
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYChapter 1AminoAcidsDepartment of Biochemistryand Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Chapter 1 Amino Acids
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYOutline*overview*structure of amino acid*acid/base properties of amino acid*other applications ofthehenderson-hasselbalchequationDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Outline *overview *structure of amino acid *acid/base properties of amino acid *other applications of the henderson-hasselbalch equation
山BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overview Proteins are the most abundant and functionallydiverse molecules in living systems> Virtually every life process depends on this classof molecules.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ➢ Proteins are the most abundant and functionally diverse molecules in living systems. ➢ Virtually every life process depends on this class of molecules. 1. overview

北BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overviewFor example:> Enzymes and polypeptide hormones direct and regulatemetabolism in the body> Contractile proteins in muscle permit movement> In bone, the protein collagen forms a framework for thedeposition of calcium phosphate crystals, acting like thesteel cables in reinforced concreteDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. overview For example: ➢ Enzymes and polypeptide hormones direct and regulate metabolism in the body. ➢ Contractile proteins in muscle permit movement. ➢ In bone, the protein collagen forms a framework for the deposition of calcium phosphate crystals, acting like the steel cables in reinforced concrete
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overviewFor example:>In the bloodstream, proteins such as hemoglobin andplasma albumin shuttle molecules essential to life.> Immunoglobulins destroy infectious bacteria and virusesDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. overview For example: ➢In the bloodstream, proteins such as hemoglobin and plasma albumin shuttle molecules essential to life. ➢Immunoglobulins destroy infectious bacteria and viruses
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overview Proteins display an incredible diversity of functions> All protein share the common structural featureof being linear polymers of amino acidDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. overview ➢ Proteins display an incredible diversity of functions. ➢ All protein share the common structural feature ➢ of being linear polymers of amino acid

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overview This chapter describes the properties of amino acids> Next chapter explores how these simple buildingblocks are joined to form proteins that have uniquethree-dimensional structures, making them capable ofperforming specific biologic functionDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. overview ➢ This chapter describes the properties of amino acids. ➢ Next chapter explores how these simple building blocks are joined to form proteins that have unique three-dimensional structures, making them capable of performing specific biologic function

2.StructureofaminoacidAlthough morethan 3o0 differentamino acids have beendescribedin nature,only20 are commonlyfoundasconstituents of mammalian protein.All these amino acids areLa-aminoacids(Exceptglycine)Carboxyl groupCOOHAmino groupHRSide chaina-carbonatom
2 . Structure of amino acid • Although more than 300 different amino acids have been described in nature, only 20 are commonly found as constituents of mammalian protein. All these amino acids are L—α—amino acids(Except glycine). H2N C H COOH R Side chain α-carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group
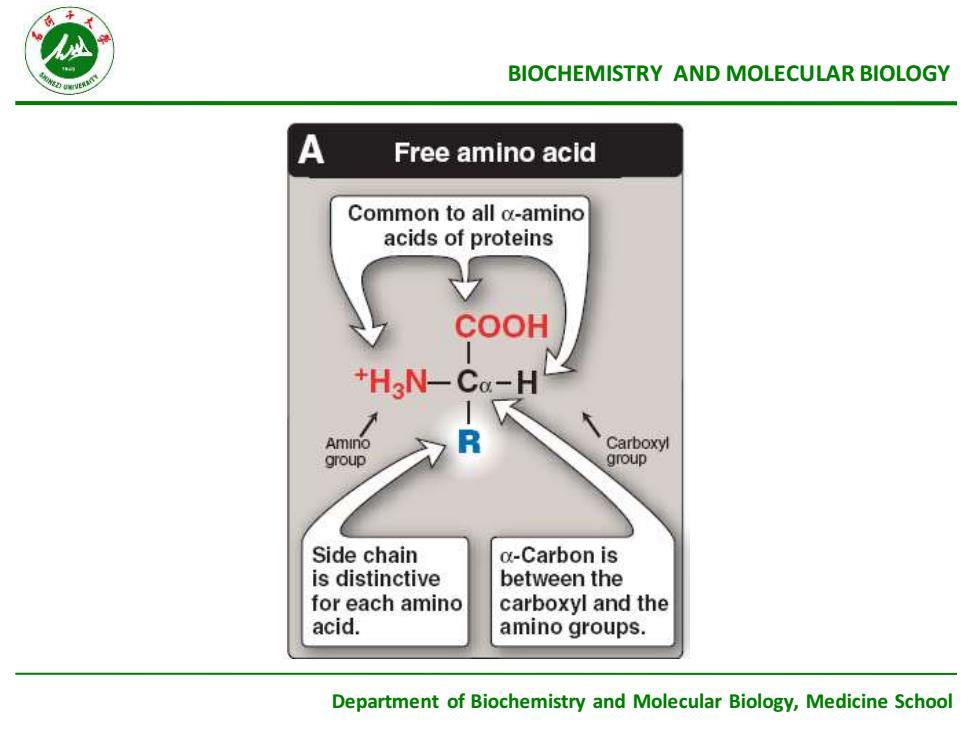
1BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYAFreeaminoacidCommontoallα-aminoacidsofproteinsCOOH+HNCa-H-7RCarboxylAminogroupgroupSide chainα-Carbonisis distinctivebetweentheforeachaminocarboxylandtheacid.aminogroups.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
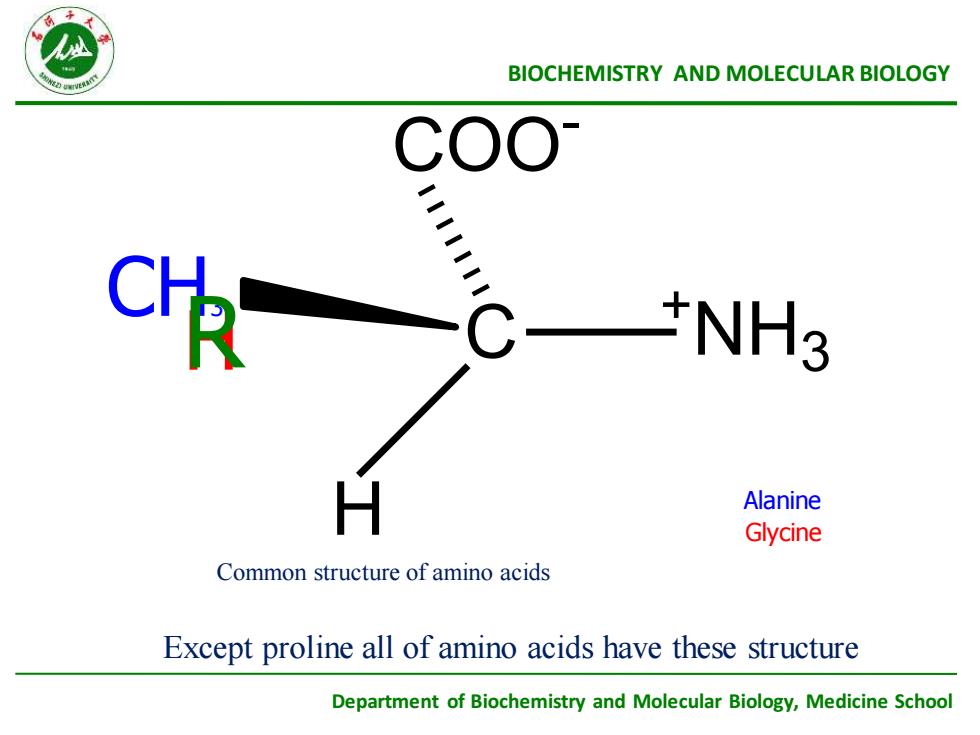
ABIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYCOOC+NH3CHAlanineGlycineCommonstructureofaminoacidsExcept proline all of amino acids have these structureDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY H Glycine CH3 Alanine Common structure of amino acids R C + NH3 COO - H Except proline all of amino acids have these structure