
Lecture 14 Antibody-Antigen Reactions
Lecture 14 Antibody-Antigen Reactions
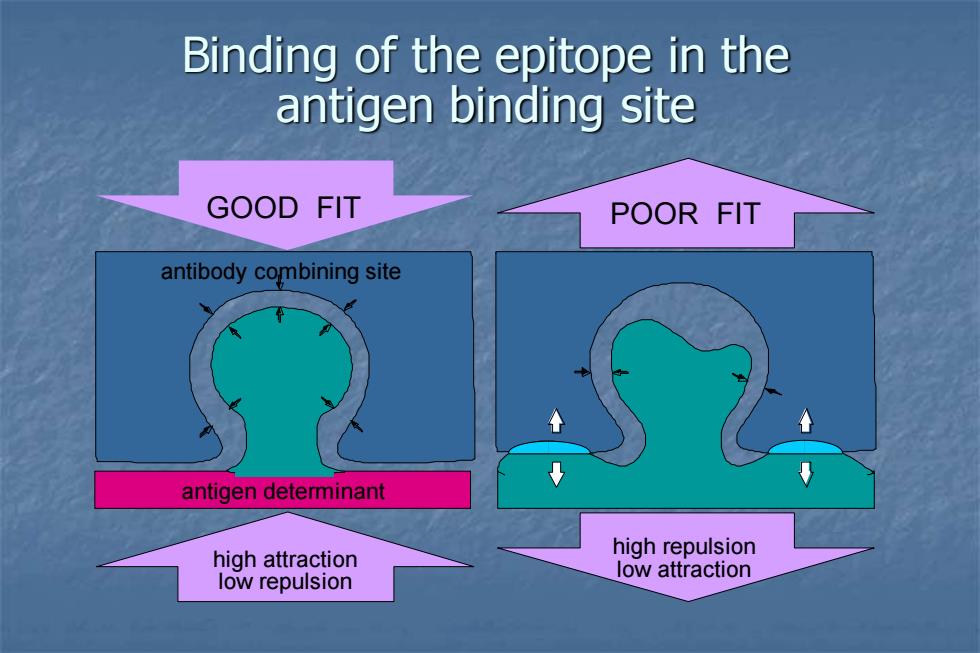
Binding of the epitope in the antigen binding site GOOD FIT POOR FIT antibody combining site antigen determinant high attraction high repulsion low attraction low repulsion
Binding of the epitope in the antigen binding site GOOD FIT POOR FIT antibody combining site antigen determinant high attraction low repulsion high repulsion low attraction

Antibody Avidity Multiple interactions between antigen binding sites and epitopes Greater than additive Similar to VelcroTM More relevant to biologic systems than affinity
Antibody Avidity ◼ Multiple interactions between antigen binding sites and epitopes ◼ Greater than additive ◼ Similar to Velcro™ ◼ More relevant to biologic systems than affinity
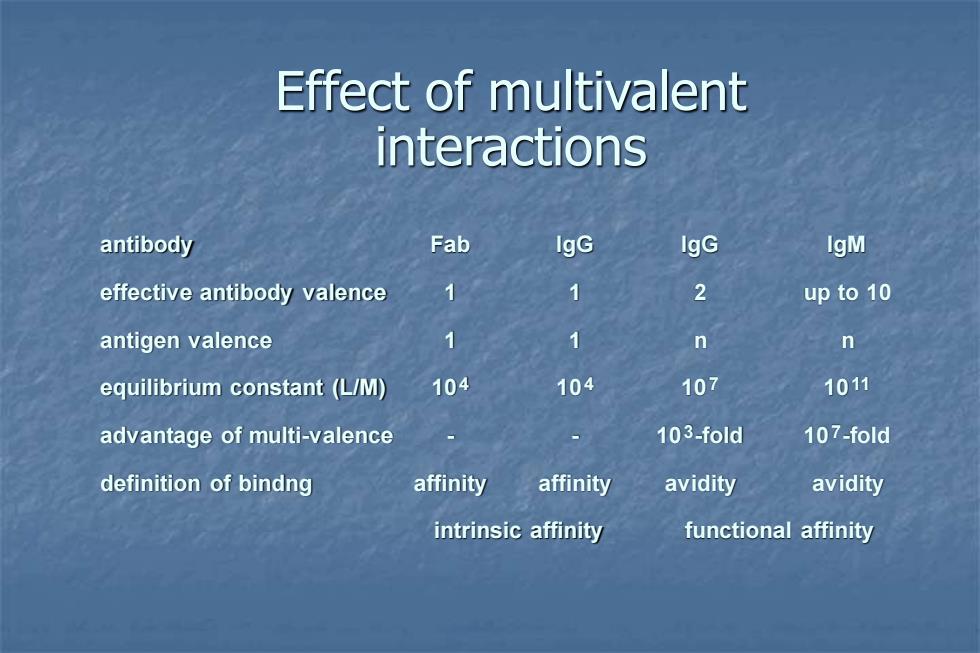
Effect of multivalent interactions antibody Fab IgG IgG IgM effective antibody valence 1 1 2 up to 10 antigen valence 1 1 n n equilibrium constant(L/M) 104 104 107 1011 advantage of multi-valence 103-fold 107-fold definition of bindng affinity affinity avidity avidity intrinsic affinity functional affinity
Effect of multivalent interactions antibody Fab IgG IgG IgM effective antibody valence 1 1 2 up to 10 antigen valence 1 1 n n equilibrium constant (L/M) 104 104 107 1011 advantage of multi-valence - - 103-fold 107-fold definition of bindng affinity affinity avidity avidity intrinsic affinity functional affinity

Biological Consequences of Antibody Affinity/Avidity Neutralization of toxins Complement activation Immune elimination of antigen Virus neutralization More intense immune complex disease in animals higher levels of circulating antigen-antibody complexes more intense localization of immune complexes on basement membranes. more severe impairment of organ function
Biological Consequences of Antibody Affinity/Avidity ◼ Neutralization of toxins ◼ Complement activation ◼ Immune elimination of antigen ◼ Virus neutralization ◼ More intense immune complex disease in animals ◼ higher levels of circulating antigen-antibody complexes ◼ more intense localization of immune complexes on basement membranes. ◼ more severe impairment of organ function
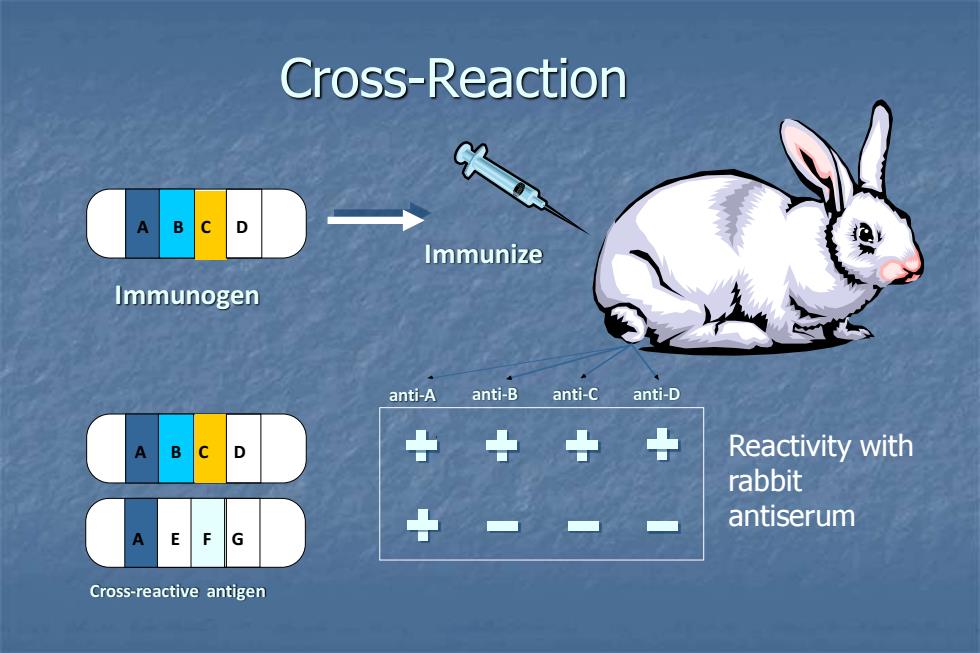
Cross-Reaction D Immunize Immunogen anti-A anti-B anti-C anti-D Reactivity with rabbit antiserum E F G Cross-reactive antigen
Cross-Reaction A B C D anti-A anti-B anti-C anti-D Immunize Immunogen Cross-reactive antigen A E F G A B C D Reactivity with rabbit antiserum
Primary Interactions Between Antigen and Antibody Determined by the interaction between epitopes and antigen-binding sites Independent of biochemical and biologic phenomena that may follow Depend only on the quantity and quality (affinity/avidity)of antibodies The basis for ELISA,RIA,IFA assays
Primary Interactions Between Antigen and Antibody ◼ Determined by the interaction between epitopes and antigen-binding sites ◼ Independent of biochemical and biologic phenomena that may follow ◼ Depend only on the quantity and quality (affinity/avidity) of antibodies ◼ The basis for ELISA, RIA, IFA assays
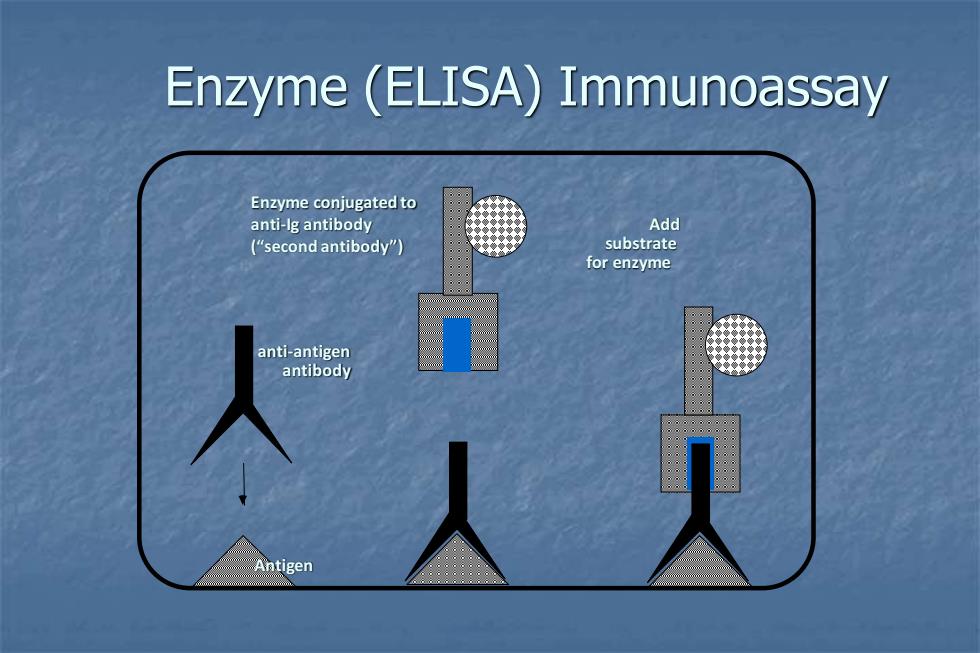
Enzyme (ELISA)Immunoassay Enzyme conjugated to anti-lg antibody Add ("second antibody") substrate for enzyme anti-antigen antibody Antigen
Enzyme (ELISA) Immunoassay Antigen anti-antigen antibody Enzyme conjugated to anti-Ig antibody (“second antibody”) Add substrate for enzyme
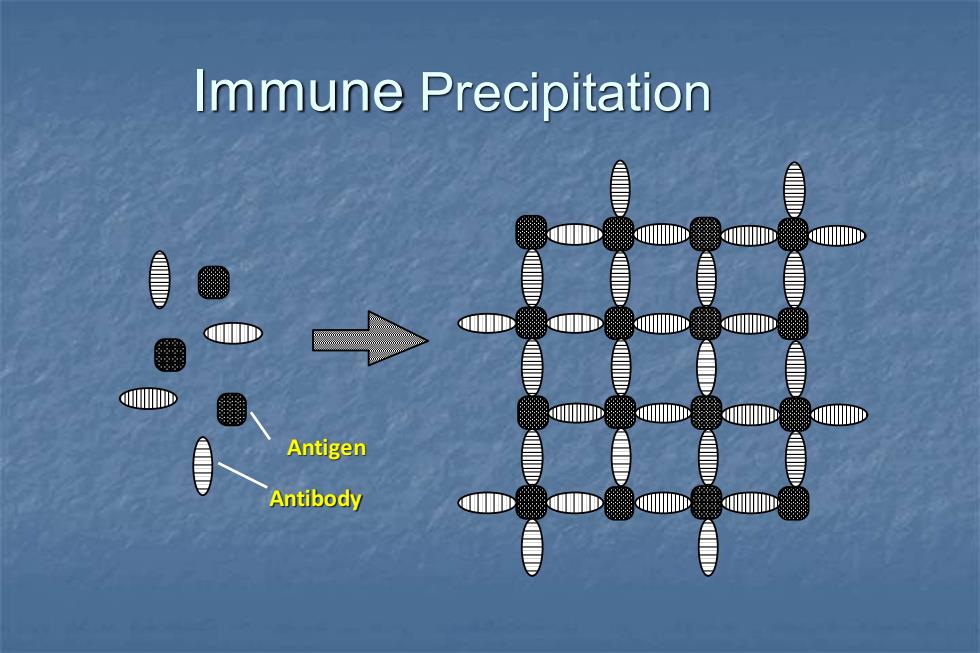
Immune Precipitation a o 刻I,个 a > I D Antigen Antibody D
Immune Precipitation Antigen Antibody

Radial Immunodiffusion Ab-containing gel Precipitin oo⊙⊙】 ring Ag/8 Ag/4 Ag/2 Ag/1 D2Ring Antigen Concentration
Radial Immunodiffusion Ab-containing gel Ag/8 Ag/4 Ag/2 Ag/1 Precipitin ring Antigen Concentration D2 Ring