
Computer Networking Chapter 1 A Top-Down Approach Introduction KUROSE ROSS A note on the use of these ppt slides: Computer We're making these slides freely available to all(faculty,students,readers) They're in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;and can add,modify. Networking:A and delete slides (including this one)and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part.In return for use,we only Top Down ask the following: If you use these slides (e.g.,in a class)that you mention their source Approach (after all,we'd like people to use our book!) 6th edition If you post any slides on a www site,that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to)our slides,and note our copyright of this Jim Kurose,Keith Ross material. Addison-Wesley Thanks and enjoy!JFK/KWR March 2012 urhts Reserved Introduction 1-1
Introduction 1-1 Chapter 1 Introduction Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 6th edition Jim Kurose, Keith Ross Addison-Wesley March 2012 A note on the use of these ppt slides: We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the following: If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) If you post any slides on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our slides, and note our copyright of this material. Thanks and enjoy! JFK/KWR All material copyright 1996-2012 J.F Kurose and K.W. Ross, All Rights Reserved

Chapter 1:introduction our goal: overview: gget“feel"and what's the Internet? terminology what's a protocol? *more depth,detail network edge;hosts,access net, physical media later in course network core:packet/circuit approach: switching,Internet structure ■use Internet as performance:loss,delay, example throughput security protocol layers,service models history Introduction 1-2
Introduction Chapter 1: introduction our goal: get “feel” and terminology more depth, detail later in course approach: use Internet as example overview: what’s the Internet? what’s a protocol? network edge; hosts, access net, physical media network core: packet/circuit switching, Internet structure performance: loss, delay, throughput security protocol layers, service models history 1-2

Chapter 1:roadmap 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge end systems,access networks,links 1.3 network core packet switching,circuit switching,network structure 1.4 delay,loss,throughput in networks 1.5 protocol layers,service models 1.6 networks under attack:security 1.7 history Introduction 1-3
Introduction Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core packet switching, circuit switching, network structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in networks 1.5 protocol layers, service models 1.6 networks under attack: security 1.7 history 1-3
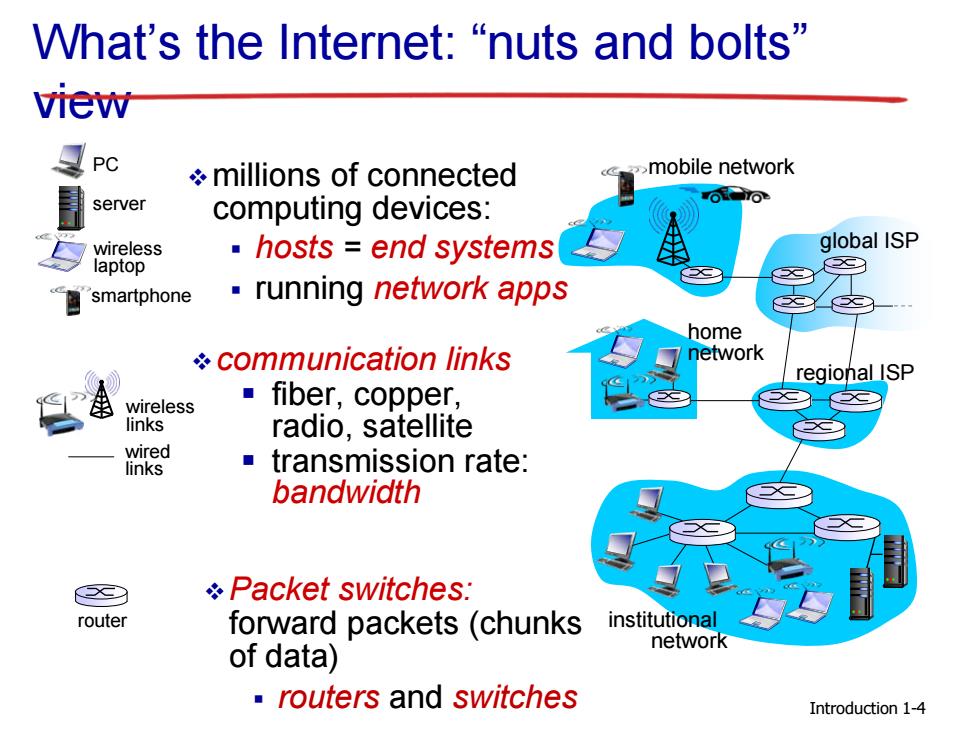
What's the Internet:“nuts and bolts'” view PC millions of connected mobile network 目 server computing devices: OLSTON wireless ·hosts=end systems global ISP laptop smartphone ·running network apps home communication links network regional ISP wireless ■fiber,copper, links radio,satellite wired links transmission rate: bandwidth Packet switches: router forward packets (chunks institutional network of data) routers and switches Introduction 1-4
Introduction What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” view millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end systems running network apps communication links fiber, copper, radio, satellite transmission rate: bandwidth Packet switches: forward packets (chunks of data) routers and switches wired links wireless links router mobile network global ISP regional ISP home network institutional network smartphone PC server wireless laptop 1-4

“Fun”internet appliances Web-enabled toaster weather forecaster IP picture frame http://www.ceiva.com/ Tweet-a-watt: monitor energy use Slingbox:watch, control cable TV remotely Internet refrigerator Internet phones Introduction 1-5
Introduction “Fun” internet appliances IP picture frame http://www.ceiva.com/ Web-enabled toaster + weather forecaster Internet phones Internet refrigerator Slingbox: watch, control cable TV remotely 1-5 Tweet-a-watt: monitor energy use

What's the Internet:“nuts and bolts” view mobile network Internet:"network of networks" OLSTON ■Interconnected ISPs global ISP protocols control sending, receiving of msgs e.g.,TCP,IP,HTTP,Skype, home 802.11 network regional ISP Internet standards RFC:Request for comments IETF:Internet Engineering Task Force institutional network Introduction 1-6
Introduction Internet: “network of networks” Interconnected ISPs protocols control sending, receiving of msgs e.g., TCP, IP, HTTP, Skype, 802.11 Internet standards RFC: Request for comments IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” view mobile network global ISP regional ISP home network institutional network 1-6
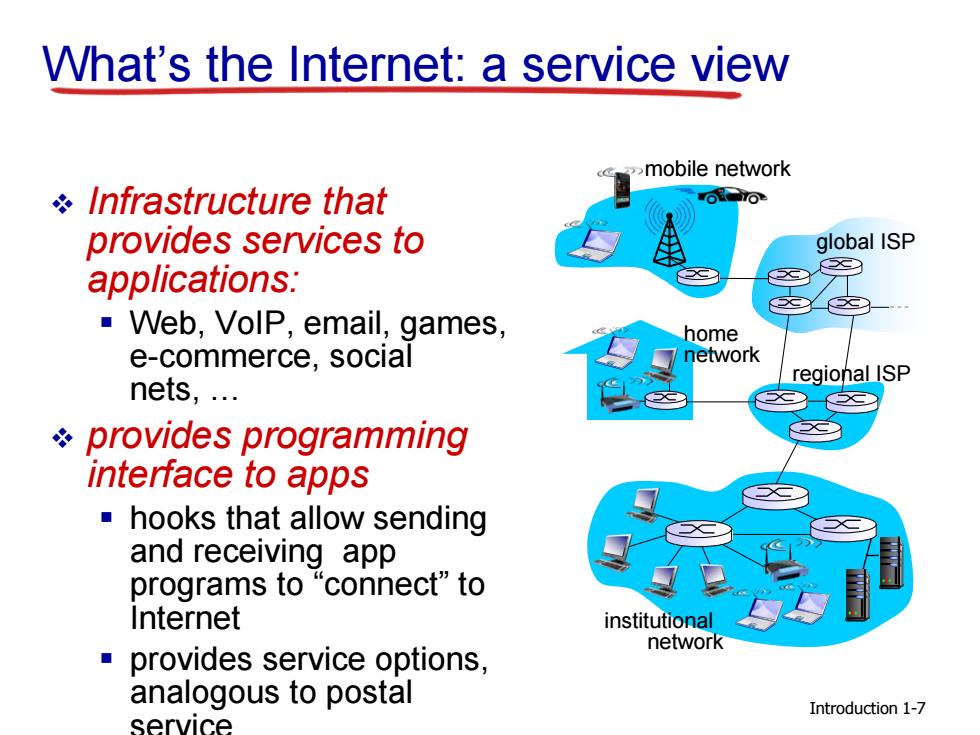
What's the Internet:a service view >mobile network Infrastructure that provides services to global ISP applications: Web,VolP,email,games, home e-commerce,social network nets,... regional ISP provides programming interface to apps hooks that allow sending and receiving app programs to“connect”to Internet institutional network provides service options, analogous to postal Introduction 1-7 service
What’s the Internet: a service view Infrastructure that provides services to applications: Web, VoIP, email, games, e-commerce, social nets, … provides programming interface to apps hooks that allow sending and receiving app programs to “connect” to Internet provides service options, analogous to postal service mobile network global ISP regional ISP home network institutional network Introduction 1-7
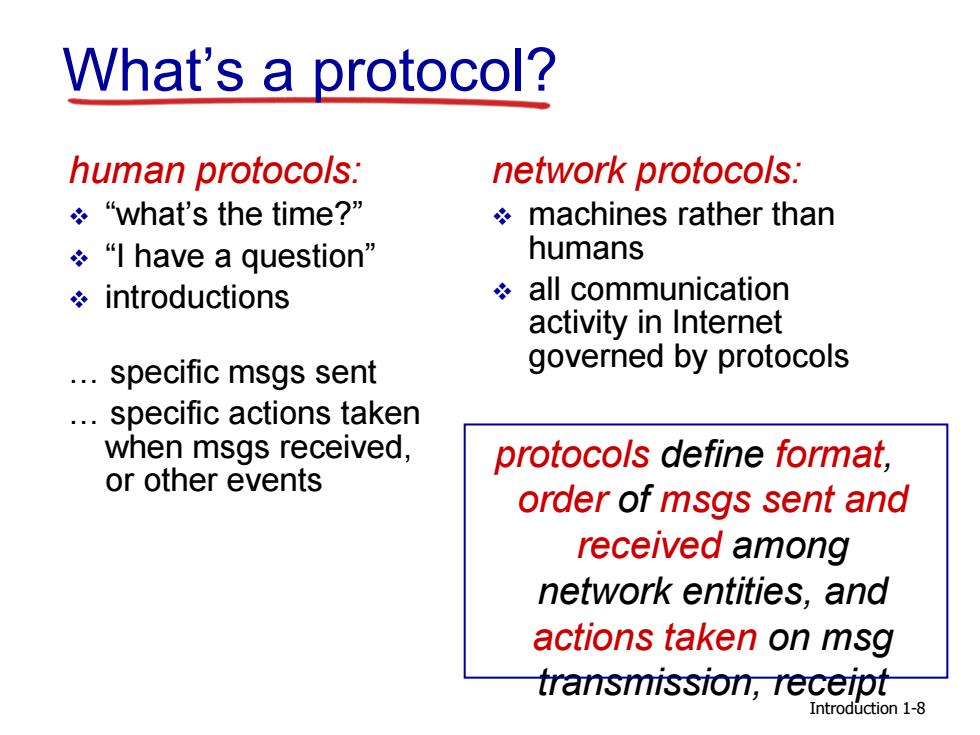
What's a protocol? human protocols: network protocols: g“what's the time?” machines rather than “|have a question” humans introductions all communication activity in Internet ..specific msgs sent governed by protocols specific actions taken when msgs received, protocols define format, or other events order of msgs sent and received among network entities,and actions taken on msg transmission,receipt Introduction 1-8
Introduction What’s a protocol? human protocols: “what’s the time?” “I have a question” introductions … specific msgs sent … specific actions taken when msgs received, or other events network protocols: machines rather than humans all communication activity in Internet governed by protocols protocols define format, order of msgs sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt 1-8
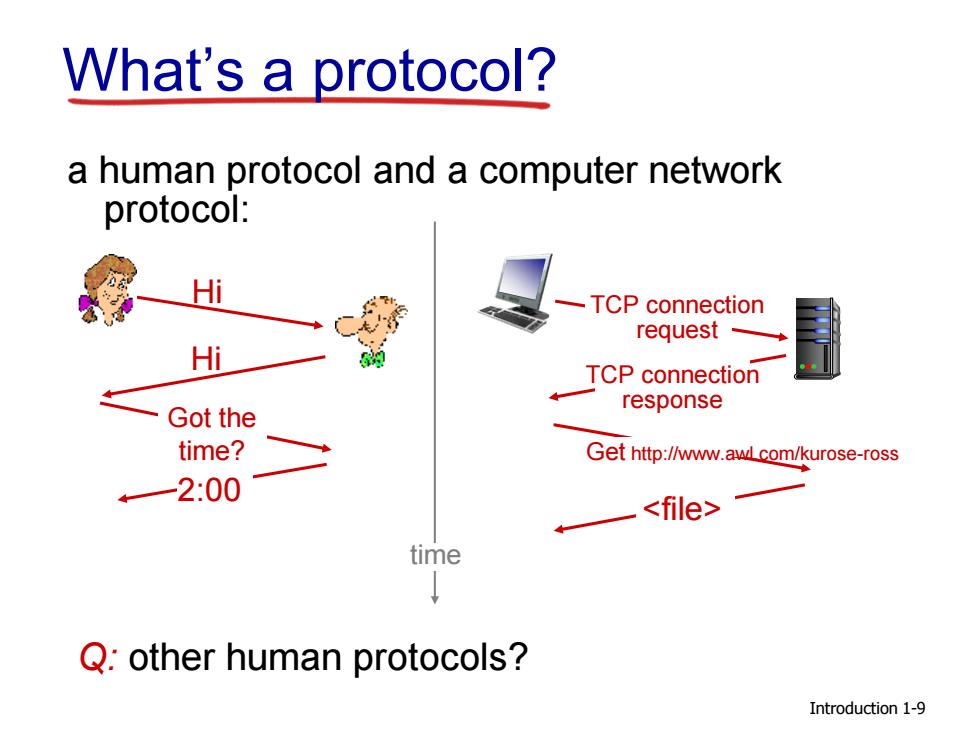
What's a protocol? a human protocol and a computer network protocol: TCP connection request Hi TCP connection response Got the time? Get http://www.awLcom/kurose-ross 42:00 time Q:other human protocols? Introduction 1-9
Introduction a human protocol and a computer network protocol: Q: other human protocols? Hi Hi Got the time? 2:00 TCP connection response Get http://www.awl.com/kurose-ross time TCP connection request What’s a protocol? 1-9

Chapter 1:roadmap 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge end systems,access networks,links 1.3 network core packet switching,circuit switching,network structure 1.4 delay,loss,throughput in networks 1.5 protocol layers,service models 1.6 networks under attack:security 1.7 history Introduction 1-10
Introduction Chapter 1: roadmap 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 network edge end systems, access networks, links 1.3 network core packet switching, circuit switching, network structure 1.4 delay, loss, throughput in networks 1.5 protocol layers, service models 1.6 networks under attack: security 1.7 history 1-10