
Apoptosis and DiseasesPathophysiology Department, ShiHeZiMedical College,HUST
Apoptosis and Diseases Pathophysiology Department, ShiHeZiMedical College, HUST

Contents1. Concept2.Majorpathways3. Key molecules4. Apoptosis-related diseasesInsufficient apoptosis in diseasesExcessive apoptosis in diseasesCoexistence of insufficient and excessiveapoptosis in diseases5.Principles of treatment
1. Concept 2. Major pathways 3. Key molecules 4. Apoptosis-related diseases • Insufficient apoptosis in diseases • Excessive apoptosis in diseases • Coexistence of insufficient and excessive apoptosis in diseases 5. Principles of treatment Contents
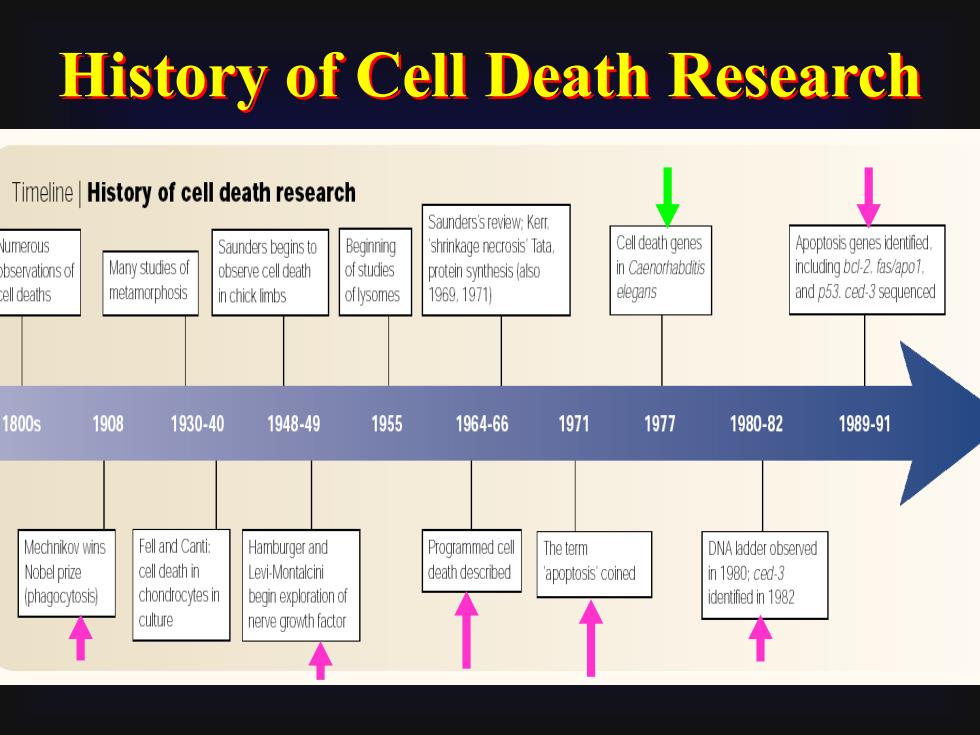
History of Cell Death ResearchTimeline History of cell death researchSaunders's review: KertCell death genesApoptosis genes identiiedNumerousBegqinringSaunders begins toshrinkage necrosis TataMany studies ofincludingbcl-2.fas/apo1inCaenorhabditisof studiesobservationsofobserve cell deathprotein synthesis (alsoelegansandp53.ced-3sequencedmetamorphosis1969, 1971)cell deathsoflysomesin chick limbs1800s19081930-401948-491955197119771980-821989-911964-66Fell and Canti:Mechnikov winsHamburger andProgrammed cellThe termDNA ladder observedNobel prizecell death inLevi-Montalcinideath describedin 1980; ced-3'apoptosis'coinedchondrocytes inbegin exploration of(phagocytosis)identified in 1982↑1culurenerve growth factor全个个
History of Cell Death Research

TheNobel Prize inPhvsiology orMedicine 2002"fortheir discoveries concerning'genetic regulation.of organdevelopmentandprogrammedcell deathSydney BrennerH.RobertHorvitz John E.Sulston1/3of theprizeO1/3oftheprize①1/3 of the prizeUnitedKingdomUSAUnited KingdomThe MolecularMassachusettsThe WellcomeTrustInstitute ofSciencesInstituteSanger InstituteTechnology (MIT)BerkeleyCA,USACambridge,UnitedCambridge, MA,KingdomUSA
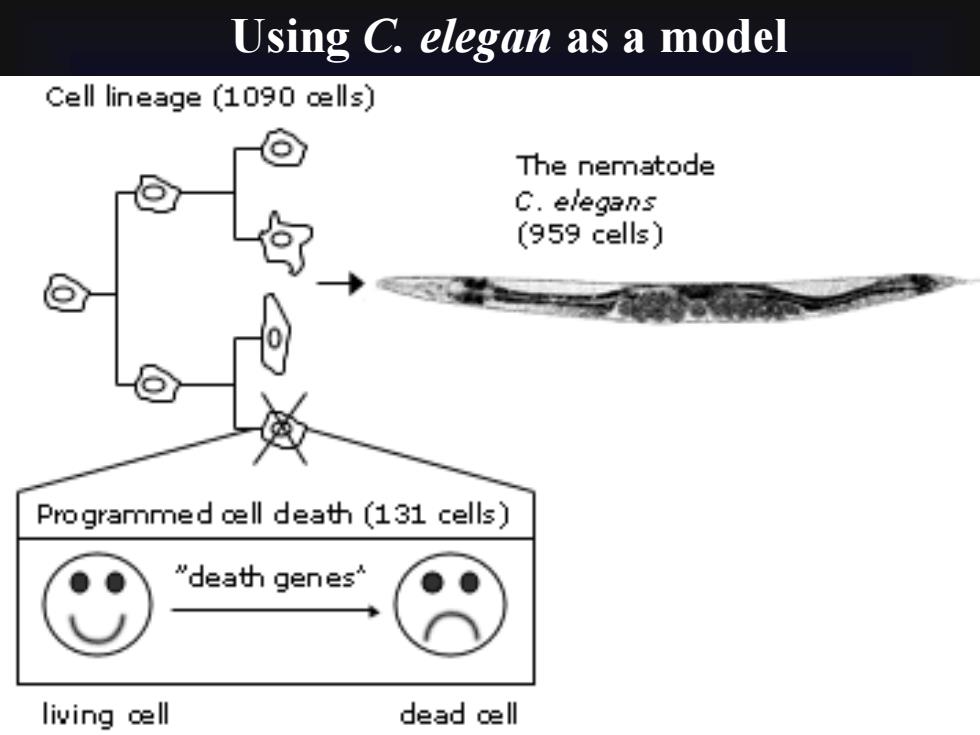
Using C. elegan as a modelCell lineage (1090 cells)The nematodeC.elegans(959 cells)Programmed cell death(131 cells)"death genes"living ce lldead cell
Using C. elegan as a model
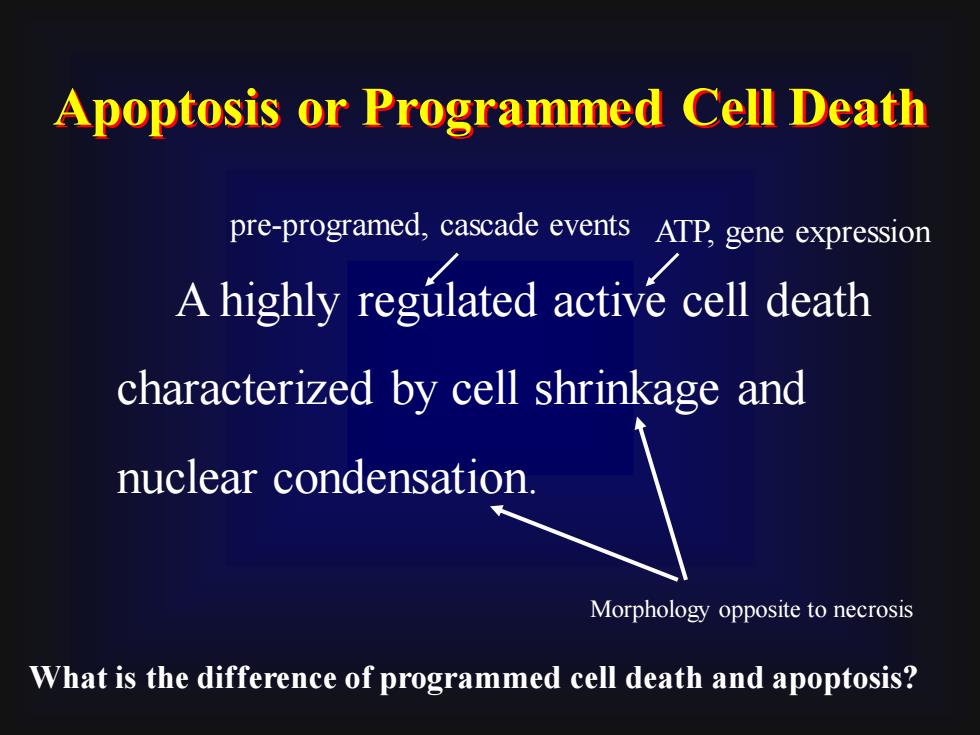
Apoptosis or Programmed Cell Deathpre-programed, cascade events ATP, gene expressionA highly regulated active cell deathcharacterized by cell shrinkage andnuclear condensationMorphology opposite to necrosisWhat is the difference of programmed cell death and apoptosis?
A highly regulated active cell death characterized by cell shrinkage and nuclear condensation. pre-programed, cascade events ATP, gene expression Morphology opposite to necrosis Apoptosis or Programmed Cell Death What is the difference of programmed cell death and apoptosis?

Apoptosis and NecrosisApoptosisNecrosisNaturePhysiologicalorPathological, accidentalpathological; specificMildStimulusStrongBiochemistryPassive,energy-independent, noActive, energy-dependentnew protein synthesisprotein synthesisDNASpecific degradation,Randomdegradationladder (180-200 bp)Intact, shrinkage,MorphologyLysis,swellingcondensationNoYesInflammationYesNoApoptotic bodyNoGene regulationYes
Apoptosis Necrosis Nature Physiological or pathological; specific Pathological, accidental Stimulus Mild Strong Biochemistry Active, energy-dependent, new protein synthesis Passive, energy-independent, no protein synthesis DNA Morphology Specific degradation, ladder (180-200 bp) Intact, shrinkage, condensation Random degradation Lysis, swelling Inflammation No Yes Apoptotic body Yes No Gene regulation Yes No Apoptosis and Necrosis
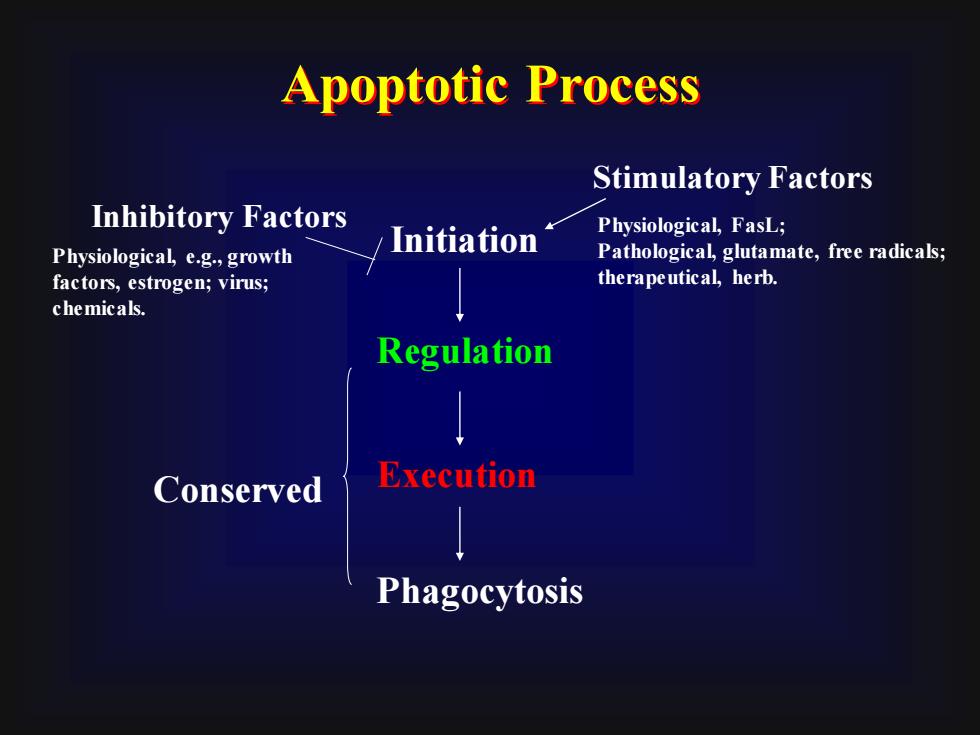
Apoptotic ProcessStimulatory FactorsInhibitory FactorsPhysiological, FasL;InitiationPathological, glutamate, free radicals;Physiological, e.g., growththerapeutical, herb.factors, estrogen;virus;chemicals.RegulationExecutionConservedPhagocytosis
Initiation Regulation Execution Phagocytosis Physiological, e.g., growth factors, estrogen; virus; chemicals. Inhibitory Factors Stimulatory Factors Physiological, FasL; Pathological, glutamate, free radicals; therapeutical, herb. Conserved Apoptotic Process
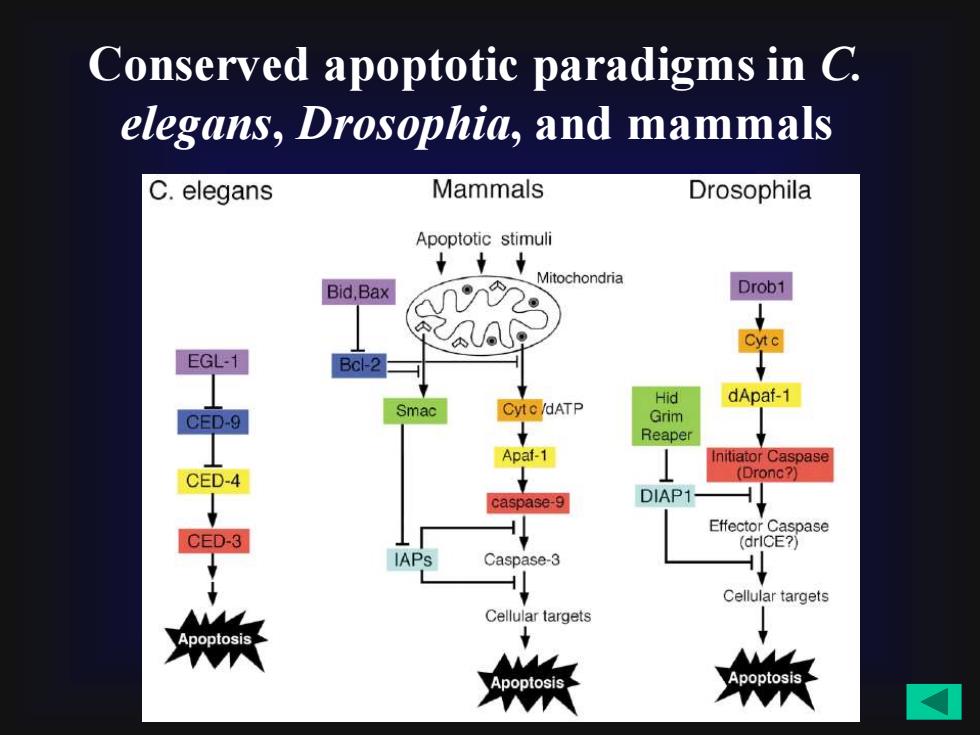
Conserved apoptotic paradigms in Celegans,Drosophia, and mammalsMammalsC. elegansDrosophilaApoptotic stimuli★★MitochondriaDrob1Bid,BaxA2CytEGL-1Bcl-2dApaf-1HidCyto/dATPSmacGrimCED-9ReaperApaf-1InitiatorCaspase(Dronc?)CED-4DIAP1caspase-9EffectorCaspaseCED-3(drICE?)IAPsCaspase-3ACellular targetsCellulartargetsApoptosisApoptosisApoptosis
Conserved apoptotic paradigms in C. elegans, Drosophia, and mammals

Apoptotic PathwaysDeath receptor-mediated apoptoticpathway Mitochondria-mediated apoptoticpathway. Nuclear-mediated apoptotic pathway
• Death receptor-mediated apoptotic pathway • Mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway • Nuclear-mediated apoptotic pathway Apoptotic Pathways