
酸碱平衡及紊乱Acid - Base Balanceand DisturbancesPathophysiology Department, ShiHeZi Medical College,HUST
酸碱平衡及紊乱 Acid – Base Balance and Disturbances Pathophysiology Department, ShiHeZi Medical College, HUST
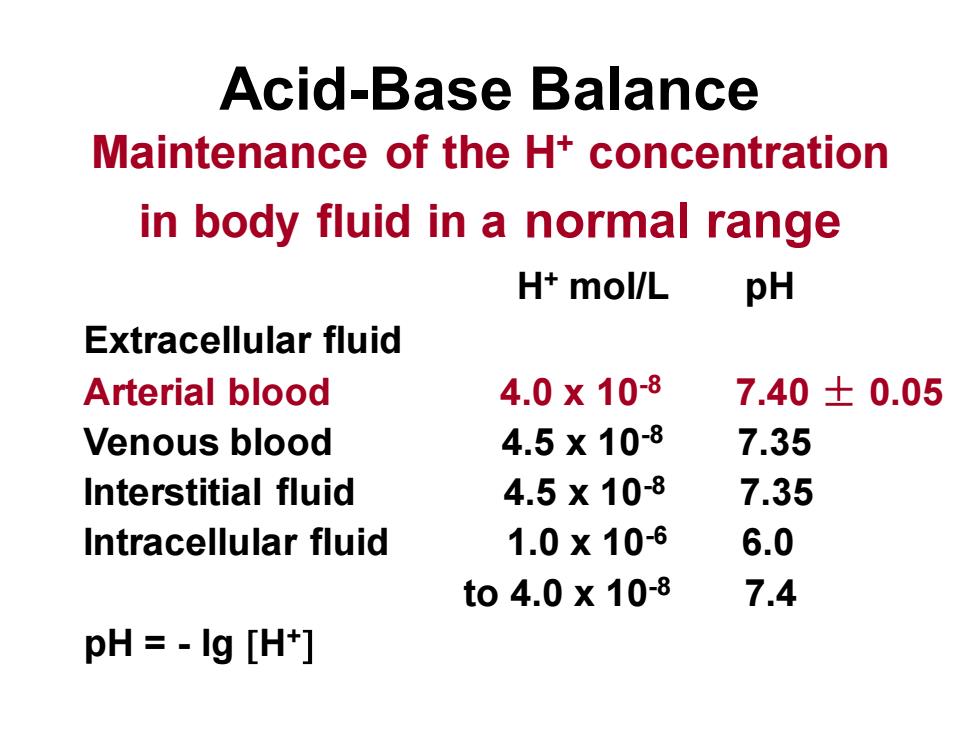
Acid-Base BalanceMaintenance of the H+ concentrationin body fluid in a normal rangepHH+ mol/LExtracellular fluid4.0 x 10-8Arterialblood7.40 ± 0.054.5 x 10-87.35Venous blood4.5 x 10-87.35Interstitial fluid1.0 x 10-66.0Intracellular fluidto 4.0 x 10-87.4pH = - Ig [H+]
Acid-Base Balance Maintenance of the H+ concentration in body fluid in a normal range H+ mol/L pH Extracellular fluid Arterial blood 4.0 x 10-8 7.40 ± 0.05 Venous blood 4.5 x 10-8 7.35 Interstitial fluid 4.5 x 10-8 7.35 Intracellular fluid 1.0 x 10-6 6.0 to 4.0 x 10-8 7.4 pH = - lg H+

Why is the acid - basebalance important for life ?
Why is the acid - base balance important for life ?
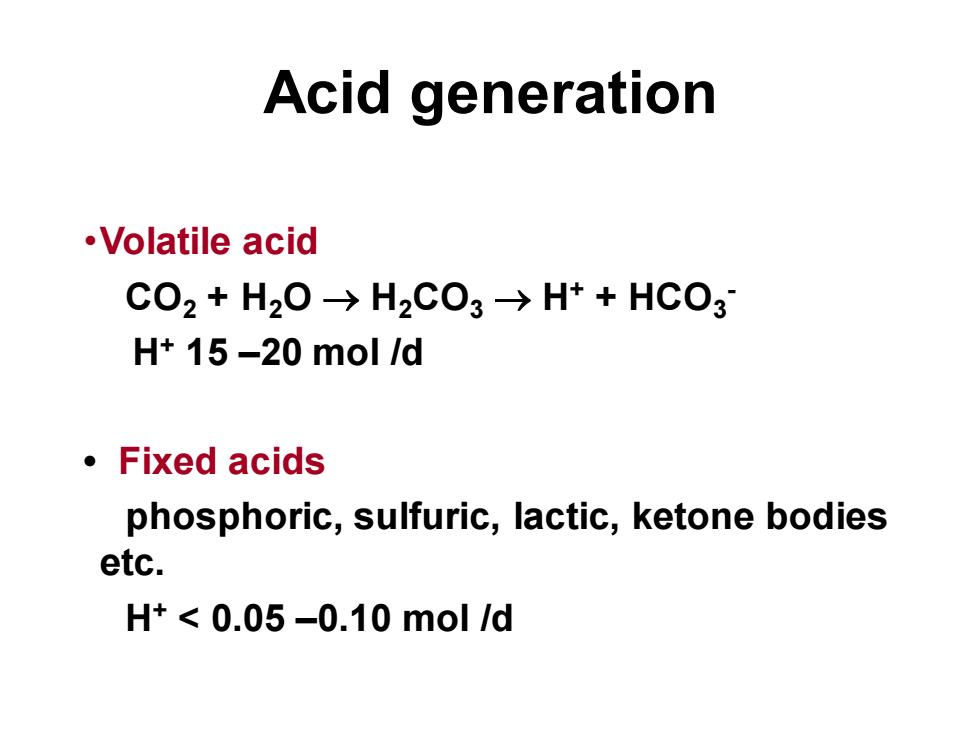
Acid generation·VolatileacidCO2 + H2O →H2CO3 →H+ + HCO3H+ 15 -20 mol /dFixedacidsphosphoric, sulfuric, lactic, ketone bodiesetc.H+ < 0.05 -0.10 mol /d
Acid generation •Volatile acid CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3 - H+ 15 –20 mol /d • Fixed acids phosphoric, sulfuric, lactic, ketone bodies etc. H+ < 0.05 –0.10 mol /d
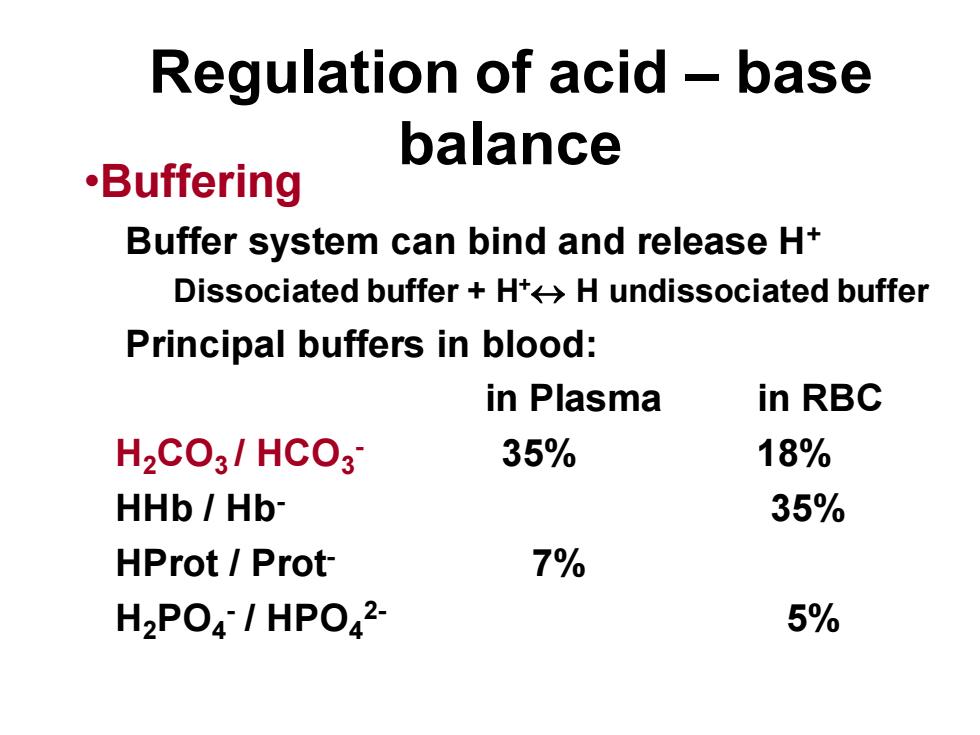
Regulation of acid - basebalance·BufferingBuffer system can bind and release H+Dissociatedbuffer+HtHundissociatedbufferPrincipal buffers in blood:in RBCin Plasma35%18%H2CO3/ HCO335%HHb / Hb*7%HProt / Prot5%H2PO4- / HPO.2
Regulation of acid – base balance •Buffering Buffer system can bind and release H+ Dissociated buffer + H+ H undissociated buffer Principal buffers in blood: in Plasma in RBC H2CO3 / HCO3 - 35% 18% HHb / Hb- 35% HProt / Prot- 7% H2PO4 - / HPO4 2- 5%
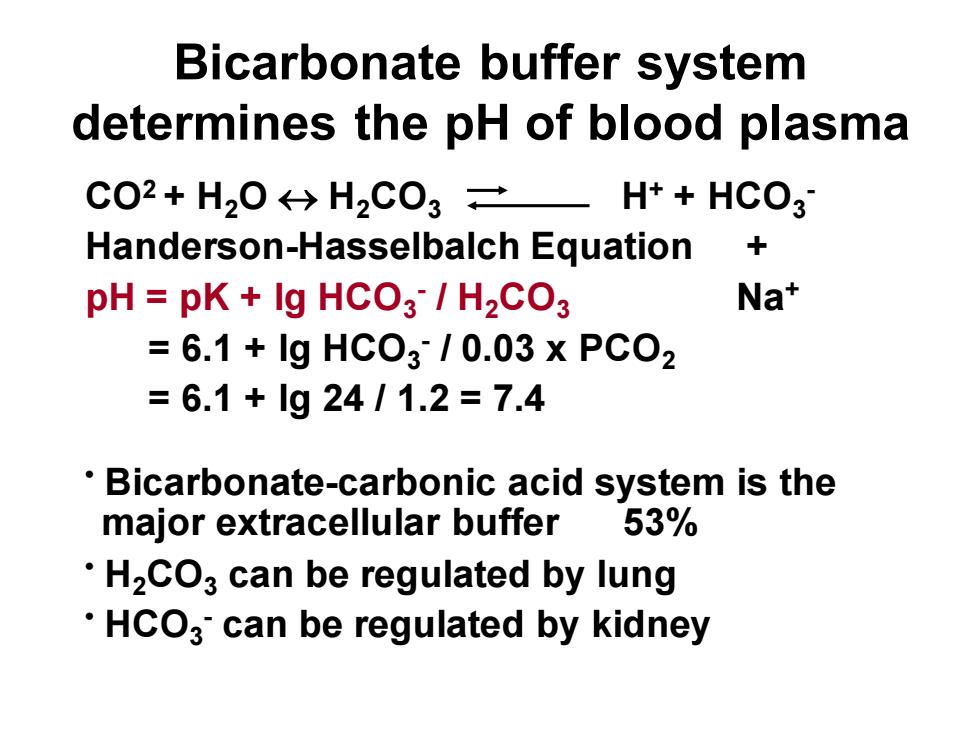
Bicarbonate buffer systemdetermines the pH of blood plasmaCO2+ H,O H2CO3 =H+ + HCO3+Handerson-Hasselbalch EquationNa*pH= pK + Ig HCO3 / H2CO3= 6.1 + Ig HCO3 / 0.03 x PCO2= 6.1 + Ig 24 / 1.2 = 7.4: Bicarbonate-carbonic acid system is the53%major extracellular buffer: HzcO3 can be regulated by lung: HcO3' can be regulated by kidney
Bicarbonate buffer system determines the pH of blood plasma CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3 - Handerson-Hasselbalch Equation + pH = pK + lg HCO3 - / H2CO3 Na+ = 6.1 + lg HCO3 - / 0.03 x PCO2 = 6.1 + lg 24 / 1.2 = 7.4 • Bicarbonate-carbonic acid system is the major extracellular buffer 53% • H2CO3 can be regulated by lung • HCO3 - can be regulated by kidney
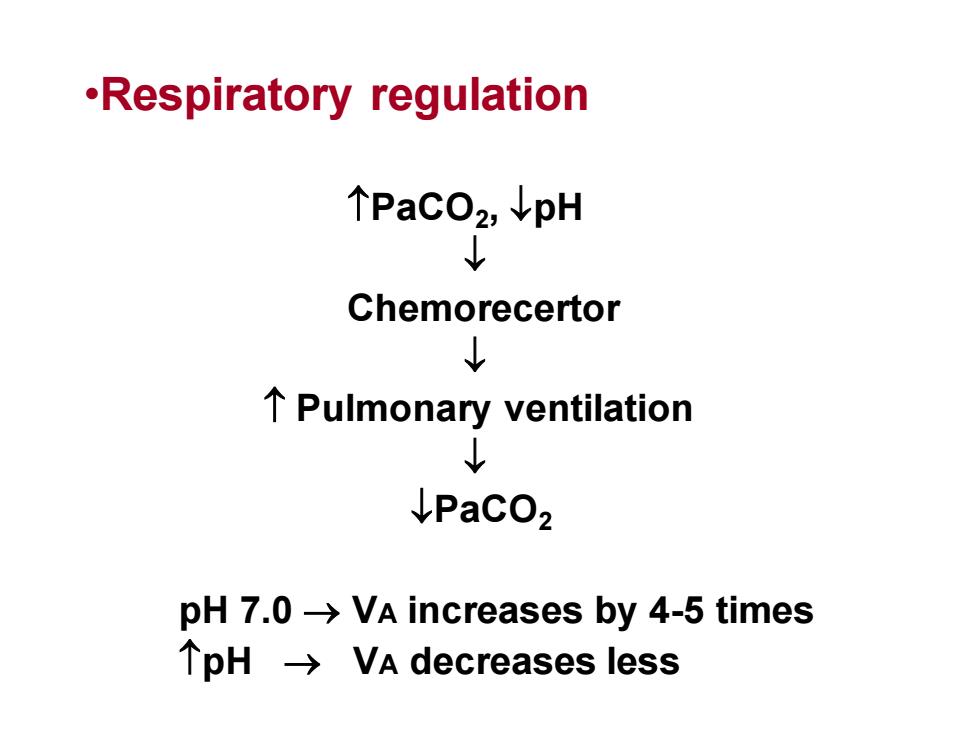
·Respiratoryregulation个PaCO2, ↓pH?ChemorecertorL个 Pulmonary ventilation?IPaCO2pH 7.0 → VA increases by 4-5 times个pH → VA decreases less
•Respiratory regulation PaCO2 , pH Chemorecertor Pulmonary ventilation PaCO2 pH 7.0 → VA increases by 4-5 times pH → VA decreases less
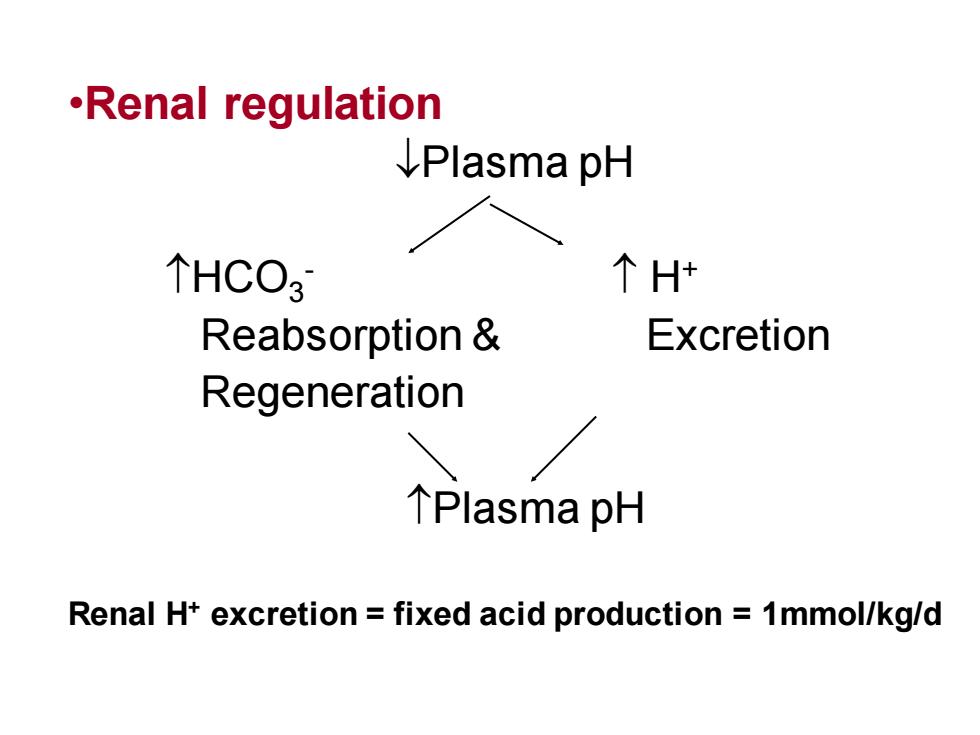
·RenalregulationIPlasmapH个 H+个HCO3ExcretionReabsorption&Regeneration个Plasma pHRenal H+ excretion=fixed acid production=1mmol/kg/d
•Renal regulation Plasma pH HCO3 - H+ Reabsorption & Excretion Regeneration Plasma pH Renal H+ excretion = fixed acid production = 1mmol/kg/d
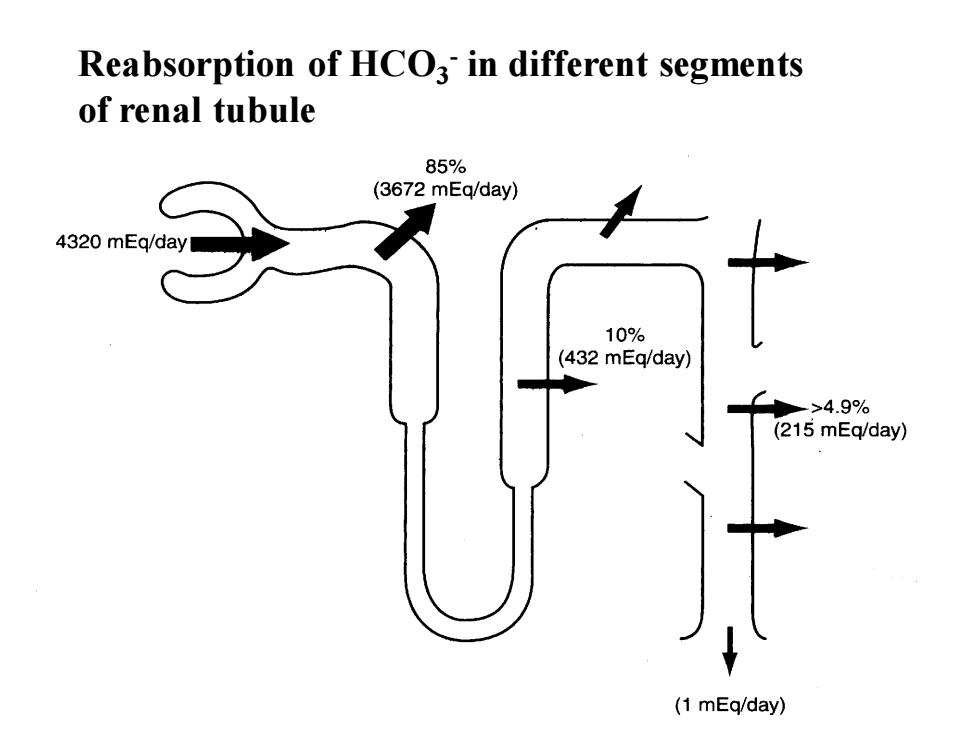
Reabsorption of HCO- in different segmentsof renal tubule85%(3672mEq/day)4320mEq/day10%(432mEq/day)>4.9%(215mEq/day)(1 mEq/day)
Reabsorption of HCO3 - in different segments of renal tubule
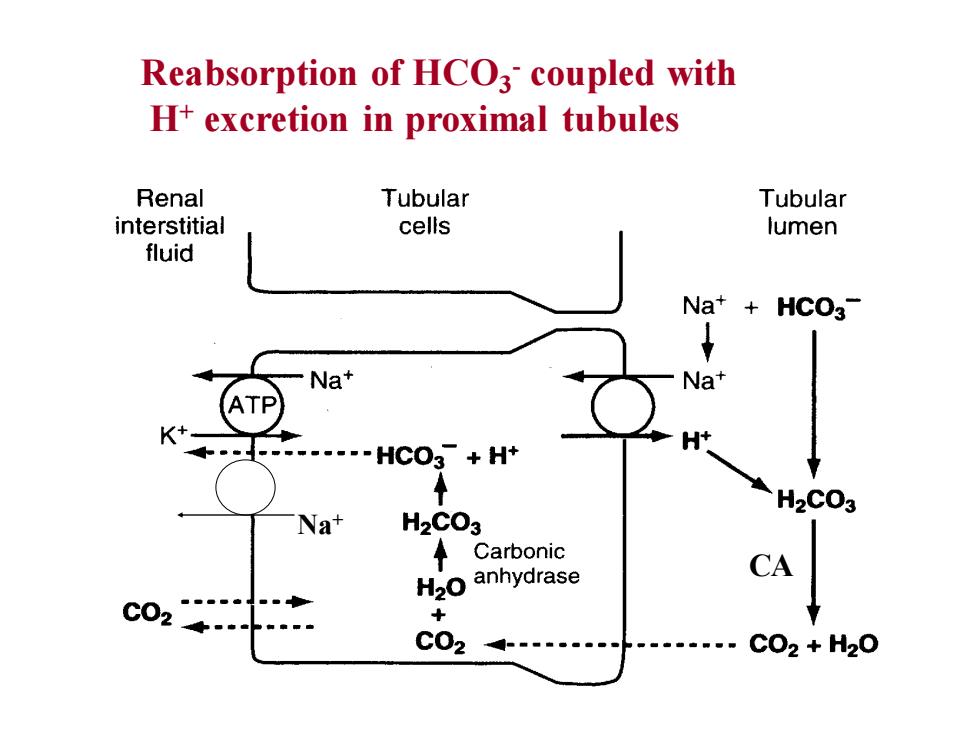
Reabsorption ofHCOcoupled withH+ excretion in proximal tubulesRenalTubularTubularinterstitialcellslumenfluidNa+ + HCO3Na*NatHCO3- + H+H2CO3H2CO3NatCarbonicCAH2o anhydraseCO2+CO2CO2 + H2O
Reabsorption of HCO3 - coupled with H+ excretion in proximal tubules CA Na+