Martin,M.2004.Biology 1:preliminary course.Milton,Qld:Jacaranda Martin,J.R.,Rose,D.2008.Genre Relation,Mapping Culture.Equinox Publishing Ltd. Scott,L.Robinson,S.1993.Australian journey:environments and communities. Melbourne:Longman Cheshire 8/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 8 / 10 EAP Class Number: ______________ Name: ______________ Student ID: ______________ Text Types adopted: _____________________ Add procedural indicators / transitions, factor-consequence transitions, steps and text type labels in the passage below. Warm air rise in hot clouds and encounters cold air, charging the particles in the cloud making them both positive and negative charges, and this is called static electricity. When enough positive and negative charges occur, they build up too much energy and explode in a flash of light that we call lightening. This flash of light helps balance out the number of negative and positive charges in atmosphere. Sometimes the flash of light is movement within the cloud and sometimes it is lightening movement between the atmosphere and the ground. The movement between the atmosphere and the ground is the reason that tall objects on earth like trees are struck by lightning. Light travels faster than sound, and because of this, we see the flash of lighting before we hear the clap of thunder. There is a direct relationship between thunder and lightning; they are not separate phenomena. Thunder and lightning lasts only as long as is necessary to get all the electrical charges in the atmosphere back in balance. Put your display below: 3. You are supposed to deal with language issues in the Lesson 9 students’ handout before Lesson 9, and bring your previous Methodology writing to the L9 classroom. References: Dennett, B & Dixon, S. 2003. Key Features of Modern History [2nd Edition]. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. Kinnear, J. & Martin, M. 2004. Biology 1: preliminary course. Milton, Qld: Jacaranda Martin, J. R., & Rose, D. 2008. Genre Relation, Mapping Culture. Equinox Publishing Ltd. Scott, L. & Robinson, S. 1993. Australian journey: environments and communities. Melbourne: Longman Cheshire
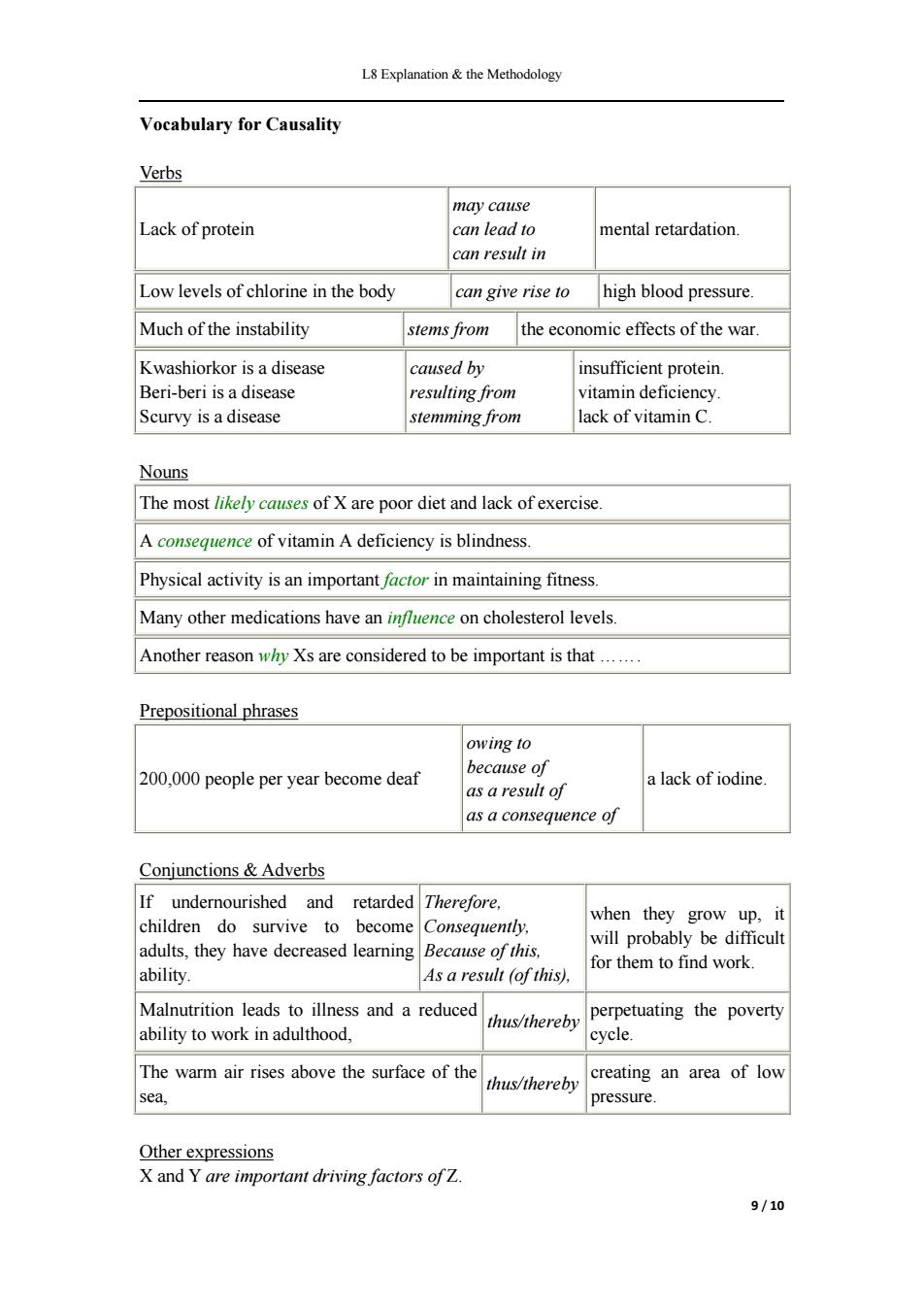
L8 Explanation&the Methodology Vocabulary for Causality Verbs may cause Lack of protein can lead to mental retardation. can result in Low levels of chlorine in the body can give rise to high blood pressure. Much of the instability stems from the economic effects of the war. Kwashiorkor is a disease caused by insufficient protein. Beri-beri is a disease resulting from vitamin deficiency. Scurvy is a disease stemming from lack of vitamin C. Nouns The most likely causes of X are poor diet and lack of exercise. A consequence of vitamin A deficiency is blindness. Physical activity is an important factor in maintaining fitness. Many other medications have an influence on cholesterol levels. Another reason why Xs are considered to be important is that....... Prepositional phrases owing to 200,000 people per year become deaf because of a lack of iodine. as a result of as a consequence of Conjunctions Adverbs If undernourished and retarded Therefore, children do survive to become when they grow up,it Consequently. will probably be difficult adults,they have decreased learning Because of this, for them to find work. ability. As a result (of this), Malnutrition leads to illness and a reduced thus/thereby perpetuating the poverty ability to work in adulthood, cycle. The warm air rises above the surface of the thus/thereby creating an area of low sea. pressure. Other expressions X and Y are important driving factors ofZ. 9/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 9 / 10 Vocabulary for Causality Verbs Lack of protein may cause can lead to can result in mental retardation. Low levels of chlorine in the body can give rise to high blood pressure. Much of the instability stems from the economic effects of the war. Kwashiorkor is a disease Beri-beri is a disease Scurvy is a disease caused by resulting from stemming from insufficient protein. vitamin deficiency. lack of vitamin C. Nouns The most likely causes of X are poor diet and lack of exercise. A consequence of vitamin A deficiency is blindness. Physical activity is an important factor in maintaining fitness. Many other medications have an influence on cholesterol levels. Another reason why Xs are considered to be important is that ……. Prepositional phrases 200,000 people per year become deaf owing to because of as a result of as a consequence of a lack of iodine. Conjunctions & Adverbs If undernourished and retarded children do survive to become adults, they have decreased learning ability. Therefore, Consequently, Because of this, As a result (of this), when they grow up, it will probably be difficult for them to find work. Malnutrition leads to illness and a reduced ability to work in adulthood, thus/thereby perpetuating the poverty cycle. The warm air rises above the surface of the sea, thus/thereby creating an area of low pressure. Other expressions X and Y are important driving factors of Z

L8 Explanation&the Methodology The mixing of X and Y exerts a powerful effect upon Z through...... This suggests a weak link may exist between X and Y. The human papilloma virus is linked to most cervical cancer. Stomach cancer in many cases may be associated with certain bacterial infections. A high consumption of seafood could be associated with infertility. 10/10
L8 Explanation & the Methodology 10 / 10 The mixing of X and Y exerts a powerful ef ect upon Z through …… This suggests a weak link may exist between X and Y. The human papilloma virus is linked to most cervical cancer. Stomach cancer in many cases may be associated with certain bacterial infections. A high consumption of seafood could be associated with infertility