
Computer Networking Chapter 4 A Top-Down Approach Network Layer KUROSE ROSS A note on the use of these ppt slides: Computer We're making these slides freely available to all(faculty,students,readers) They're in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;and can add,modify. Networking:A and delete slides (including this one)and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part.In return for use,we only Top Down ask the following: If you use these slides (e.g.,in a class)that you mention their source Approach (after all,we'd like people to use our book!) 6th edition If you post any slides on a www site,that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to)our slides,and note our copyright of this Jim Kurose,Keith Ross material. Addison-Wesley Thanks and enjoy!JFK/KWR March 2012 urRhts Reserved Network Layer 4-1
Chapter 4 Network Layer Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 A note on the use of these ppt slides: We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the following: If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) If you post any slides on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our slides, and note our copyright of this material. Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR All material copyright 1996-2013 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved Network Layer 4-1
Chapter 4:network layer chapter goals: understand principles behind network layer services: network layer service models forwarding versus routing how a router works routing (path selection) broadcast,multicast instantiation,implementation in the Internet Network Layer 4-2
Network Layer 4-2 Chapter 4: network layer chapter goals: understand principles behind network layer services: network layer service models forwarding versus routing how a router works routing (path selection) broadcast, multicast instantiation, implementation in the Internet
Chapter 4:outline 4.1 introduction 4.5 routing algorithms 4.2 virtual circuit and link state datagram networks distance vector 4.3 what's inside a router hierarchical routing 4.4 IP:Internet Protocol 4.6 routing in the Internet RIP datagram format ■lPv4 addressing OSPF ■ICMP BGP ■IPV6 4.7 broadcast and multicast routing Network Layer 4-3
Network Layer 4-3 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 what’s inside a router 4.4 IP: Internet Protocol datagram format IPv4 addressing ICMP IPv6 4.5 routing algorithms link state distance vector hierarchical routing 4.6 routing in the Internet RIP OSPF BGP 4.7 broadcast and multicast routing Chapter 4: outline
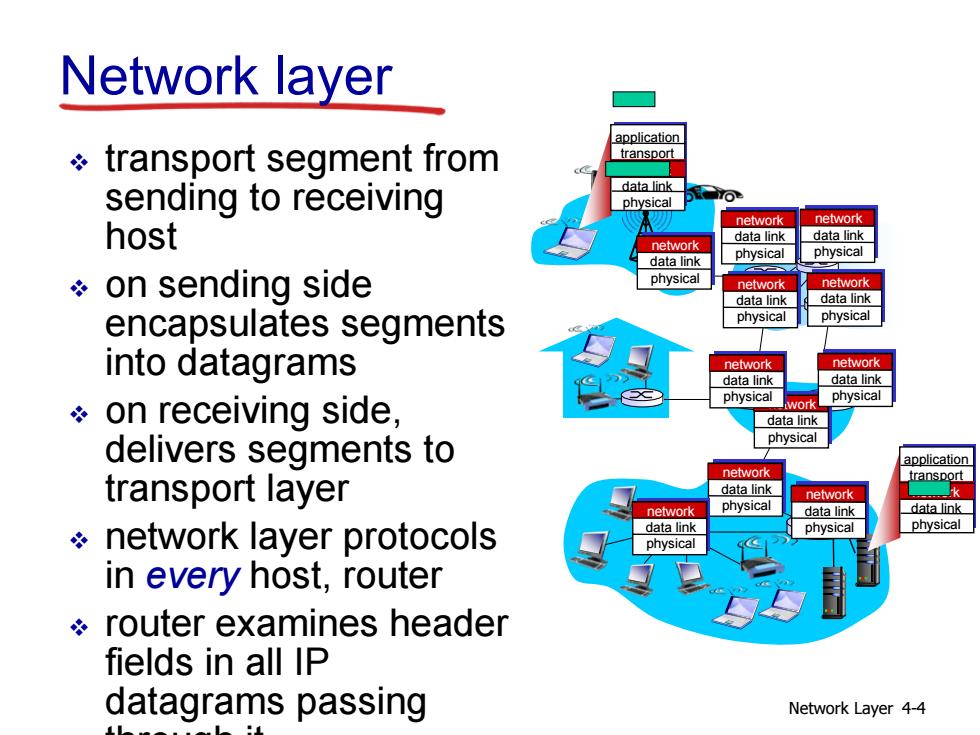
Network layer application transport segment from transport sending to receiving data link physica network network host data link data link network data link physical physical on sending side network network data link data link encapsulates segments physical physical into datagrams etwork network data link data link on receiving side, physical work physical data link delivers segments to physical application network transport layer transport data link network network physical data link data link network layer protocols data link physical physical physical in every host,router router examines header fields in all IP datagrams passing Network Layer 4-4
Network Layer 4-4 Network layer transport segment from sending to receiving host on sending side encapsulates segments into datagrams on receiving side, delivers segments to transport layer network layer protocols in every host, router router examines header fields in all IP datagrams passing through it application transport network data link physical application transport network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical network data link physical
Two key network-layer functions forwarding:move analogy: packets from router's input to appropriate routing:process of router output planning trip from source to dest routing:determine route taken by packets forwarding:process of from source to dest. getting through single interchange routing algorithms Network Layer 4-5
Network Layer 4-5 Two key network-layer functions forwarding: move packets from router’s input to appropriate router output routing: determine route taken by packets from source to dest. routing algorithms analogy: routing: process of planning trip from source to dest forwarding: process of getting through single interchange
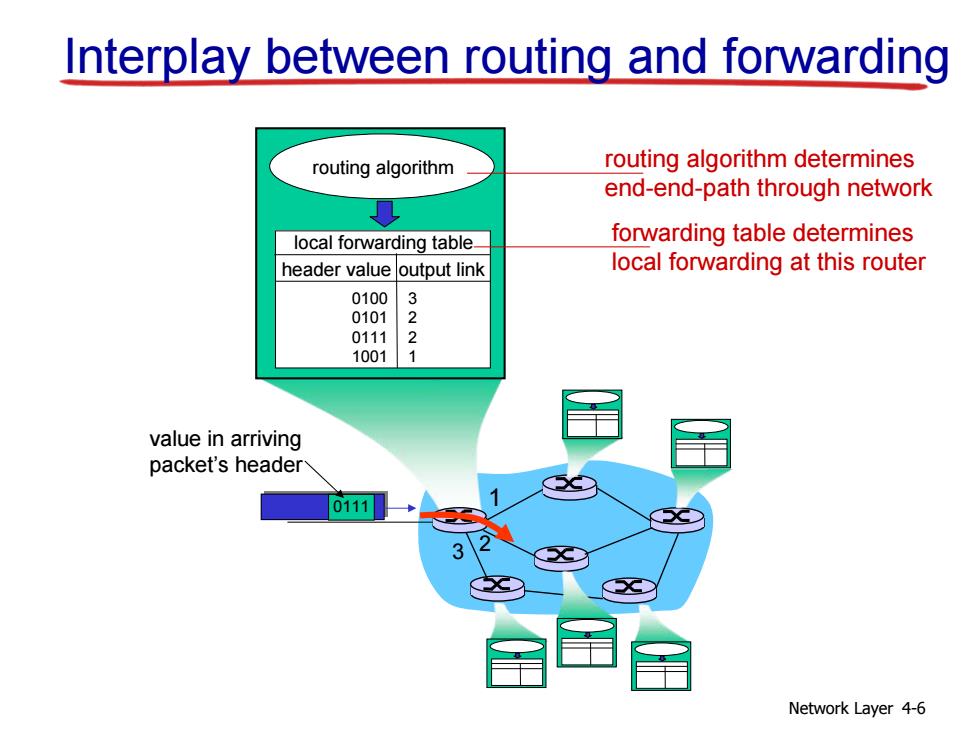
Interplay between routing and forwarding routing algorithm routing algorithm determines end-end-path through network 夏 local forwarding table- forwarding table determines header value output link local forwarding at this router 0100 3 0101 0111 10011 value in arriving packet's header 0111 Network Layer 4-6
Network Layer 4-6 1 2 3 0111 value in arriving packet’s header routing algorithm local forwarding table header value output link 0100 0101 0111 1001 3 2 2 1 Interplay between routing and forwarding routing algorithm determines end-end-path through network forwarding table determines local forwarding at this router

Connection setup 3rd important function in some network architectures: ATM,frame relay,X.25 before datagrams flow,two end hosts and intervening routers establish virtual connection routers get involved network vs transport layer connection service: network:between two hosts (may also involve intervening routers in case of VCs) transport:between two processes Network Layer 4-7
Network Layer 4-7 Connection setup 3rd important function in some network architectures: ATM, frame relay, X.25 before datagrams flow, two end hosts and intervening routers establish virtual connection routers get involved network vs transport layer connection service: network: between two hosts (may also involve intervening routers in case of VCs) transport: between two processes
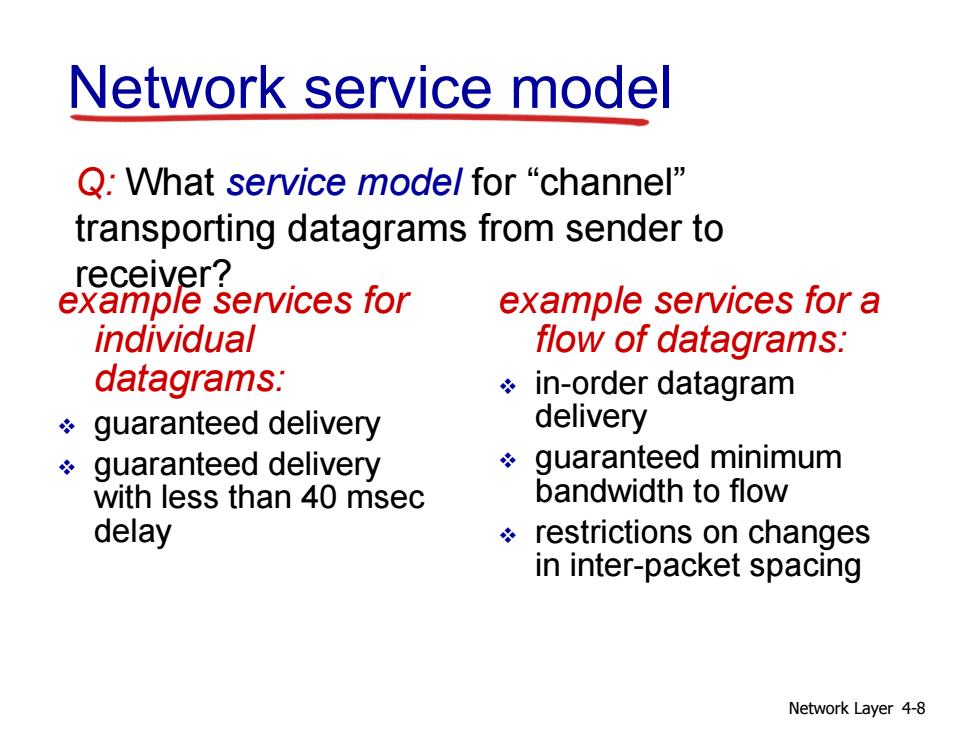
Network service model Q:What service model for "channel" transporting datagrams from sender to receiver? example services for example services for a individual flow of datagrams: datagrams: in-order datagram guaranteed delivery delivery guaranteed delivery 冬 guaranteed minimum with less than 40 msec bandwidth to flow delay restrictions on changes in inter-packet spacing Network Layer 4-8
Network Layer 4-8 Network service model Q: What service model for “channel” transporting datagrams from sender to receiver? example services for individual datagrams: guaranteed delivery guaranteed delivery with less than 40 msec delay example services for a flow of datagrams: in-order datagram delivery guaranteed minimum bandwidth to flow restrictions on changes in inter-packet spacing
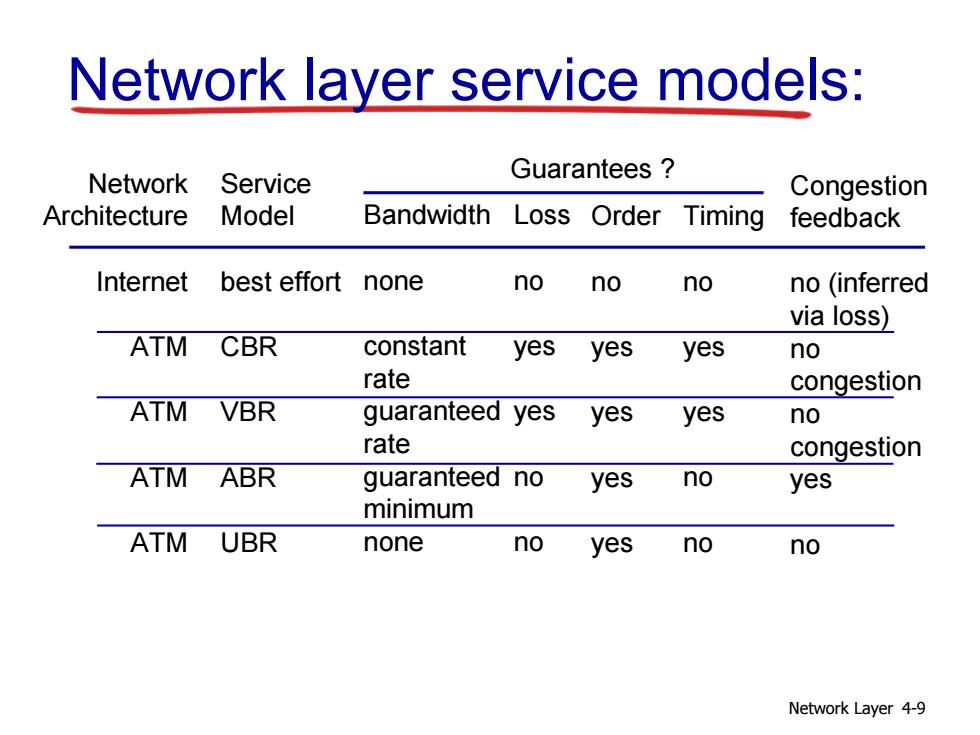
Network layer service models: Network Service Guarantees Congestion Architecture Model Bandwidth Loss Order Timing feedback Internet best effort none no no no no (inferred via loss) ATM CBR constant yes yes yes no rate congestion ATM VBR guaranteed yesyes yes no rate congestion ATM ABR guaranteed no yes no yes minimum ATM UBR none no yes no no Network Layer 4-9
Network Layer 4-9 Network layer service models: Network Architecture Internet ATM ATM ATM ATM Service Model best effort CBR VBR ABR UBR Bandwidth none constant rate guaranteed rate guaranteed minimum none Loss no yes yes no no Order no yes yes yes yes Timing no yes yes no no Congestion feedback no (inferred via loss) no congestion no congestion yes no Guarantees ?
Chapter 4:outline 4.1 introduction 4.5 routing algorithms 4.2 virtual circuit and ·link state datagram networks distance vector 4.3 what's inside a router hierarchical routing 4.4 IP:Internet Protocol 4.6 routing in the Internet ■datagram format ■RIP ■lPv4 addressing ·OSPF ICMP ■BGP ■IPv6 4.7 broadcast and multicast routing Network Layer 4-10
Network Layer 4-10 4.1 introduction 4.2 virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 what’s inside a router 4.4 IP: Internet Protocol datagram format IPv4 addressing ICMP IPv6 4.5 routing algorithms link state distance vector hierarchical routing 4.6 routing in the Internet RIP OSPF BGP 4.7 broadcast and multicast routing Chapter 4: outline