
ntroduction
Introduction

An operating system is a program that manages a computer's hardware.It also provides a basis for application programs and acts as an intermediary between the computer user and the computer hardware What Operating Systems Do Computer-System Organization Computer-System Architecture Operating-System Structure 。 Operating-System Operations ·Process Management ·Memory Management ·Storage Management Protection and Security Kernel Data Structures* Computing Environments Open-Source Operating Systems
• An operating system is a program that manages a computer’s hardware. It also provides a basis for application programs and acts as an intermediary between the computer user and the computer hardware • What Operating Systems Do • Computer-System Organization • Computer-System Architecture • Operating-System Structure • Operating-System Operations • Process Management • Memory Management • Storage Management • Protection and Security • Kernel Data Structures* • Computing Environments • Open-Source Operating Systems
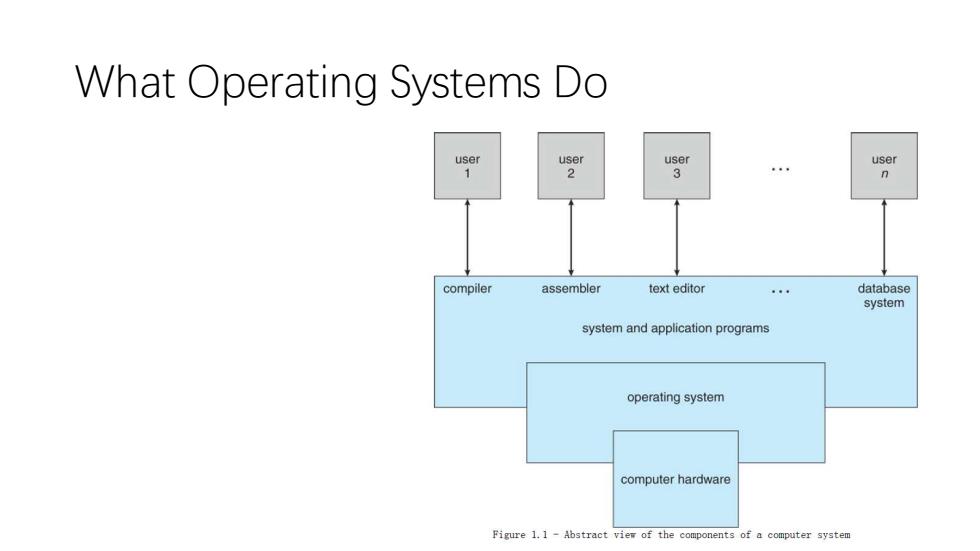
What Operating Systems Do user user 1 n compiler assembler text editor database system system and application programs operating system computer hardware Figure 1.1-Abstract view of the components of a computer system
What Operating Systems Do

Computer HW OS Apps Users OS provides services for Apps Users Make the computer system convenient to use OS manages resources Government model,it doesn't produce anything.) Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner Debates about what is included in the OS -Just the kernel,or everything the vendor ships?(Consider the distinction between system applications and 3rd party or user apps
• Computer = HW + OS + Apps + Users • OS provides services for Apps & Users • Make the computer system convenient to use • OS manages resources ( Government model, it doesn't produce anything. ) • Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner • Debates about what is included in the OS - Just the kernel, or everything the vendor ships? ( Consider the distinction between system applications and 3rd party or user apps. )
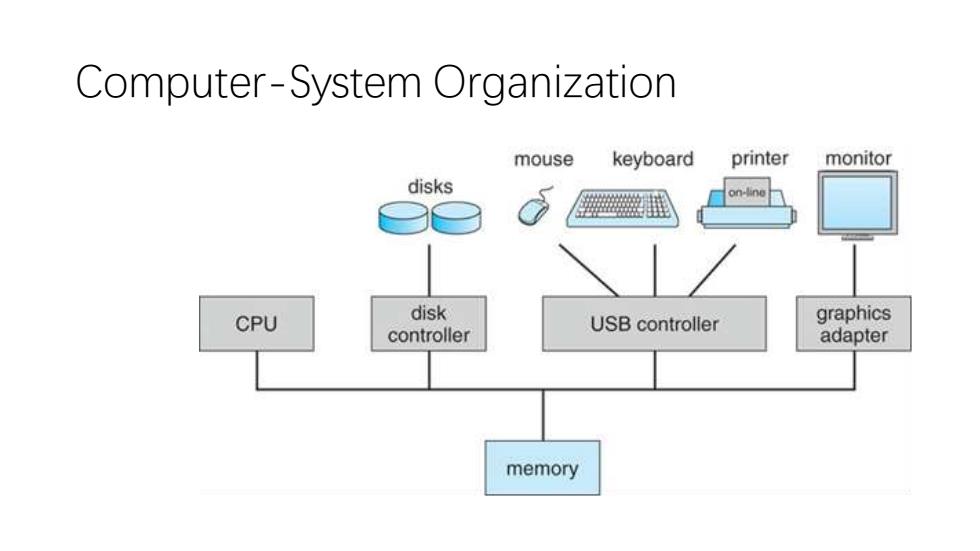
Computer-System Organization mouse keyboard printer monitor disks on-line CPU disk USB controller graphics controller adapter memory
Computer-System Organization

Computer-System Operation ·Bootstrap program Shared memory between CPU and I/O cards Time slicing for multi-process operation Interrupt handling clock,HW,SW Implementation of system calls
- Computer-System Operation • Bootstrap program • Shared memory between CPU and I/O cards • Time slicing for multi-process operation • Interrupt handling - clock, HW, SW • Implementation of system calls

CPU user process executing 1/O interrupt processing 1/0 idle device transferring 1/O transfer 1/O transfer request done request done
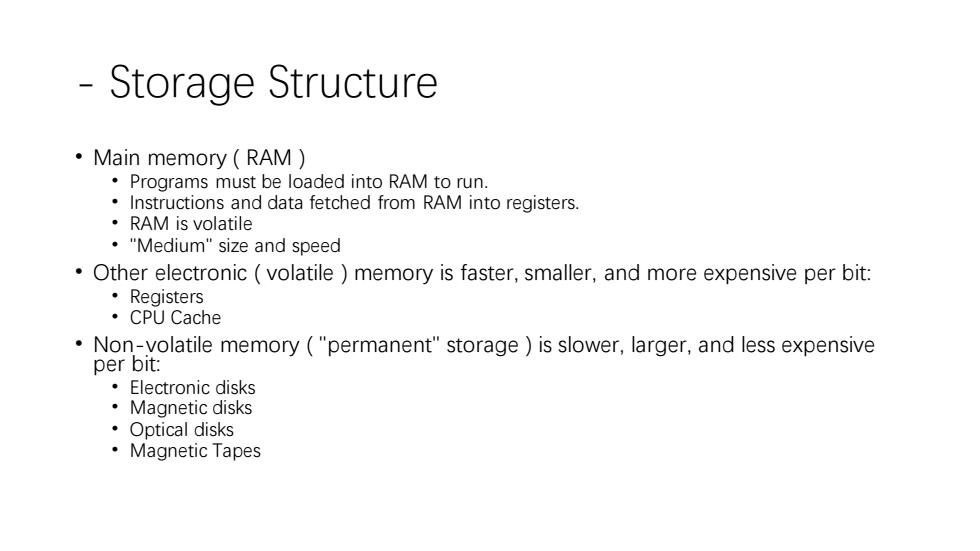
Storage Structure ·Main memory(RAM) Programs must be loaded into RAM to run. Instructions and data fetched from RAM into registers. ·RAM is volatile "Medium"size and speed Other electronic volatile )memory is faster,smaller,and more expensive per bit: ·Registers ·CPU Cache Non-volatile memory("permanent"storage )is slower,larger,and less expensive per bit: ·Electronic disks ·Magnetic disks ·Optical disks ·Magnetic Tapes
- Storage Structure • Main memory ( RAM ) • Programs must be loaded into RAM to run. • Instructions and data fetched from RAM into registers. • RAM is volatile • "Medium" size and speed • Other electronic ( volatile ) memory is faster, smaller, and more expensive per bit: • Registers • CPU Cache • Non-volatile memory ( "permanent" storage ) is slower, larger, and less expensive per bit: • Electronic disks • Magnetic disks • Optical disks • Magnetic Tapes
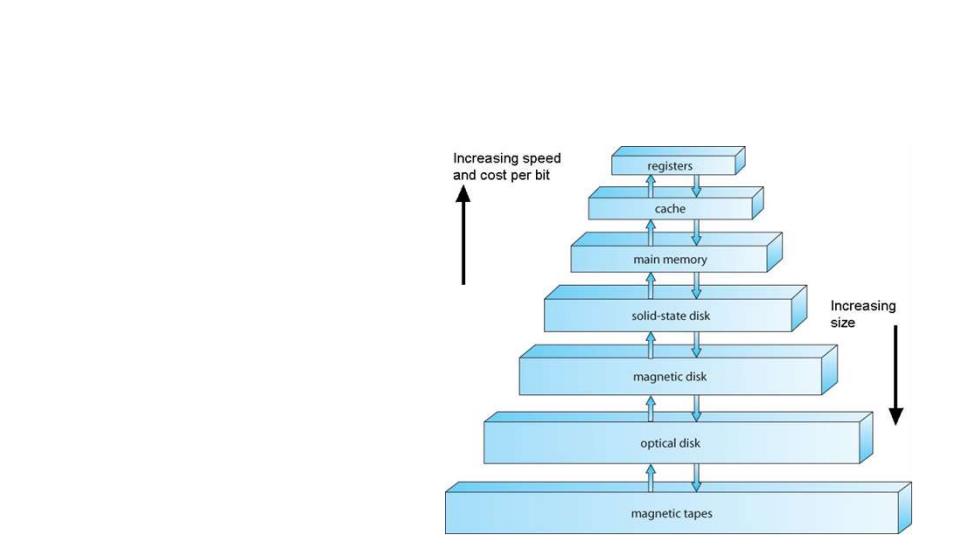
Increasing speed registers and cost per bit cache main memory Increasing solid-state disk size magnetic disk optical disk magnetic tapes
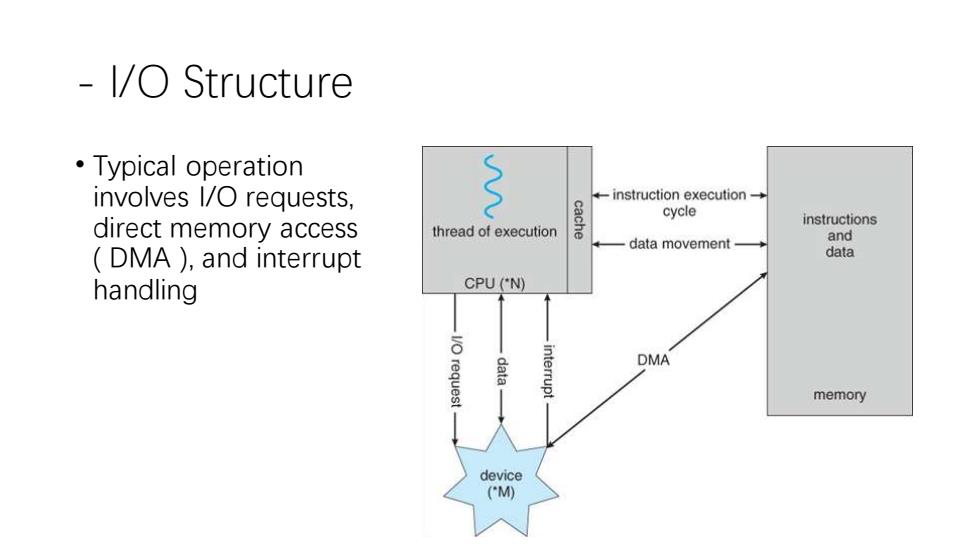
1/O Structure 。Typical operation involves 1/O requests, -instruction execution- cycle direct memory access cache instructions thread of execution data movement. and DMA),and interrupt data handling CPU(N) DMA request interrupt memory device (M)
- I/O Structure • Typical operation involves I/O requests, direct memory access ( DMA ), and interrupt handling