
第二十章颅脑损伤Craniocerebral TraumaNeurosurgeryDepartmentofThe1stAffiliatedHospitals Of Shihezi University Medical School
第二十章 颅 脑 损 伤 Craniocerebral Trauma Neurosurgery Department of The 1st Affiliated Hospitals Of Shihezi University Medical School
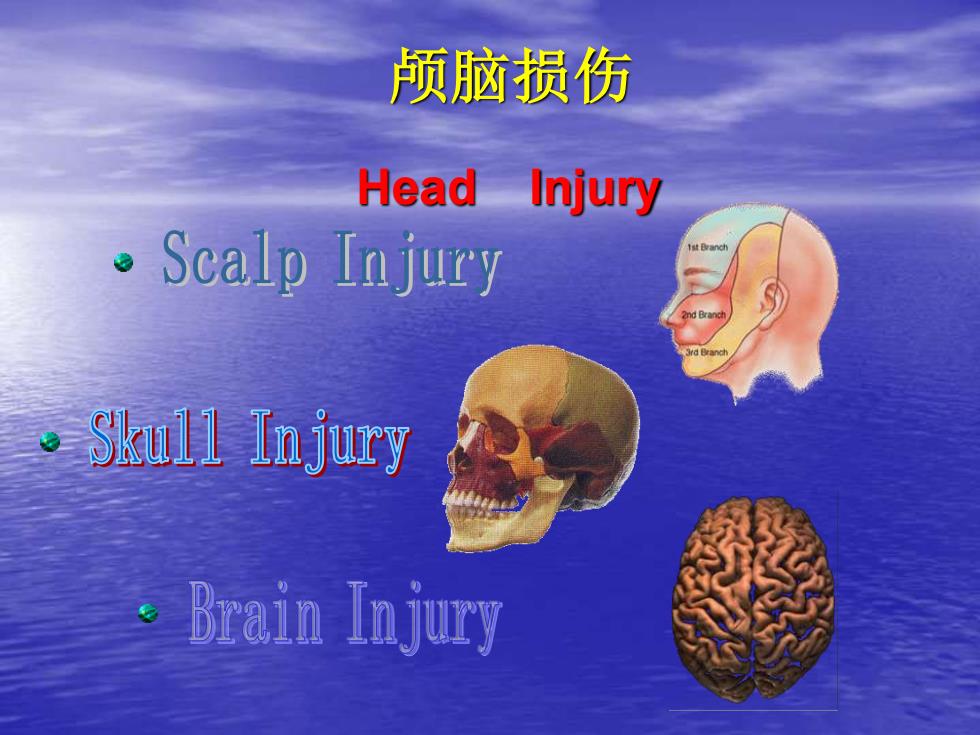
脑损伤HeadInjuryScalp InjurystBranchSkull In juryBrain In jury
颅脑损伤 Head Injury

脑损伤概述Craniocerebral InjuryINTRODUCTIONMorbidityCausePopulation10:56
颅脑损伤概述 Craniocerebral Injury INTRODUCTION Morbidity Cause Population
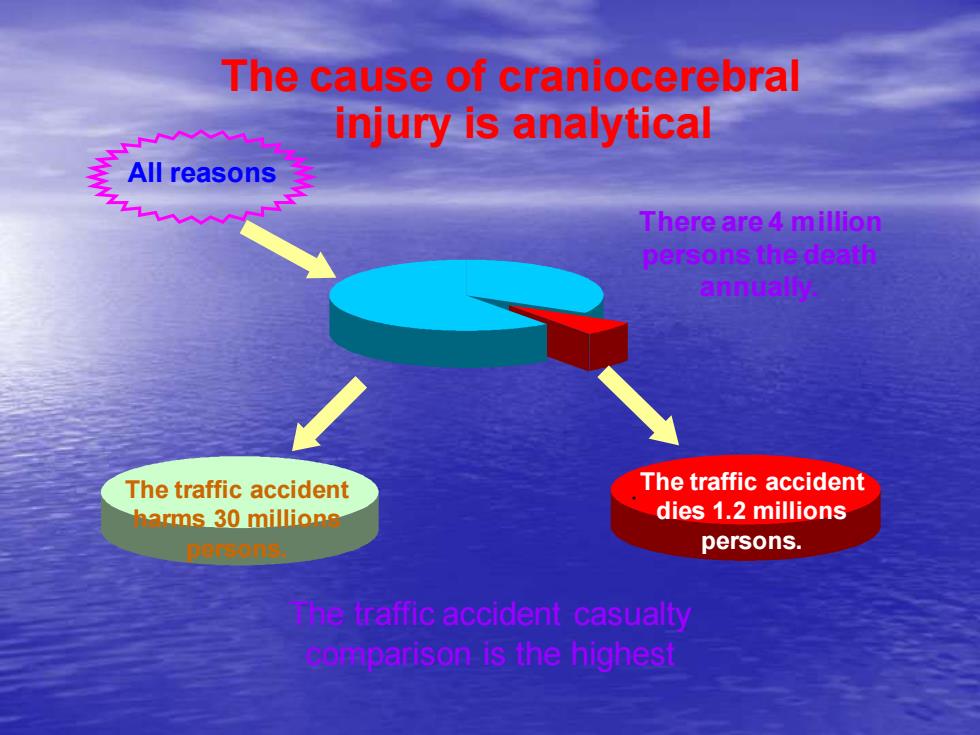
The cause of craniocerebralinjury is analyticalAllreasonsThereare4millionpersonsthedeathannuallyThetraffic accidentThetraffic accidentdies1.2millionsharms30millionspersons.parsons.The traffic accident casualtycomparison is the highest
The cause of craniocerebral injury is analytical All reasons There are 4 million persons the death annually. . The traffic accident casualty comparison is the highest The traffic accident dies 1.2 millions persons. The traffic accident harms 30 millions persons
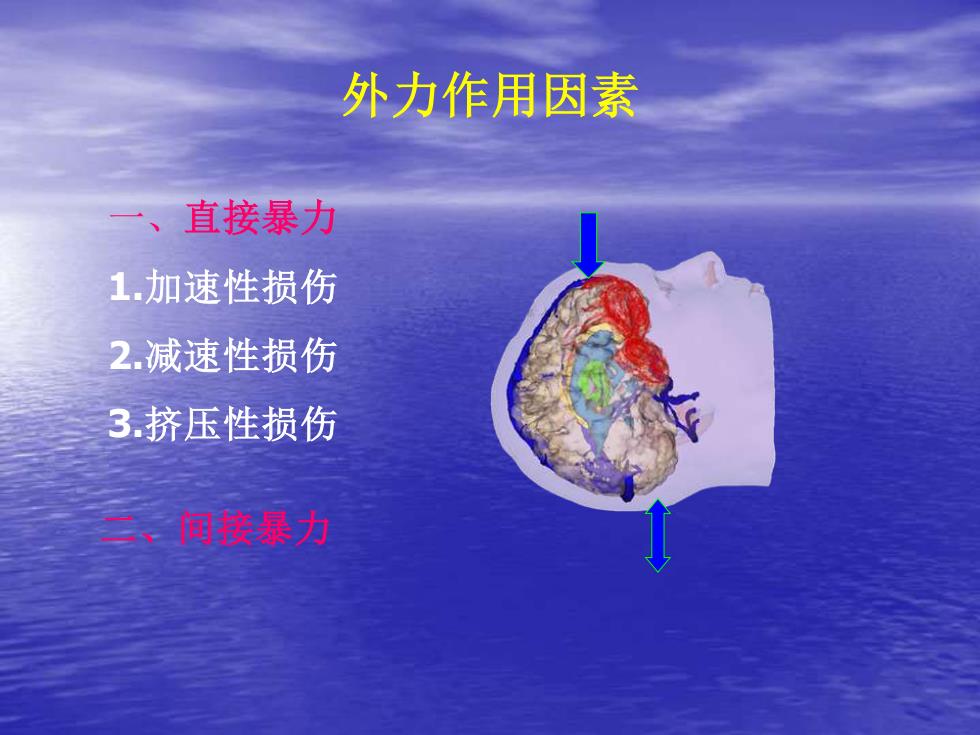
外力作用因素、直接暴力1.加速性损伤2.减速性损伤3.挤压性损伤二、间接暴力
外力作用因素 一、直接暴力 1.加速性损伤 2.减速性损伤 3.挤压性损伤 二、间接暴力
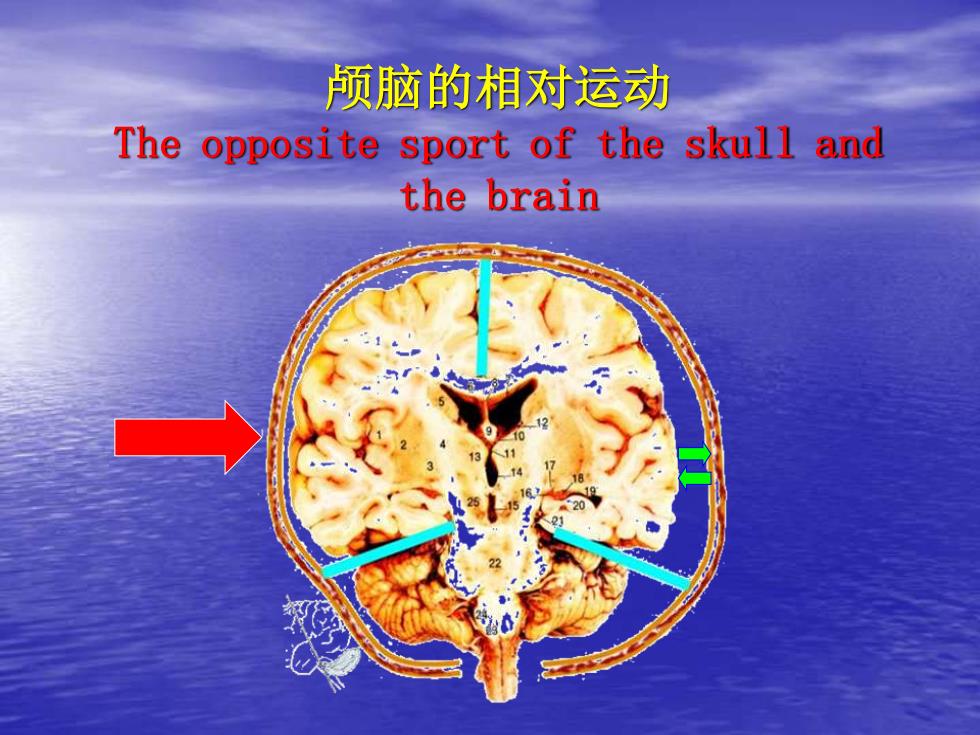
颅脑的相对运动The opposite sport of the skull andthe brain
颅脑的相对运动 The opposite sport of the skull and the brain

外力与脑损伤关系一、弥漫性轴突伤:由于旋转运动外力所致二、后颅窝着力时的脑损伤1>.对冲伤2>.对冲伤的发生与年龄有密切关系3>.伤情一般较重4>.迟发性颅内血肿的发生率高
外力与脑损伤关系 一、弥漫性轴突伤:由于旋转运动外力所致 二、后颅窝着力时的脑损伤 1>.对冲伤 2>.对冲伤的发生与年龄有密切关系 3>.伤情一般较重 4>.迟发性颅内血肿的发生率高
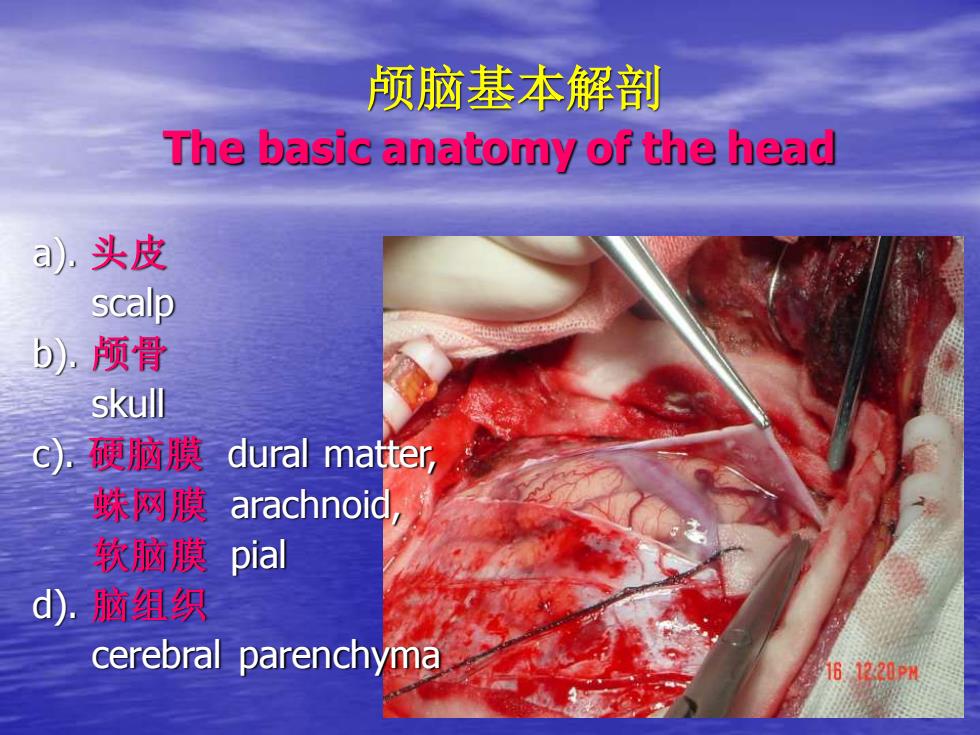
脑基本解部The basicanatomyof the head头皮a.scalpb).颅骨skull硬脑膜dural matter蛛网膜arachnoidpial软脑膜脑组织dcerebral parenchyma1612-20PM
颅脑基本解剖 The basic anatomy of the head a). 头皮 scalp b). 颅骨 skull c). 硬脑膜 dural matter, 蛛网膜 arachnoid, 软脑膜 pial d). 脑组织 cerebral parenchyma

脑损伤的分类根据临床应用分开放性、闭合性根据损伤机理和病理改变分原发性、继发性根据GCS计分法及病情轻重分轻型、中型、重型、特重型
颅脑损伤的分类 • 根据临床应用分 开放性、闭合性 • 根据损伤机理和病理改变分 原发性、继发性 • 根据GCS计分法及病情轻重分 轻型、中型、重型、特重型

根据临床应用分类·开放性·闭合性根据损伤机理和病理改变分类·原发性继发性
• 根据临床应用分类 •开放性 •闭合性 • 根据损伤机理和病理改变分类 •原发性 •继发性