
“物联网技术导论”课程专题报告 专题1:RFID的识别与估算机制 谢磊教授 南京大学计算机科学与技术系
专题1:RFID的识别与估算机制 谢磊 教授 南京大学计算机科学与技术系 “物联网技术导论”课程专题报告

主要内容: 一、RFD的基本通信原理 二、基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制 三、RFID标签估算机制(Estimation) 四、开放性问题(Open Problem) 五、参考文献
二、基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制 主要内容: 五、参考文献 三、RFID标签估算机制(Estimation) 一、RFID的基本通信原理 四、开放性问题(Open Problem)
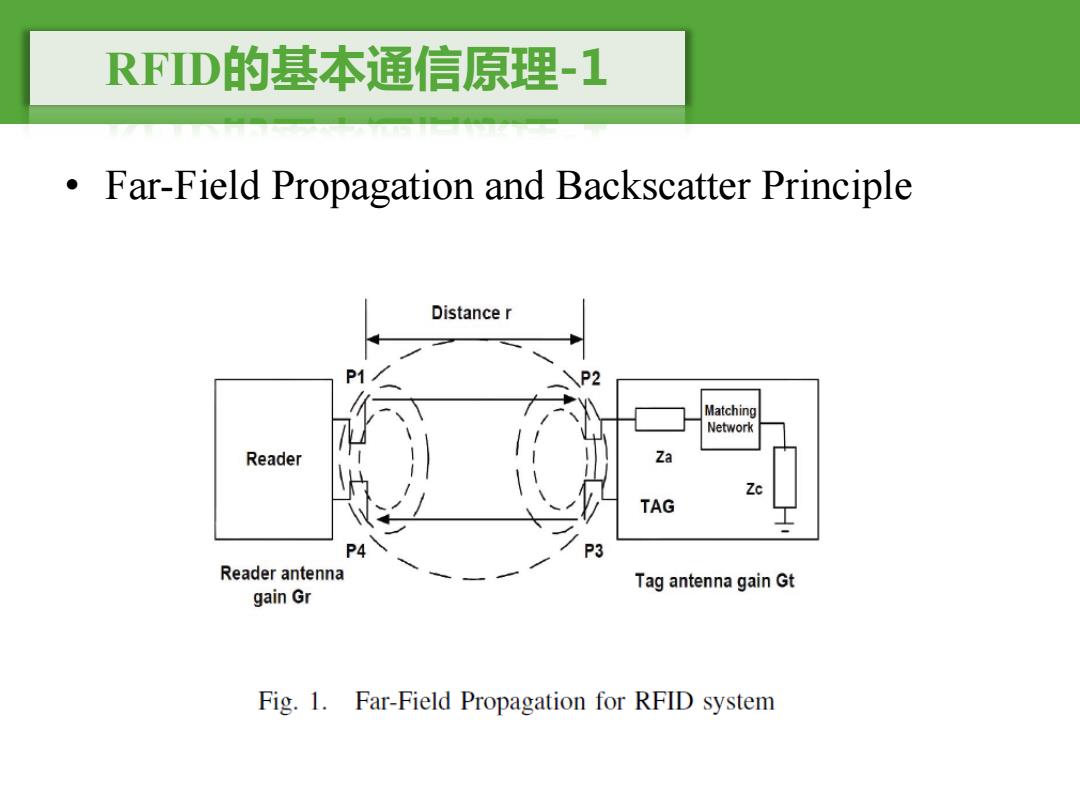
RFD的基本通信原理-1 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle Distance r o" Matching Network Reader Za TAG P4 P3 Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-1 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle
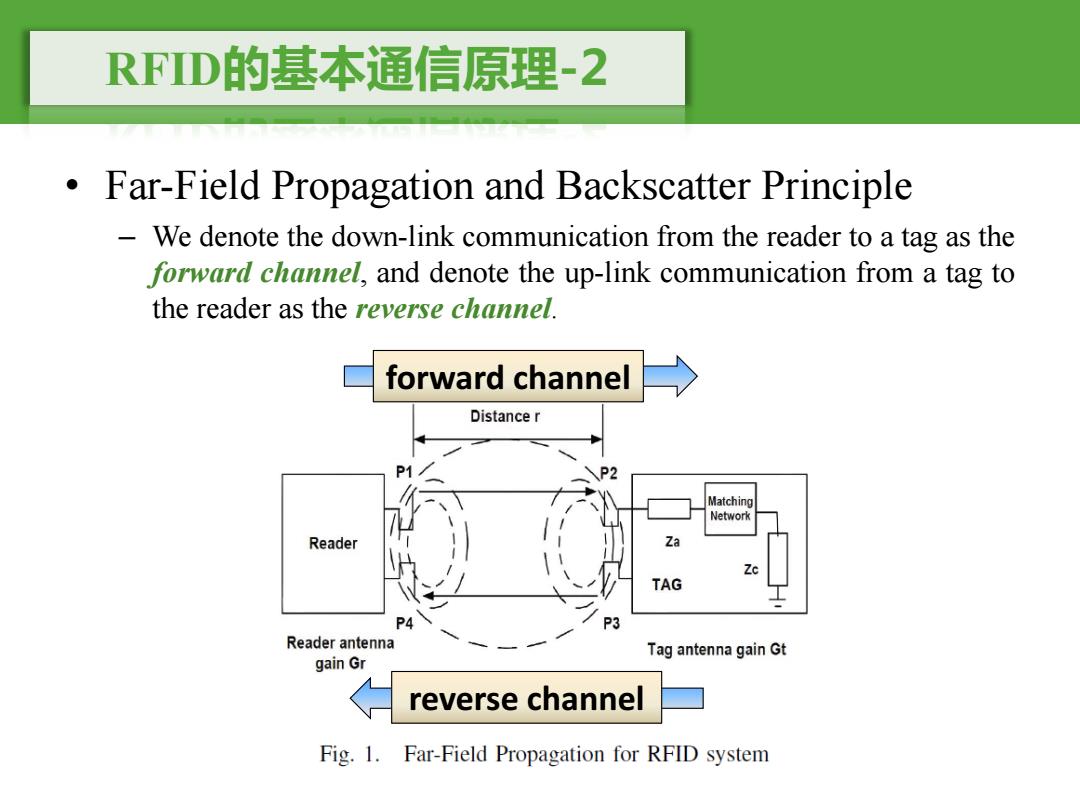
RFD的基本通信原理-2 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle We denote the down-link communication from the reader to a tag as the forward channel,and denote the up-link communication from a tag to the reader as the reverse channel. forward channel Distance r P2 Matching Network Reader Za TAG Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr reverse channel Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-2 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle – We denote the down-link communication from the reader to a tag as the forward channel, and denote the up-link communication from a tag to the reader as the reverse channel. forward channel reverse channel
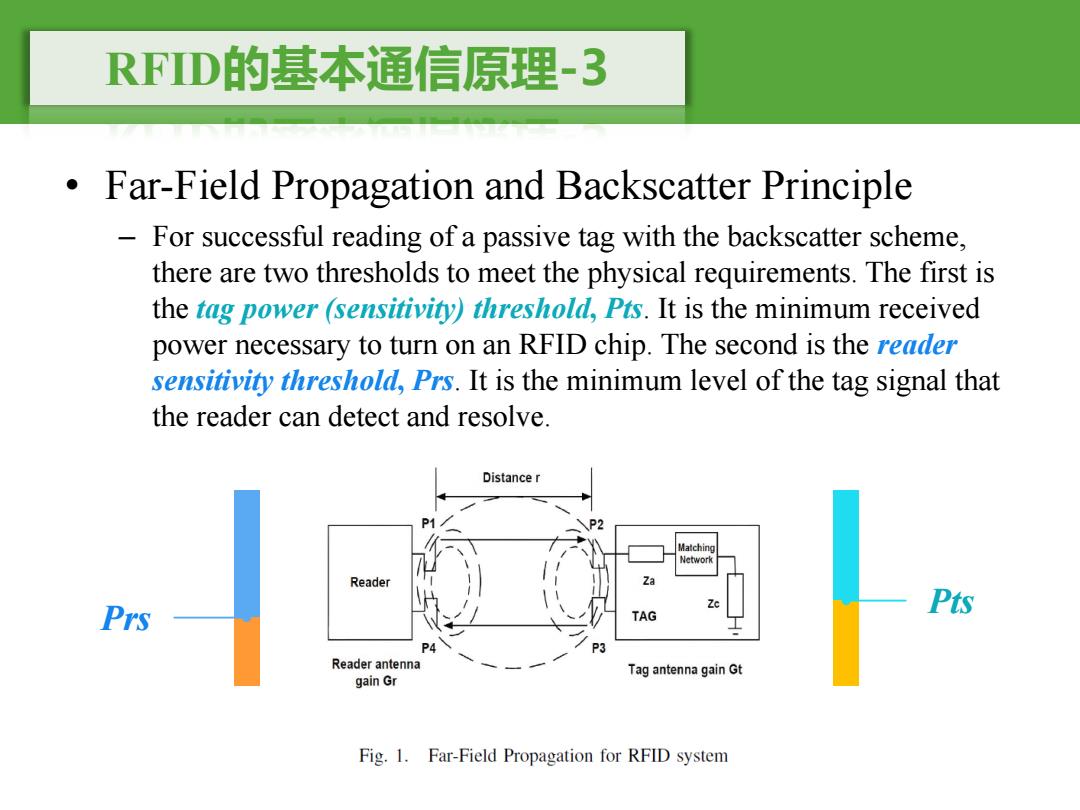
RFD的基本通信原理-3 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle For successful reading of a passive tag with the backscatter scheme, there are two thresholds to meet the physical requirements.The first is the tag power (sensitivity)threshold,Pts.It is the minimum received power necessary to turn on an RFID chip.The second is the reader sensitivity threshold,Prs.It is the minimum level of the tag signal that the reader can detect and resolve. Distance r Matching Network Reader Za 9 Prs Pt灯 TAG P4 Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-3 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle – For successful reading of a passive tag with the backscatter scheme, there are two thresholds to meet the physical requirements. The first is the tag power (sensitivity) threshold, Pts. It is the minimum received power necessary to turn on an RFID chip. The second is the reader sensitivity threshold, Prs. It is the minimum level of the tag signal that the reader can detect and resolve. Pts Prs
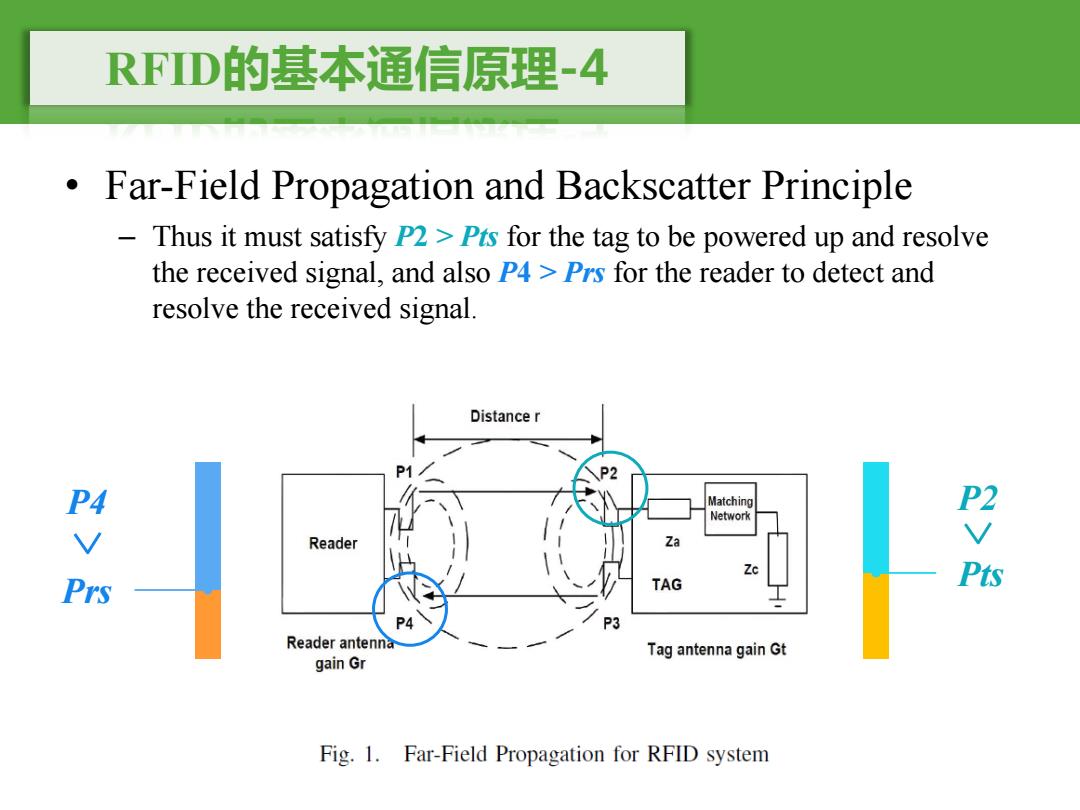
RFD的基本通信原理-4 Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle Thus it must satisfy P2>Pts for the tag to be powered up and resolve the received signal,and also P4 Prs for the reader to detect and resolve the received signal. Distance r P2 Matching Network Reader Za 四V胶 TAG Reader antenna Tag antenna gain Gt gain Gr Fig.1.Far-Field Propagation for RFID system
RFID的基本通信原理-4 • Far-Field Propagation and Backscatter Principle – Thus it must satisfy P2 > Pts for the tag to be powered up and resolve the received signal, and also P4 > Prs for the reader to detect and resolve the received signal. Pts Prs P4 P2

基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-1 Tag inventory and access Interrogator cw Select CW Query cw Ack Cw QueryRep CW NAK Cw Tag PC+EPC RN16 +CRC16 Interrogator cw Query Cw QueryRep CW QueryRep Cw QueryRep CW INo ReplyI Collision Detected Single Reply Tag RN16 RN16 Fig.2.C1G2 protocol
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-1 • Tag inventory and access

基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-2 Tag inventory and access The MAC protocol for the C1G2 system is based on Slotted ALOHA, where each frame has a number of slots and each active tag will reply in a randomly selected slot per frame. When a reader(interrogator)wishes to read a set of tags,it first powers up and transmits a continuous wave(CW)to energize the tags.It then initiates a series of frames,varying the number of slots in each frame to best accommodate the number of tags.After all tags are read,the reader powers down.We refer to an individual frame as a Query Round,and the series of Query Rounds between power down periods as a Query Cycle. Query Cycle Query Round Query Round cee0。 Query Round
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-2 • Tag inventory and access – The MAC protocol for the C1G2 system is based on Slotted ALOHA, where each frame has a number of slots and each active tag will reply in a randomly selected slot per frame. – When a reader (interrogator) wishes to read a set of tags, it first powers up and transmits a continuous wave (CW) to energize the tags. It then initiates a series of frames, varying the number of slots in each frame to best accommodate the number of tags. After all tags are read, the reader powers down. We refer to an individual frame as a Query Round, and the series of Query Rounds between power down periods as a Query Cycle. Query Round Query Round …… Query Round Query Cycle
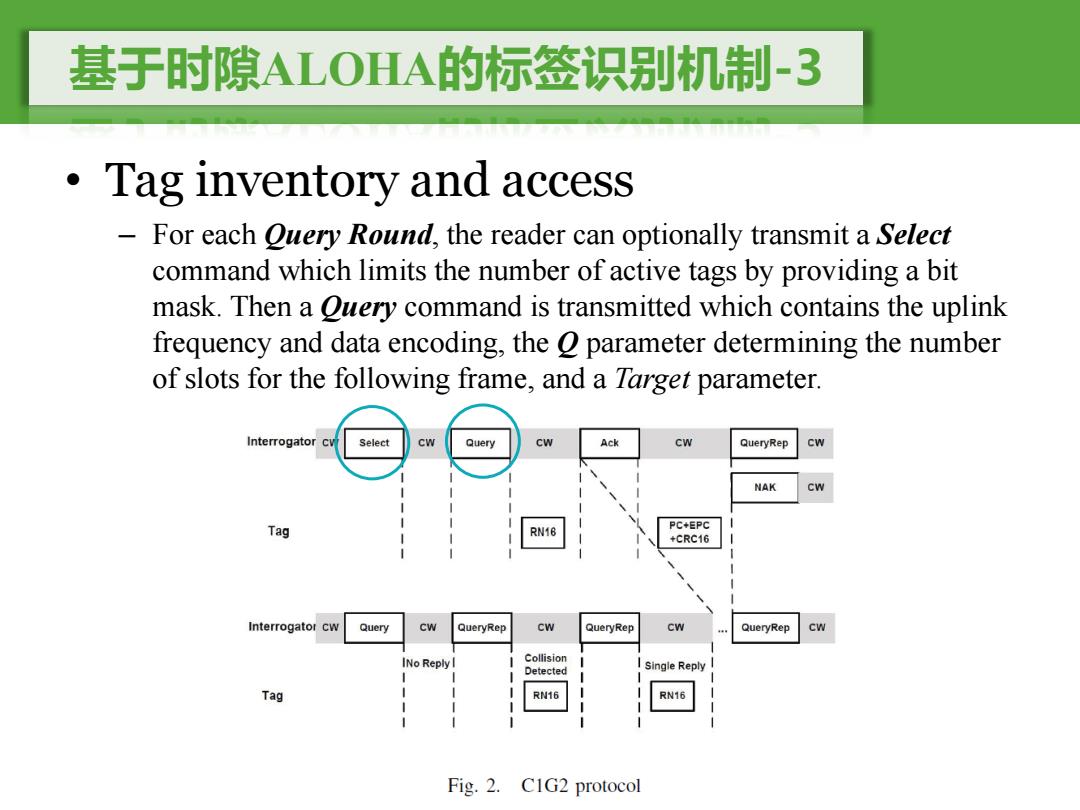
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-3 Tag inventory and access - For each Query Round,the reader can optionally transmit a Select command which limits the number of active tags by providing a bit mask.Then a Ouery command is transmitted which contains the uplink frequency and data encoding,the o parameter determining the number of slots for the following frame,and a Target parameter. Interrogator Select cw Query cw Ack Cw QueryRep Cw NAK Cw Tag RN16 PC+EPC +CRC16 Interrogator Query CW QueryRep Cw QueryRep Cw QueryRep INo Reply I Collision Detected Single Reply Tag RN16 Fig.2.C1G2 protocol
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-3 • Tag inventory and access – For each Query Round, the reader can optionally transmit a Select command which limits the number of active tags by providing a bit mask. Then a Query command is transmitted which contains the uplink frequency and data encoding, the Q parameter determining the number of slots for the following frame, and a Target parameter
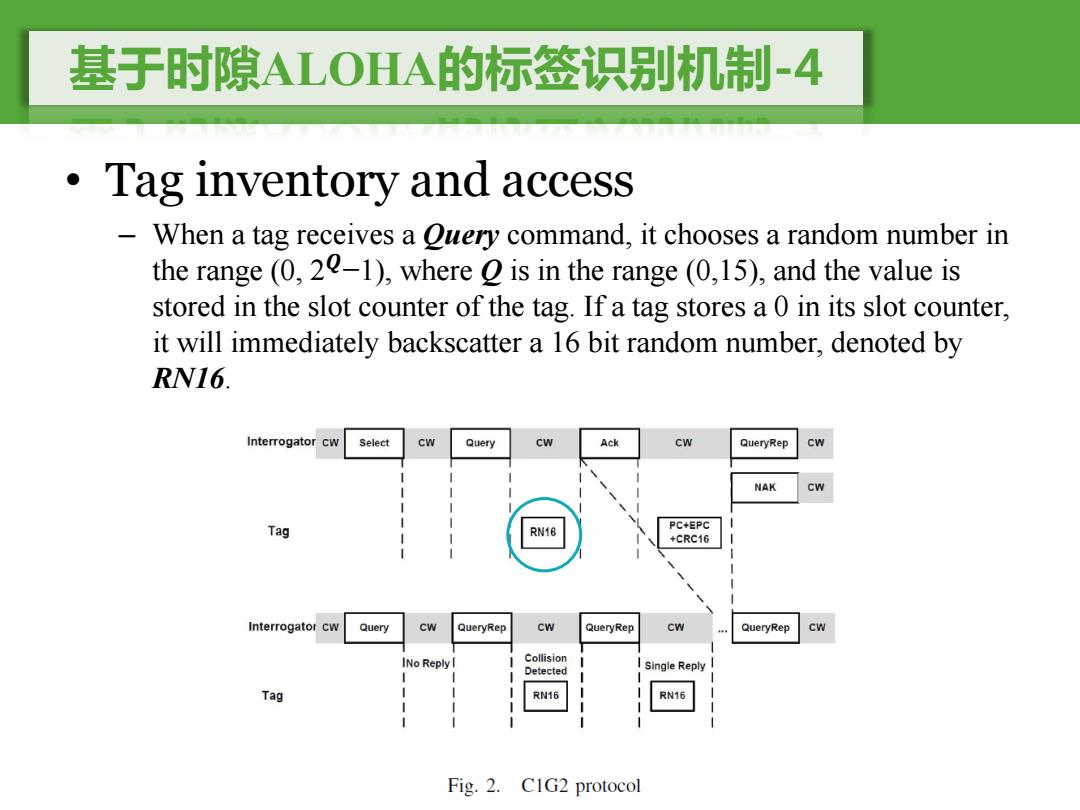
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-4 Tag inventory and access 一 When a tag receives a Ouery command,it chooses a random number in the range (0,20-1),where is in the range (0,15),and the value is stored in the slot counter of the tag.If a tag stores a 0 in its slot counter, it will immediately backscatter a 16 bit random number,denoted by RN16. Interrogator Cw Select Cw Query cw Ack Cw QueryRep Cw NAK CW Tag RN16 PC+EPC +CRC16 Interrogator Cw Query CW QueryRep Cw QueryRep Cw QueryRep INo Reply I Collision Detected Single Reply Tag RN16 Fig.2.C1G2 protocol
基于时隙ALOHA的标签识别机制-4 • Tag inventory and access – When a tag receives a Query command, it chooses a random number in the range (0, 2�−1), where Q is in the range (0,15), and the value is stored in the slot counter of the tag. If a tag stores a 0 in its slot counter, it will immediately backscatter a 16 bit random number, denoted by RN16