
移动互联网技术-传输层移动性 苏锐丹
移动互联网技术-传输层移动性 苏锐丹
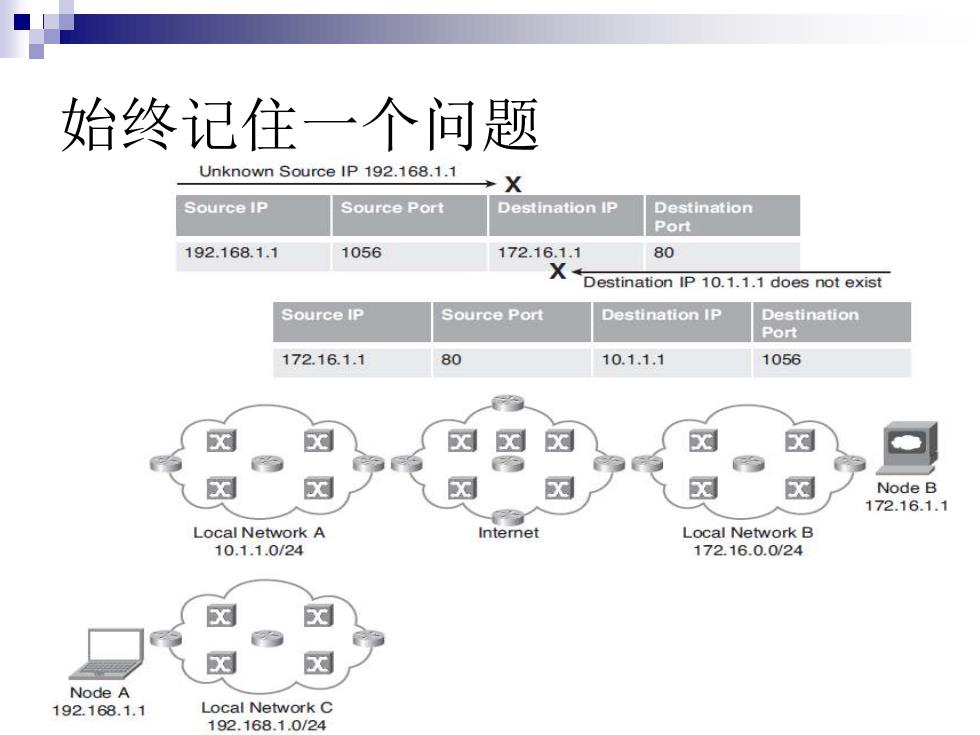
始终记住一个问题 Unknown Source IP 192.168.1.1 →X Source IP Source Port Destination IP Destination Port 192.168.1.1 1056 172.16.1.1 80 XDestination IP 10.1.1.1 does not exist Source IP Source Port Destination IP Destination Port 172.16.1.1 80 10.1.1.1 1056 Node B 172.16.1.1 Local Network A Internet Local Network B 10.1.1.0/24 172.16.0.0/24 Node A 192.168.1.1 Local Network C 192.168.1.0/24
始终记住一个问题

Inherent route optimization 口不用tunnel,开销小 口不会出现“三角路由” Inherent traversal of security elements Mobile IP ueses topologically incorrect source IP addresses on the mobile node for transmission uses topologically correct source IP addresses
◼ Inherent route optimization 不用tunnel,开销小 不会出现“三角路由” ◼ Inherent traversal of security elements Mobile IP ueses topologically incorrect source IP addresses on the mobile node for transmission uses topologically correct source IP addresses
Ability to pause transmissions during temporary disconnection Because the transport layer is aware of the mobility-induced disconnection,existing transmissions might be paused until reachability is reestablished. Ability to apply unique mobility ptimization mechanisms to different flows from the same mobile node
◼ Ability to pause transmissions during temporary disconnection Because the transport layer is aware of the mobility-induced disconnection, existing transmissions might be paused until reachability is reestablished. ◼ Ability to apply unique mobility ptimization mechanisms to different flows from the same mobile node
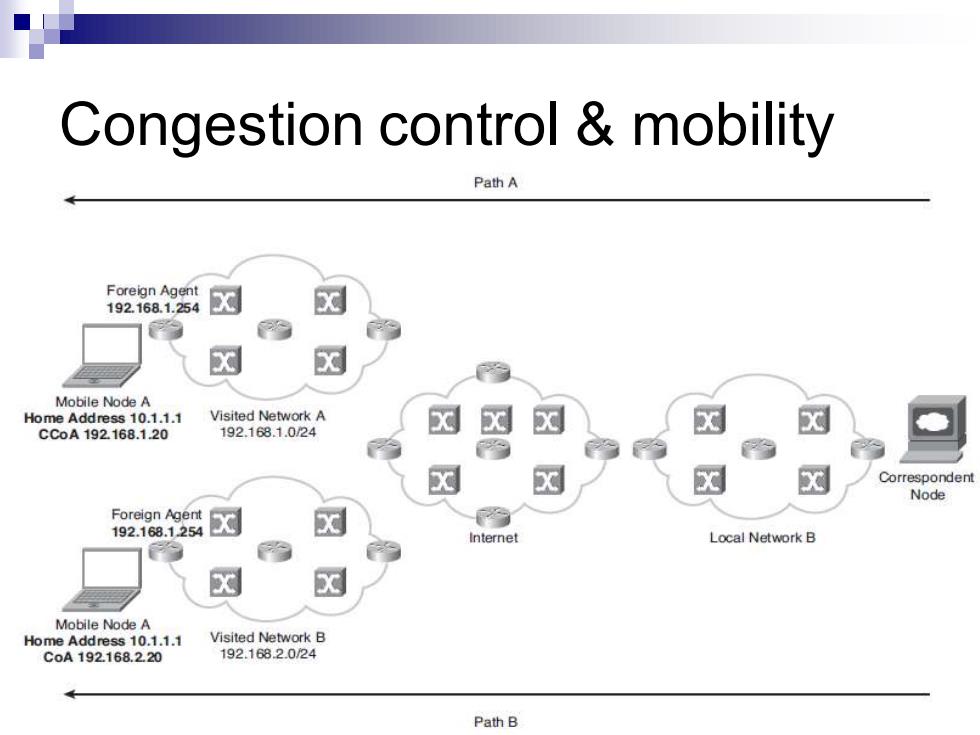
Congestion control mobility PathA Foreign Agent 192.168.1.254 Mobile Node A Home Address 10.1.1.1 Visited Network A CCoA192168.120 192.168.1.024 Correspondent Node 2a2级☒ Internet Local Network B Mobile Node A Home Address 10.1.1.1 Visited Network B CoA192.168.2.20 192.1682.0/24 Path B
Congestion control & mobility

TCP has limited support for congestion control These congestion control algorithms are slow to adapt to new path characteristics, creating inefficiencies at the transport layer when the path characteristic changes are significant. 口拥塞控制适应mobility
◼ TCP has limited support for congestion control ◼ These congestion control algorithms are slow to adapt to new path characteristics, creating inefficiencies at the transport layer when the path characteristic changes are significant. 拥塞控制适应mobility

Solving Mobility Above the Network Layer ■ Reconfiguration of the host for its new network:Protocols discussed in Chapter 1, “ntroduction to“Mobility”,”such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP),IP auto-configuration,and router discovery mechanisms,are widely deployed techniques for accomplishing this function. Ensuring reachability for new connections:Protocols discussed in Chapter 2, "Internet "Sessions","such as Dynamic DNS,provide sufficient capabilities for this function. Updating existing connections and rebinding these connections to the new IP address:Numerous protocols can provide this function
Solving Mobility Above the Network Layer

Stream Control Transmission Protocol natively supports multiple addresses per host, and allows the addition or deletion of addresses from an existing association Multipath TCP extensions to the original TCP to support many of the functions defined by SCTP ■MSOCKS relies on a proxy to provide seamless mobility of the mobile node
◼ Stream Control Transmission Protocol natively supports multiple addresses per host, and allows the addition or deletion of addresses from an existing association ◼ Multipath TCP extensions to the original TCP to support many of the functions defined by SCTP ◼ MSOCKS relies on a proxy to provide seamless mobility of the mobile node

常规TCP ■三次握手建立连接 ■全双工传输 ■三次握手建立连接 ■拥塞控制 口滑动窗口
常规TCP ◼ 三次握手建立连接 ◼ 全双工传输 ◼ 三次握手建立连接 ◼ 拥塞控制 滑动窗口

SCTP Point-to-point connections Connection-oriented services Reliable delivery Congestion control mechanism Packet loss recovery ■Rate adaptation
SCTP ◼ Point-to-point connections ◼ Connection-oriented services ◼ Reliable delivery ◼ Congestion control mechanism ◼ Packet loss recovery ◼ Rate adaptation