
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY22ChapterAmino acids: metabolismof carbon skeletonsDepartmentof Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Amino acids: metabolism of carbon skeletons Chapter 22
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsofaminoacids>The catalolism of the carbon skeletons converges toform seven products: oxaloacetate, a-ketoglutarate pyruvate, fumarate, acetyl CoA, acetoacetyl CoA, andsuccinyl CoA.> These products enter the pathways of intermediarymetabolism , Resulting either in the synthesis of glucoseor lipid ,or in the production of energy through theiroxidation to CO2 and water by the citric acid cycle.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids ➢The catalolism of the carbon skeletons converges to form seven products: oxaloacetate, α-ketoglutarate , pyruvate, fumarate, acetyl CoA, acetoacetyl CoA, and succinyl CoA. ➢ These products enter the pathways of intermediary metabolism , Resulting either in the synthesis of glucose or lipid ,or in the production of energy through their oxidation to CO2 and water by the citric acid cycle
生BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY>Amino acids can be classified as essential ornonessential according to whether or not they can besynthesized in humans.>Amino acids can be classified as ketogenic orglucogenic according to the nature of their metabolicend products.Department ofBiochemistry and Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ➢Amino acids can be classified as essential or nonessential according to whether or not they can be synthesized in humans. ➢Amino acids can be classified as ketogenic or glucogenic according to the nature of their metabolic end products
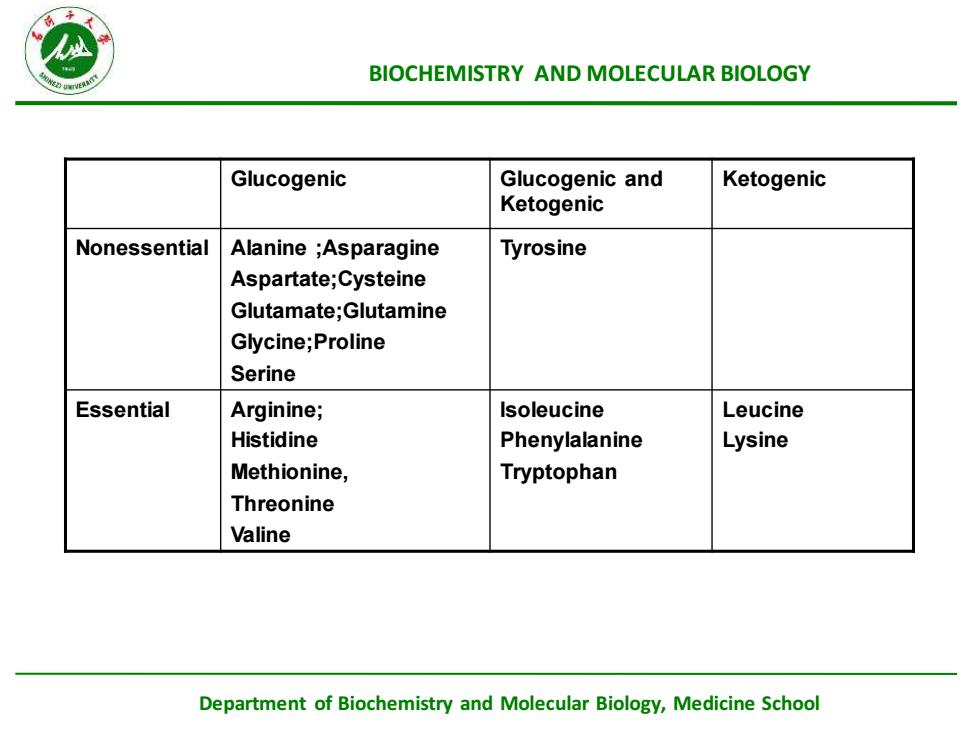
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYGlucogenicGlucogenicandKetogenicKetogenicTyrosineNonessentialAlanine;AsparagineAspartate;CysteineGlutamate;GlutamineGlycine;ProlineSerineEssentialArginine;IsoleucineLeucineHistidinePhenylalanineLysineMethionine,TryptophanThreonineValineDepartment ofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchoo
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Glucogenic Glucogenic and Ketogenic Ketogenic Nonessential Alanine ;Asparagine Aspartate;Cysteine Glutamate;Glutamine Glycine;Proline Serine Tyrosine Essential Arginine; Histidine Methionine, Threonine Valine Isoleucine Phenylalanine Tryptophan Leucine Lysine
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYEssential amino acids: these amino acids cannotbe synthesized in humans (or cannot be produced insufficient amounts), and therefore must obtained inthe diet in order for normal protein synthesis to occur.Department ofBiochemistry and Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Essential amino acids: these amino acids cannot be synthesized in humans (or cannot be produced in sufficient amounts), and therefore must obtained in the diet in order for normal protein synthesis to occur
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYEssential amino acids: Includingphenylalaninevaline,tryptophan,threonine, isoleucine, methioninehistidine, arginine, leucine, lysine.PVTTIMHALLDepartmentofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Essential amino acids: Including phenylalanine , valine, tryptophan , threonine, isoleucine, methionine, histidine, arginine, leucine, lysine. PVT TIM HALL
Essential amino acidsBeans(richGrains Crich ininlysine)methionine)MilkPastaefagioli (pasta andbeans,ahealthyItaliansouptiff13.mov
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsof aminoacidsA. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acidsKetogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yieldseither acetoacetate or one of its precursors, acetylCoA or acetoacetyl CoA(ketone bodies), are termedketogenic.Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenicamino acids found in proteinDepartment ofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY A. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids Ketogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yields either acetoacetate or one of its precursors, acetyl CoA or acetoacetyl CoA(ketone bodies), are termed ketogenic. Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids found in protein
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsof aminoacidsA.Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acidsGlucogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yieldspyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acidcycle are termed glucogenic or glycogenic.forTheseintermediatessubstratesaregluconeogenesis and therefore can give rise to the netformation of glycogen in liver and muscle.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY A. Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids Glucogenic: amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle are termed glucogenic or glycogenic. These intermediates are substrates for gluconeogenesis and therefore can give rise to the net formation of glycogen in liver and muscle
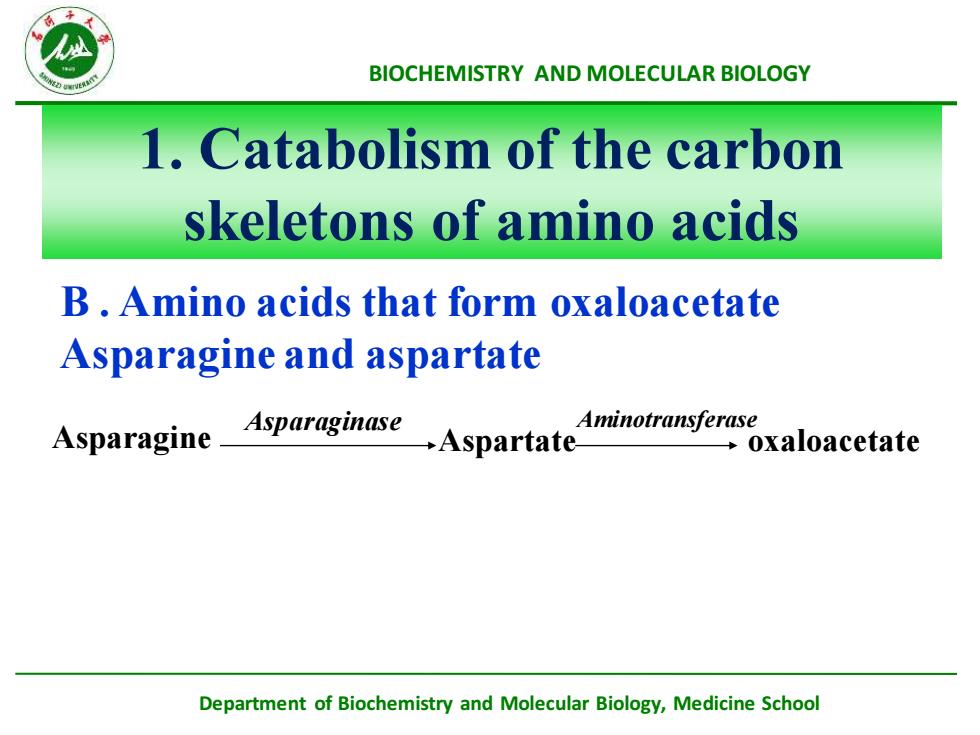
ABIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYl. Catabolism of the carbonskeletonsofaminoacidsB.Amino acids that form oxaloacetateAsparagineandaspartateAminotransferase Asparaginase Aspartate-AsparagineoxaloacetateDepartment ofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY B . Amino acids that form oxaloacetate Asparagine and aspartate 1. Catabolism of the carbon skeletons of amino acids Asparagine Aspartate oxaloacetate Asparaginase Aminotransferase