
国家重点实验室 Chapter One Networking basics and trend ● 1.1 Networking basics O1.2 Network trend 2020/4/23 Dr.Zhangi xu,National Key Lab on ISN,Xidian University 1
2020/4/23 Dr. Zhanqi XU, National Key Lab on ISN, Xidian University 1 Chapter One Networking basics and trend 1.1 Networking basics 1.2 Network trend
国家重点实验室 1.The main components/elements of an information network The network in this course denotes the information network,since there are a lot of networks that are different from this one,such as the network of an organization,postal network railway network,the relation network of a family,etc. Mathematically,a network can be represented as a graph G=(n,v),where n is the set of nodes and y denotes a set of links to which nodes are connected. For an information network,a node can be the device or equipment that belongs to either users or network operators
2020/4/23 Dr. Zhanqi XU, National Key Lab on ISN, Xidian University 2 The network in this course denotes the information network, since there are a lot of networks that are different from this one, such as the network of an organization, postal network , railway network, the relation network of a family, etc. Mathematically, a network can be represented as a graph G=(n , v), where n is the set of nodes and v denotes a set of links to which nodes are connected. For an information network, a node can be the device or equipment that belongs to either users or network operators. 1. The main components/elements of an information network

国家重点实验室 1)Terminal Terminal could be divided to two types:user terminal and network terminal (also known as Server) a)User terminal:It performs the capturing,processing and transmission of user information,and has the functions of control and management. Examples of user terminal >a telephone a notebook a mobile phone a computer
1) Terminal Terminal could be divided to two types: user terminal and network terminal (also known as Server) a) User terminal: It performs the capturing, processing and transmission of user information, and has the functions of control and management. Examples of user terminal a telephone a notebook a mobile phone a computer

b)Network terminal (aka Server):It implements the 国家重片 following functions: information capturing and/or storage voice recorder,video camera,data store server (mixed)processing and transmission of users'information video conferencing server control and management for itself and users corresponding example are Web server and Session Initiation Protocol(SP#,会话(W会晤)发起/启动协议)call processing server. Cisco IP/VC 3510 SIP Videoconferencing Web Server Multipoint Control Unit SIP Server (MPCU#)
b) Network terminal (aka Server): It implements the following functions: information capturing and/or storage voice recorder, video camera, data store server (mixed) processing and transmission of users’ information video conferencing server Web Server Cisco IP/VC 3510 Videoconferencing Multipoint Control Unit (MPCU#) SIP Server control and management for itself and users corresponding example are Web server and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP#, 会话(/会晤)发起/启动协议) call processing server
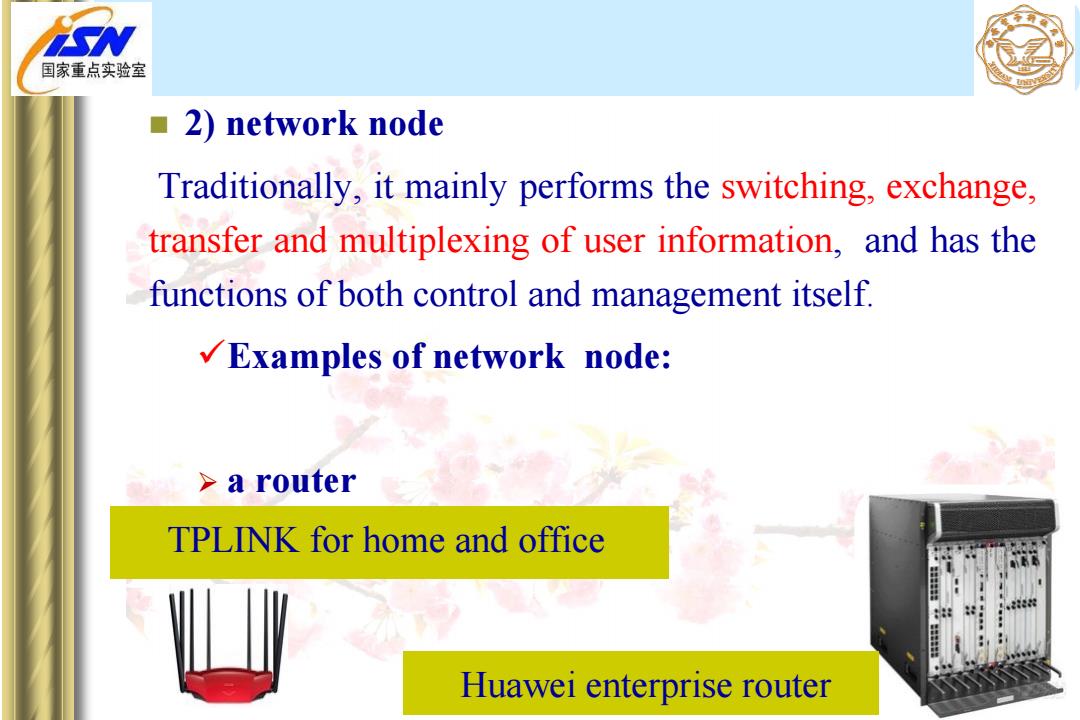
国家重点实验室 ■2)network node Traditionally,it mainly performs the switching,exchange, transfer and multiplexing of user information,and has the functions of both control and management itself. Examples of network node: a router TPLINK for home and office Huawei enterprise router
2) network node Traditionally, it mainly performs the switching, exchange, transfer and multiplexing of user information, and has the functions of both control and management itself. Examples of network node: a router TPLINK for home and office Huawei enterprise router

L2/L3 Switch#:it implements the frame or packet switching according to six-byte MAC address or IP 4-byte address. r7r Digital eXchange Cross connect DXC,数字 交叉连接)#:it performs time slot-,! port-, wavelength-switch by configuring manually. Multiplexor (复用器)#:it can multiplex several low channels (say 64Kbps)into one high speed channel (say E1),and vice versa. ETUO2-MUX/PLUS E1数据、语音复用器 Concentrator (集中器)#:it usually collects information from quite a number of users, and transfers the information captured to a 据吴生器子阳 high-level server,e.g., remote electricity /=旦土右小台
L2/L3 Switch#: it implements the frame or packet switching according to six-byte MAC address or IP 4-byte address. Multiplexor ( 复 用 器 )#: it can multiplex several low channels (say 64Kbps) into one high speed channel (say E1) , and vice versa. Digital eXchange Cross connect (DXC,数字 交叉连接)#: it performs time slot-, port-, wavelength-switch by configuring manually. Concentrator (集中器)#: it usually collects information from quite a number of users, and transfers the information captured to a high-level server, e.g., remote electricity meters reading (远程电力抄表)
国家重点实验室 2)network node As network evolves,except the switching function,it also performs transforming or mixing of user information,and has the functions of both control and management for users. Examples of network node: an IP telephone gateway could perform: Transforming coding between a/u voice in TDM with 64Kbps and IP voice coding,say G.729A with 8Kbps Transforming PSTN signalling and VolP signaling. More details in both later slides and Chapter seven of Access network PPT
2) network node As network evolves , except the switching function, it also performs transforming or mixing of user information, and has the functions of both control and management for users. Examples of network node: an IP telephone gateway could perform: • Transforming coding between a/μ voice in TDM with 64Kbps and IP voice coding, say G.729A with 8Kbps • Transforming PSTN signalling and VoIP signaling. More details in both later slides and Chapter seven of Access network PPT
3)transmission link a)It performs transmit information between adjacent nodes. Equally,a pair of two nodes or more nodes are connected physically by it in the forms of either a single channel or a broadcast one b)It usually includes the various transmission facilities(设施), equipment or devices and their combinations.More specially,it maybe used by physical transmission network like Synchronous Digital Hierarch(SDH#,同步数字体系)link,( or even Asynchronous Transfer Mode(TM#,异步转移模式)link More details in both Chapter three of Access network and broadband ATM techniques PPT
3) transmission link a) It performs transmit information between adjacent nodes. Equally, a pair of two nodes or more nodes are connected physically by it in the forms of either a single channel or a broadcast one . b) It usually includes the various transmission facilities (设施), equipment or devices and their combinations. More specially, it maybe used by physical transmission network like Synchronous Digital Hierarch (SDH#,同步数字体系) link , or even Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM#,异步转移模式) link . More details in both Chapter three of Access network and broadband ATM techniques PPT
N 国家重点实验室 c)In the same network,the transmission rate close to user sides is lower while transmission rate close to network provider side is extremely higher with three orders at least Examples of transmission link:
c) In the same network, the transmission rate close to user sides is lower while transmission rate close to network provider side is extremely higher with three orders at least. Examples of transmission link:
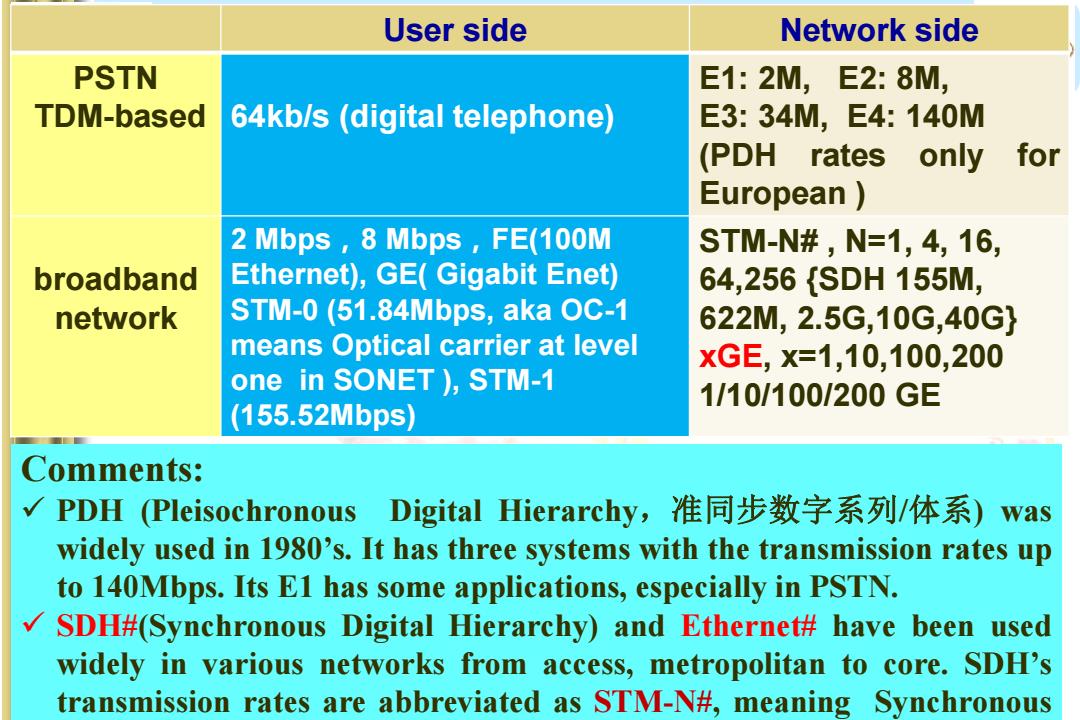
User side Network side PSTN E1:2M,E2:8M, TDM-based 64kb/s (digital telephone) E3:34M,E4:140M (PDH rates only for European 2 Mbps,8 Mbps,FE(100M STM-N#,N=1,4,16, broadband Ethernet),GE(Gigabit Enet) 64,256{SDH155M, network STM-0(51.84Mbps,aka OC-1 622M,2.5G,10G,40G} means Optical carrier at level xGE,X=1,10,100,200 one in SONET),STM-1 1/10/100/200GE (155.52Mbps) Comments: √ PDH(Pleisochronous Digital Hierarchy,准同步数字系列/体系) was widely used in 1980's.It has three systems with the transmission rates up to 140Mbps.Its E1 has some applications,especially in PSTN. √ SDH#(Synchronous Digital Hierarchy)and Ethernet#have been used widely in various networks from access,metropolitan to core.SDH's transmission rates are abbreviated as STM-N#,meaning Synchronous
User side Network side PSTN TDM-based 64kb/s (digital telephone) E1: 2M, E2: 8M, E3: 34M, E4: 140M (PDH rates only for European ) broadband network 2 Mbps,8 Mbps,FE(100M Ethernet), GE( Gigabit Enet) STM-0 (51.84Mbps, aka OC-1 means Optical carrier at level one in SONET ), STM-1 (155.52Mbps) STM-N# , N=1, 4, 16, 64,256 {SDH 155M, 622M, 2.5G,10G,40G} xGE, x=1,10,100,200 1/10/100/200 GE Comments: PDH (Pleisochronous Digital Hierarchy,准同步数字系列/体系) was widely used in 1980’s. It has three systems with the transmission rates up to 140Mbps. Its E1 has some applications, especially in PSTN. SDH#(Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) and Ethernet# have been used widely in various networks from access, metropolitan to core. SDH’s transmission rates are abbreviated as STM-N#, meaning Synchronous Transfer Module at N level, while the later can be denoted as xGE#