
Nature and nature's law 自然和自然规律 lay hid in night: 隐藏在黑夜之中, God said,let Newton be!上帝说让牛顿降生吧”, And all was light. 切就有了光明; 上海交大董占海
上海交大 董占海 1 Nature and nature's law lay hid in night: God said, let Newton be! And all was light. *

恩格斯说: “牛顿由于发现了万有引力定律而创立了天文 学,由于进行光的分解而创立了科学的光学,由 于创立了二项式定理和无穷级数理论而创立了科 学的数学,由于认识了力学的本性而创立了科学 的力学。”牛顿在自然科学领域里作了奠基的 贡献,堪称科学巨匠。 牛顿一生很谦逊,他临终前说:“如果我的 见识,真有超过笛卡尔的地方,那也是因为我是 站在前辈伟人的肩上,才能望得远啊!”。 2 上海交大董占海
上海交大 董占海 2 恩格斯说: “牛顿由于发现了万有引力定律而创立了天文 学,由于进行光的分解而创立了科学的光学,由 于创立了二项式定理和无穷级数理论而创立了科 学的数学,由于认识了力学的本性而创立了科学 的力学。” 牛顿在自然科学领域里作了奠基的 贡献,堪称科学巨匠。 牛顿一生很谦逊,他临终前说:“如果我的 见识,真有超过笛卡尔的地方,那也是因为我是 站在前辈伟人的肩上,才能望得远啊!

第二章 质点动力学
上海交大 董占海 3 第二章 质点动力学

Outline ·§2.1 Newton's Laws of Motion -Force -Newton's Laws -Application of Newton's Laws ·§2.2 Galilean Principle of Relativity& Noninertial Reference Frames 4 上海交大董占海
上海交大 董占海 4 Outline •§2.1 Newton’s Laws of Motion –Force –Newton’s Laws –Application of Newton’s Laws •§ 2.2 Galilean Principle of Relativity & Noninertial Reference Frames

一、FORCE 5 上海交大董占海
上海交大 董占海 5 一、FORCE
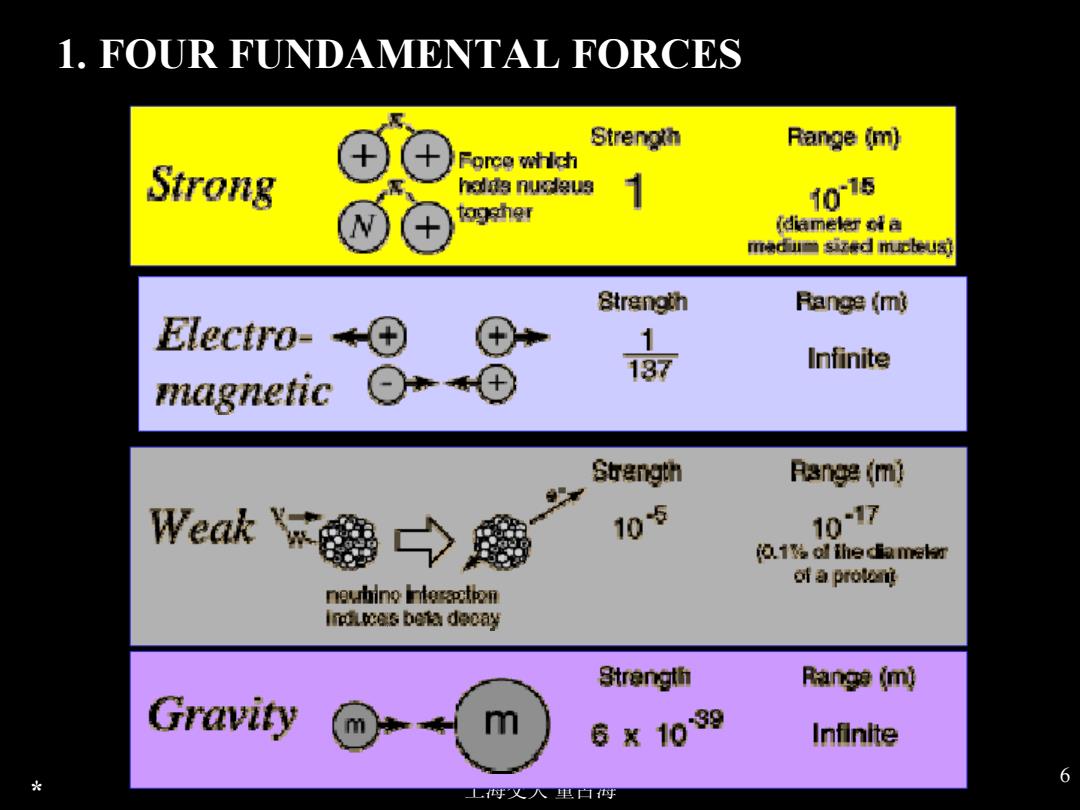
1.FOUR FUNDAMENTAL FORCES Strength Range (m) Force which Strong h岛好s 1 9h图 107s diamele数da m晚d国d击U间 8trangth Range (mi Electro-H⊕ 1 137 Infinite magnetic Strangth Range (m) Wek' 105 10-7 设.1酸ol thed重amr 时protont neurhino interapctoon Induces bota deony Strength Range (mj Gravity m 8器1099 Infinite 光 6
上海交大 董占海 6 * 1. FOUR FUNDAMENTAL FORCES
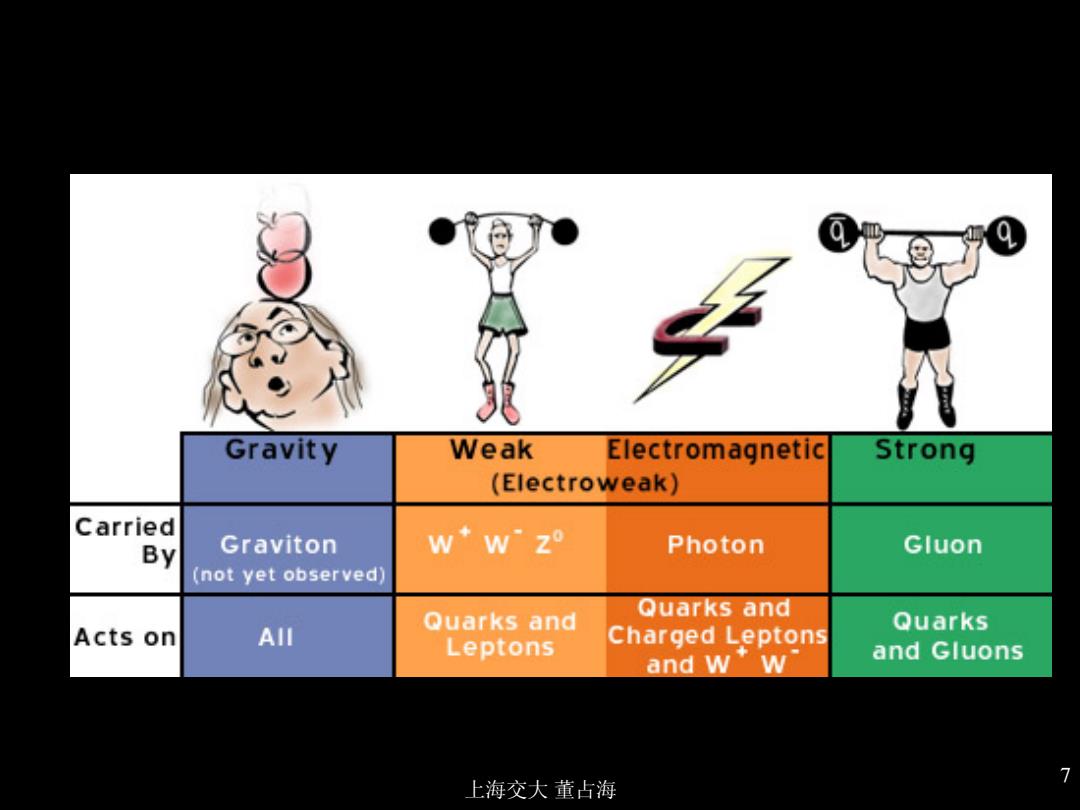
Gravity Weak Electromagnetic Strong (Electroweak) Carried By Graviton w◆w°z Photon Gluon (not yet observed) Quarks and AIl Quarks and Charged Leptons Quarks Acts on Leptons and wW and Gluons 7 上海交大董占海
上海交大 董占海 7
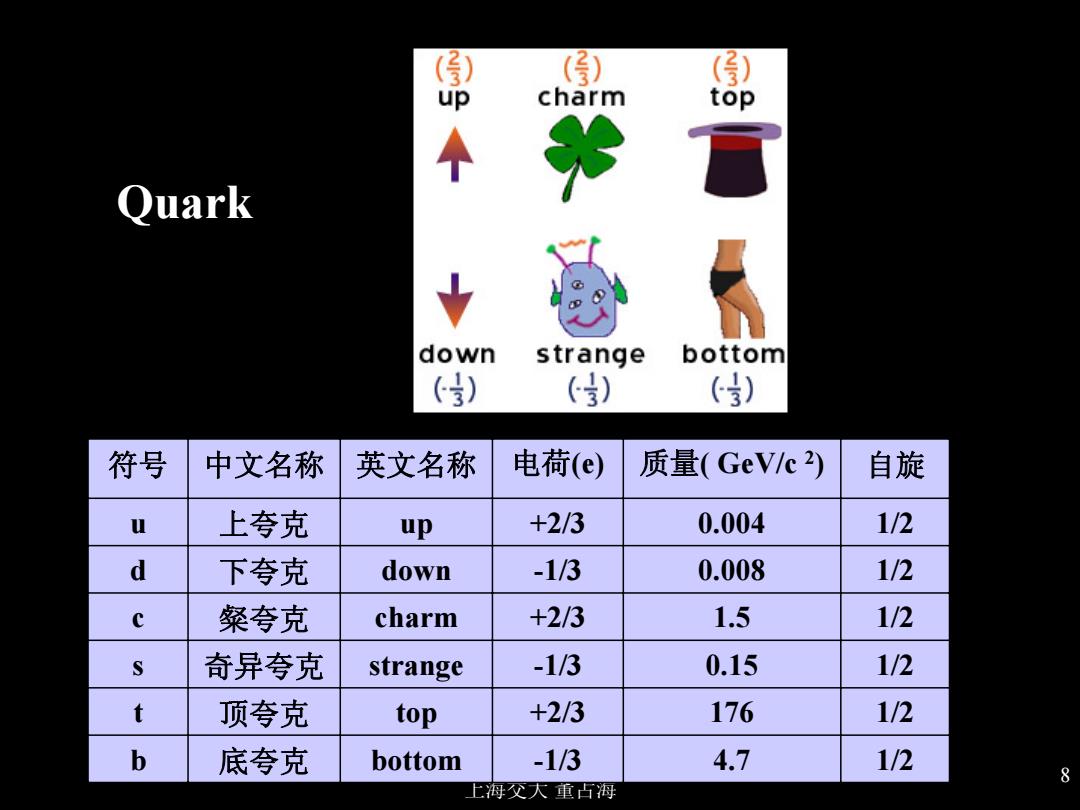
) () () up charm top 个 Quark down strange bottom ) ) () 符号 中文名称 英文名称 电荷(e) 质量(GeV/c) 自旋 u 上夸克 up +2/3 0.004 1/2 d 下夸克 down -1/3 0.008 1/2 c 粲夸克 charm +2/3 1.5 1/2 奇异夸克 strange -1/3 0.15 1/2 t 顶夸克 top +2/3 176 1/2 b 底夸克 bottom -1/3 4.7 1/2 8 上海父大重占海
上海交大 董占海 8 符号 中文名称 英文名称 电荷(e) 质量( GeV/c 2) 自旋 u 上夸克 up +2/3 0.004 1/2 d 下夸克 down -1/3 0.008 1/2 c 粲夸克 charm +2/3 1.5 1/2 s 奇异夸克 strange -1/3 0.15 1/2 t 顶夸克 top +2/3 176 1/2 b 底夸克 bottom -1/3 4.7 1/2 Quark

The Standard Model 6 quarks (those little The Standard Model 4 fellows in the nucleus) Fermions Bosons and their antiparticles C t Quarks up charm 6 leptons (of which the d b down electron is an example) Ve W electron muon tau W boson ers and their antiparticles eptons poutnno cutnno e T g 4 force carrier particles electron muon tau (of which the photon is Higgs" boson an example) Source:AAAS "Yet to be confirmed All known matter is composed of composites of quarks and leptons which interact by exchanging force carriers. 9 上海交大董占海
上海交大 董占海 9 The Standard Model • 6 quarks (those little fellows in the nucleus) and their antiparticles. • 6 leptons (of which the electron is an example) and their antiparticles • 4 force carrier particles (of which the photon is an example) • All known matter is composed of composites of quarks and leptons which interact by exchanging force carriers
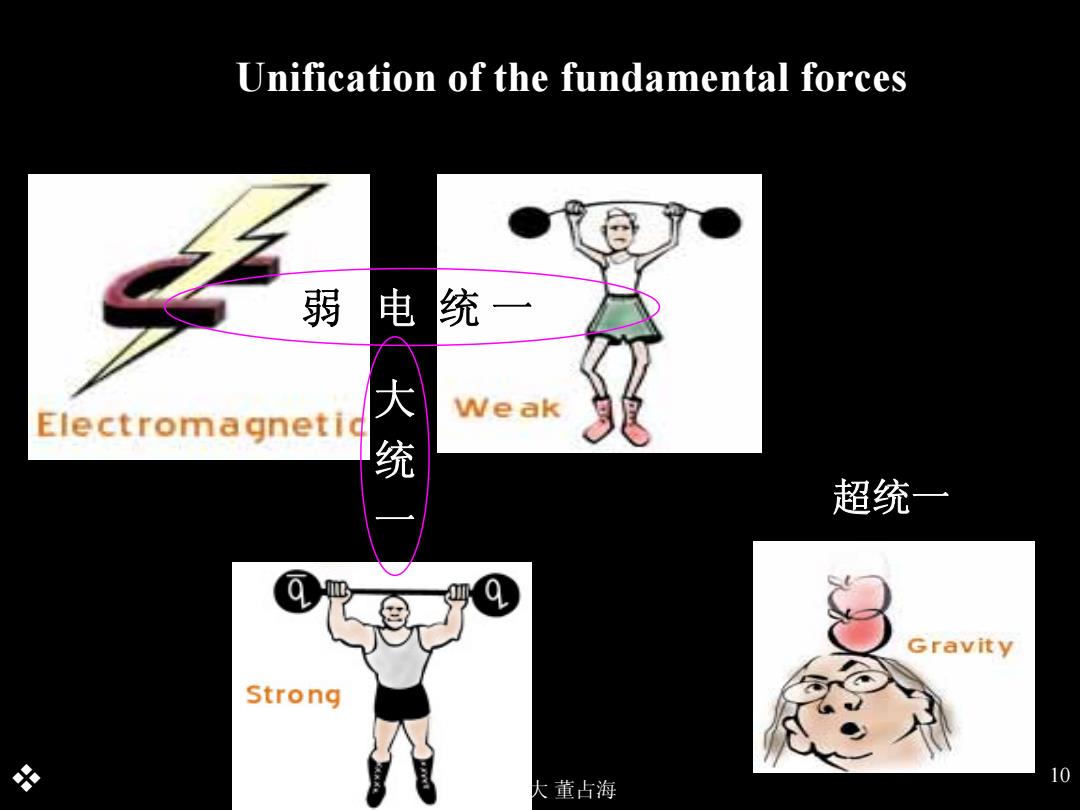
Unification of the fundamental forces 弱电统 一 Electromagnetid 大 Weak 超统一 Gravity Strong 出 10 大董占海
上海交大 董占海 10 超统一 弱 电 统 一 大 统 一 Unification of the fundamental forces