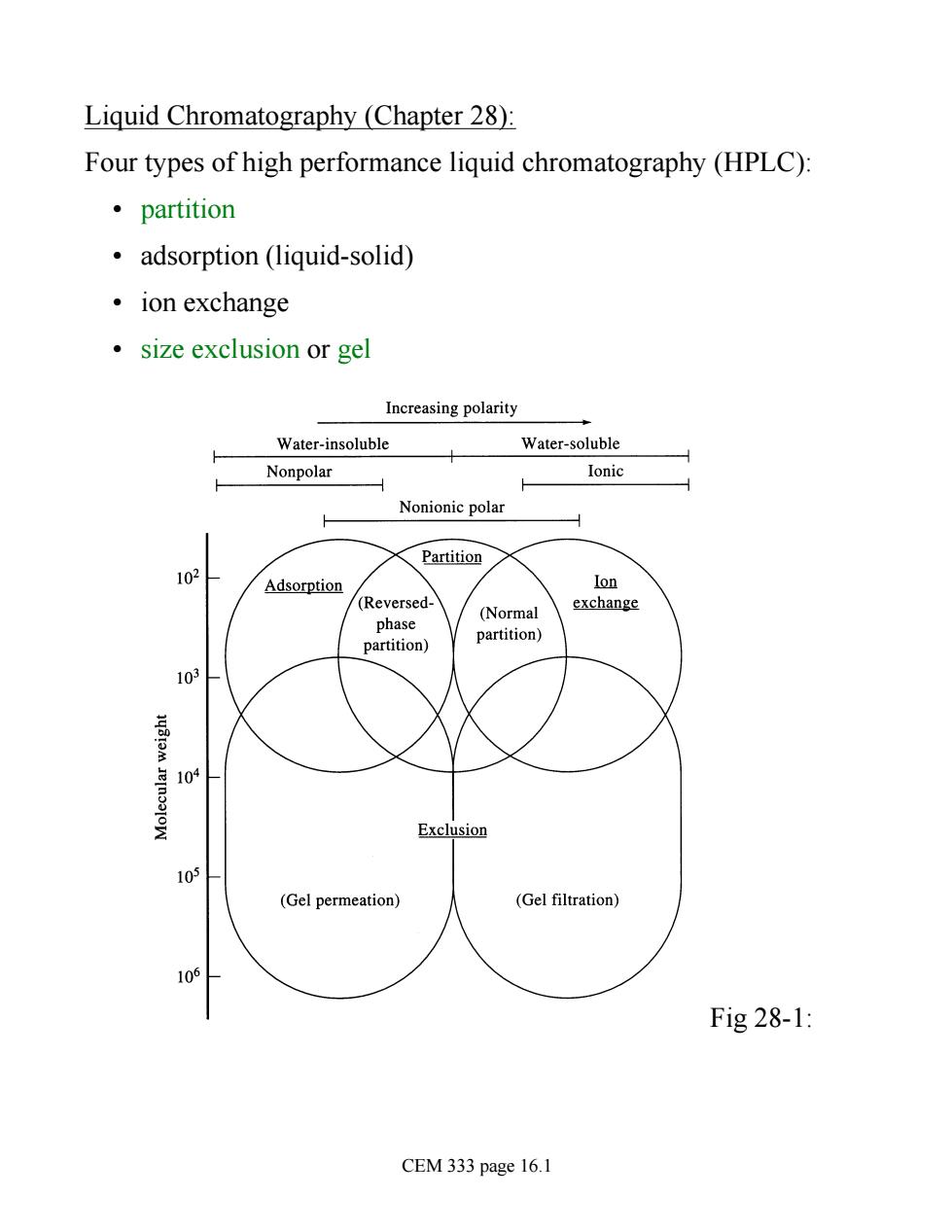
Liquid Chromatography (Chapter 28) Four types of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): ·partition adsorption (liquid-solid) ·ion exchange ·size exclusion or gel Increasing polarity Water-insoluble Water-soluble Nonpolar Ionic Nonionic polar 人 、Partition Adsorption lon /(Reversed exchange (Normal phase partition) partition) 103 10 Exclusion 10 (Gel permeation) (Gel filtration) 0 Fig28-1: CEM 333 page 16.1
Liquid Chromatography (Chapter 28): Four types of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): • partition • adsorption (liquid-solid) • ion exchange • size exclusion or gel Fig 28-1: CEM 333 page 16.1
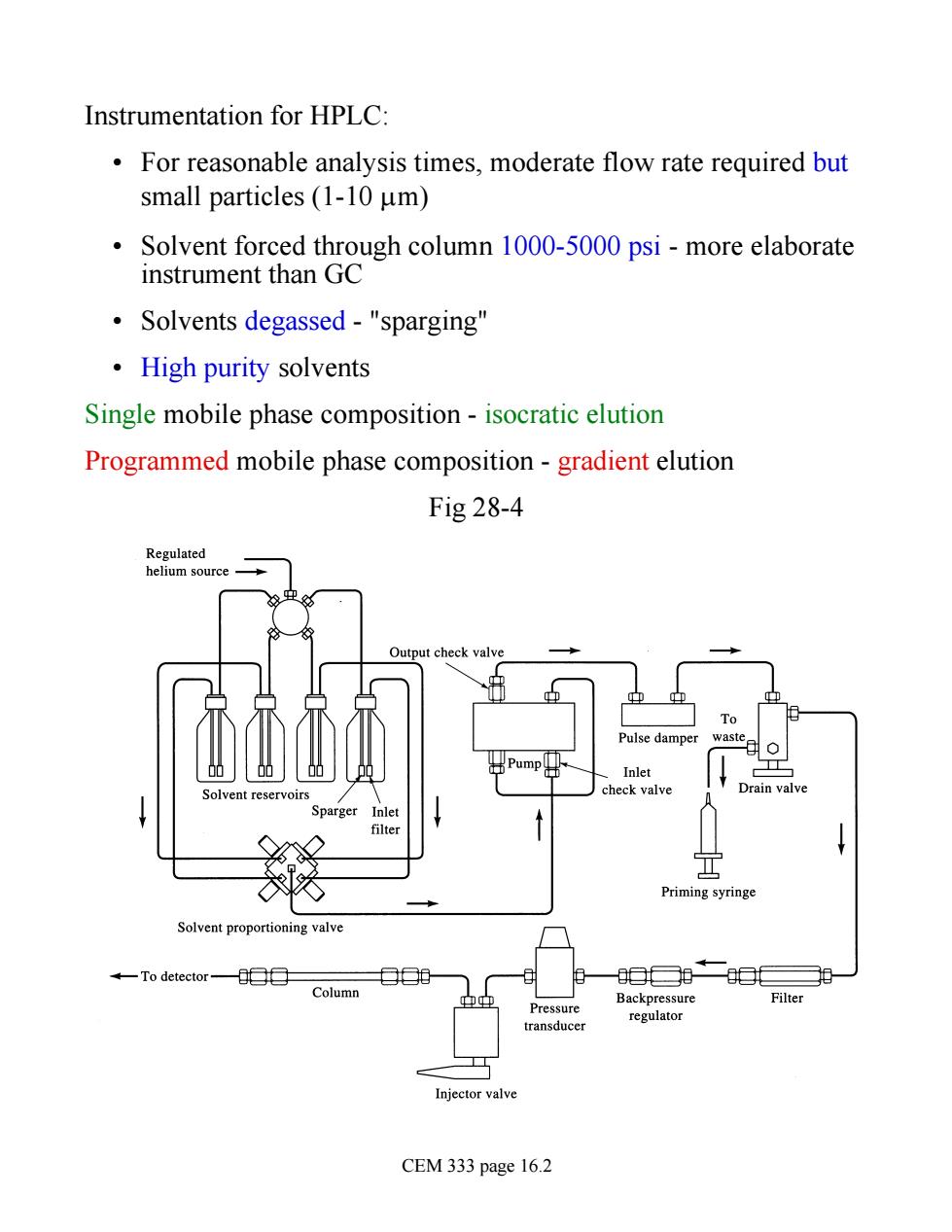
Instrumentation for HPLC: For reasonable analysis times,moderate flow rate required but small particles (1-10 um) Solvent forced through column 1000-5000 psi-more elaborate instrument than GC Solvents degassed-"sparging" ·High purity solvents Single mobile phase composition-isocratic elution Programmed mobile phase composition-gradient elution Fig 28-4 Pum nlet rain valye Priming syringe Solvent proportioning valve -To detector Column Backpre Filter ransduce regulator CEM 333 page 16.2
Instrumentation for HPLC: • For reasonable analysis times, moderate flow rate required but small particles (1-10 mm) • Solvent forced through column 1000-5000 psi - more elaborate instrument than GC • Solvents degassed - "sparging" • High purity solvents Single mobile phase composition - isocratic elution Programmed mobile phase composition - gradient elution Fig 28-4 CEM 333 page 16.2
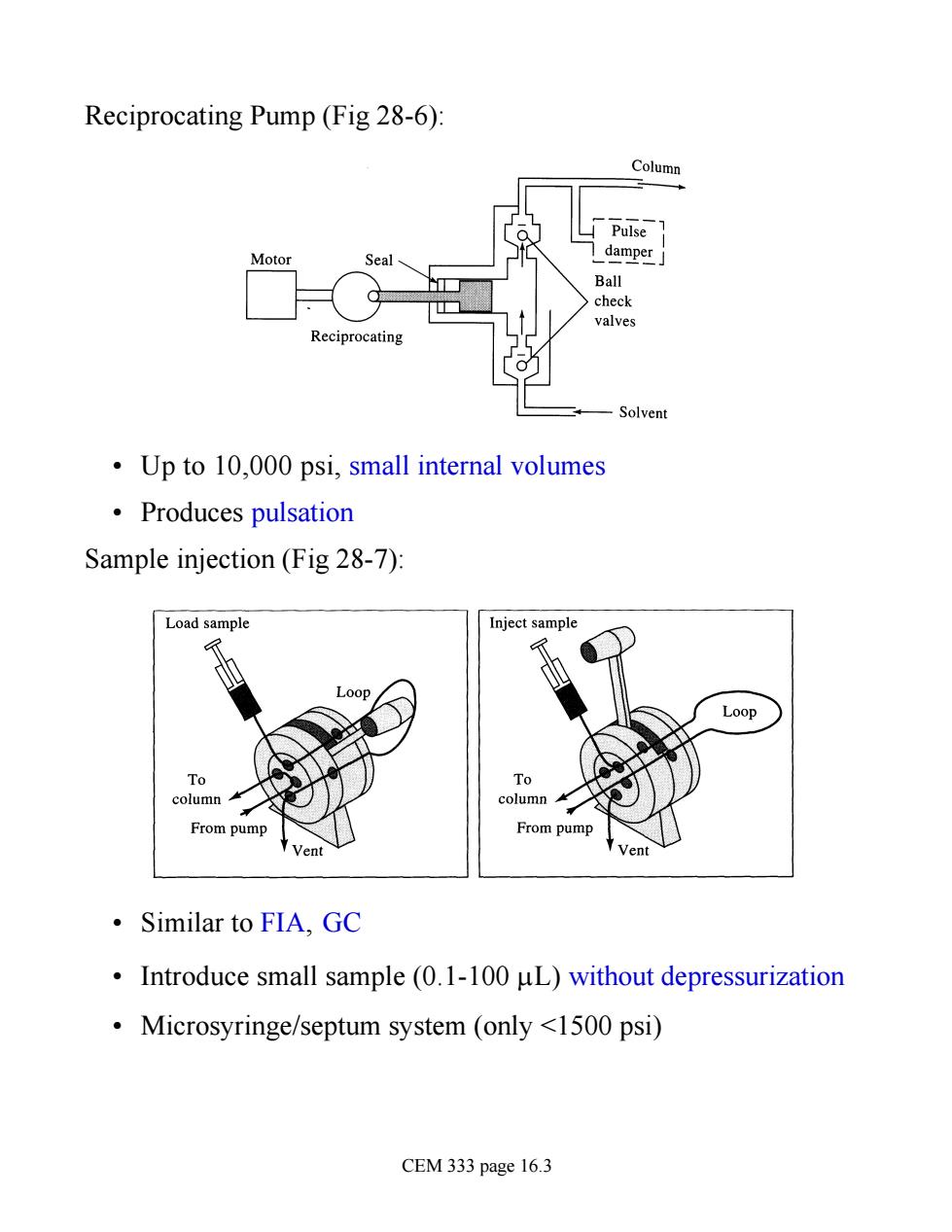
Reciprocating Pump (Fig 28-6) Column 凵Pulse Motor Seal damper Ball check valves Reciprocating Solvent Up to 10,000 psi,small internal volumes ·Produces pulsation Sample injection(Fig 28-7): Load sample Inject sample 00p column From pump From pump ·Similar to FIA,GC Introduce small sample (0.1-100 uL)without depressurization Microsyringe/septum system (only <1500 psi) CEM 333 page 16.3
Reciprocating Pump (Fig 28-6): • Up to 10,000 psi, small internal volumes • Produces pulsation Sample injection (Fig 28-7): • Similar to FIA, GC • Introduce small sample (0.1-100 mL) without depressurization • Microsyringe/septum system (only <1500 psi) CEM 333 page 16.3
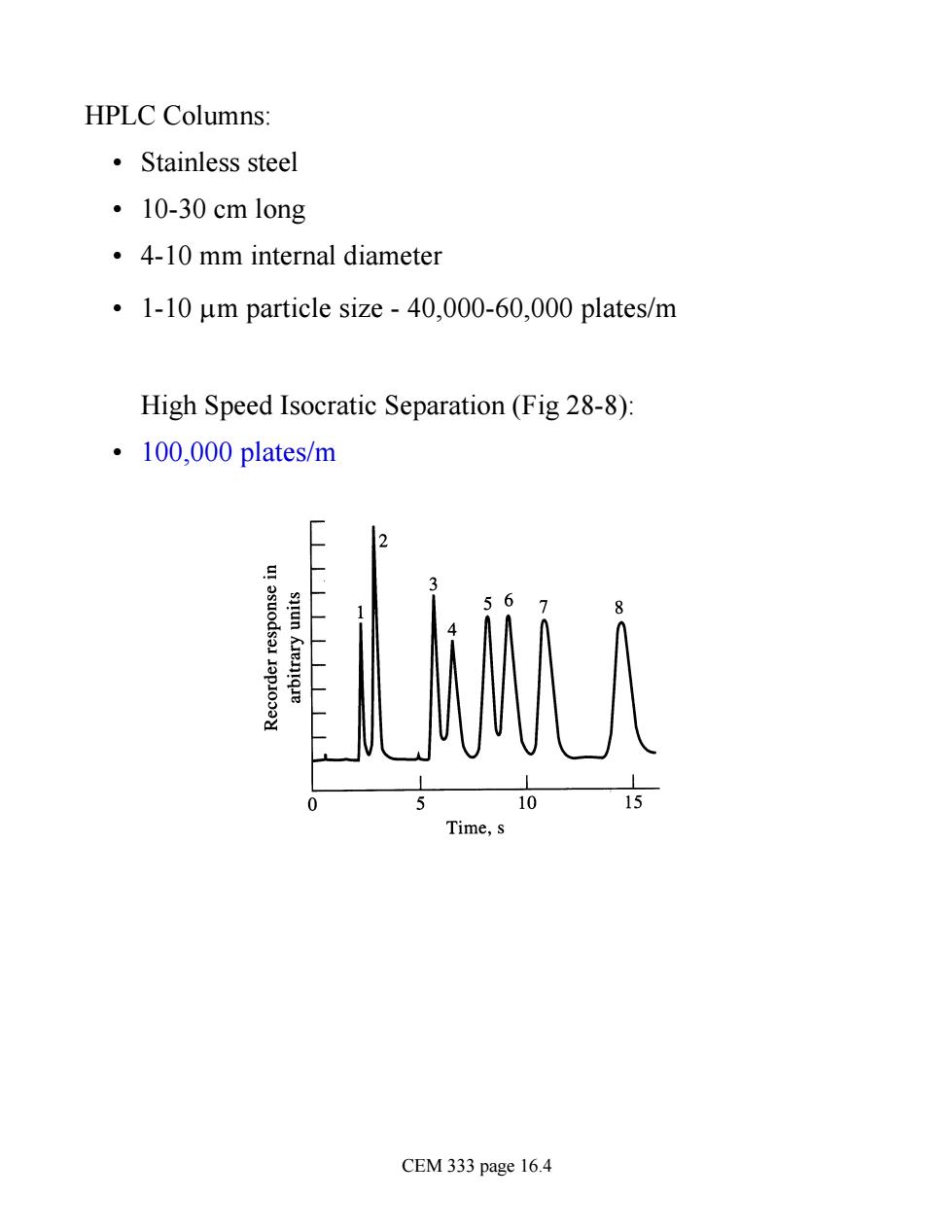
HPLC Columns: ·Stainless steel ·10-30 cm long 4-10 mm internal diameter .1-10 um particle size-40,000-60,000 plates/m High Speed Isocratic Separation (Fig 28-8): ·100,000 plates/m 10 Time. CEM 333 page 16.4
HPLC Columns: • Stainless steel • 10-30 cm long • 4-10 mm internal diameter • 1-10 mm particle size - 40,000-60,000 plates/m High Speed Isocratic Separation (Fig 28-8): • 100,000 plates/m CEM 333 page 16.4
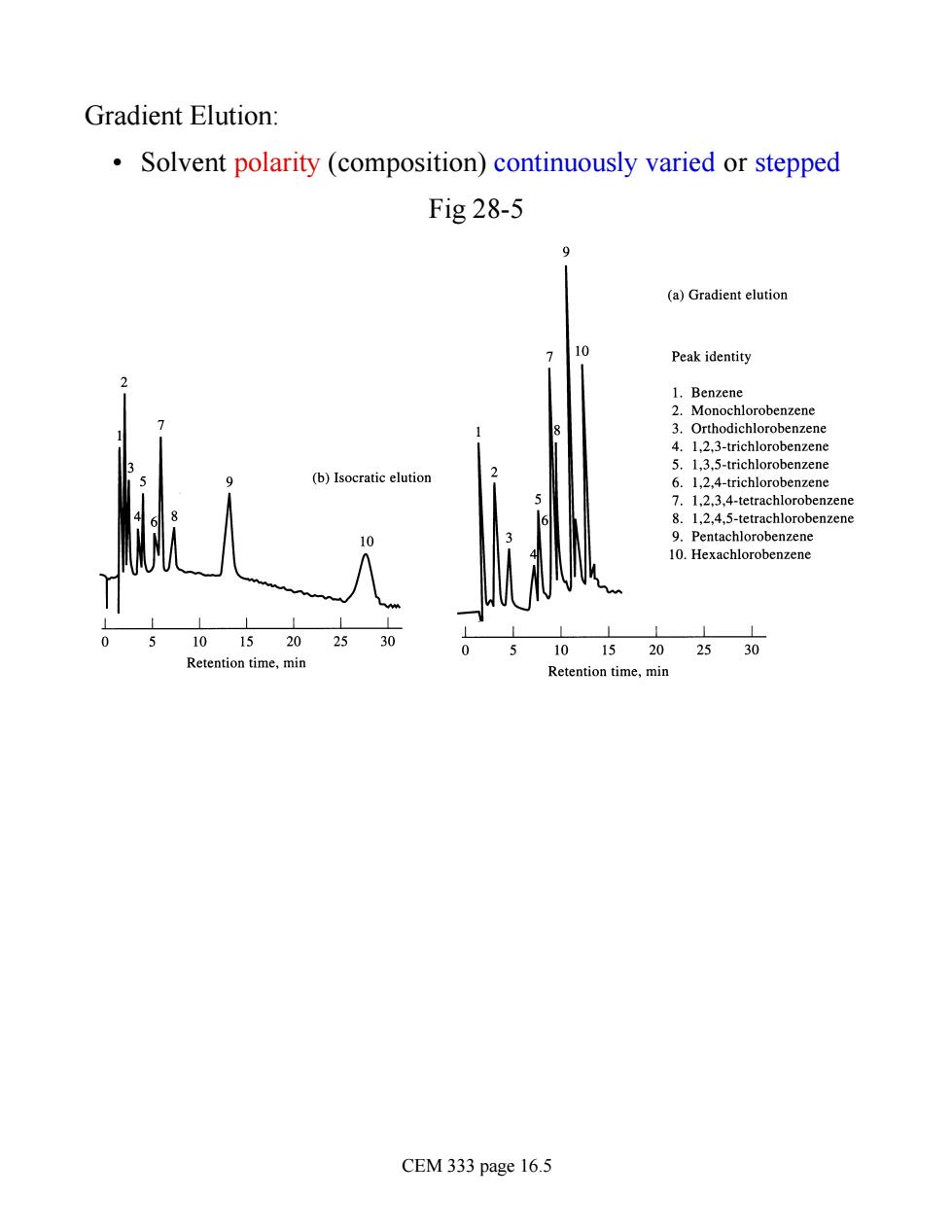
Gradient Elution: Solvent polarity (composition)continuously varied or stepped Fig 28-5 (a)Gradient elution Peak identity -trichlorobenzen (b)Isocratic elution 二 10.Hexachlorobenzene 5 1015202530 Retention time.min CEM 333 page 16.5
Gradient Elution: • Solvent polarity (composition) continuously varied or stepped Fig 28-5 CEM 333 page 16.5
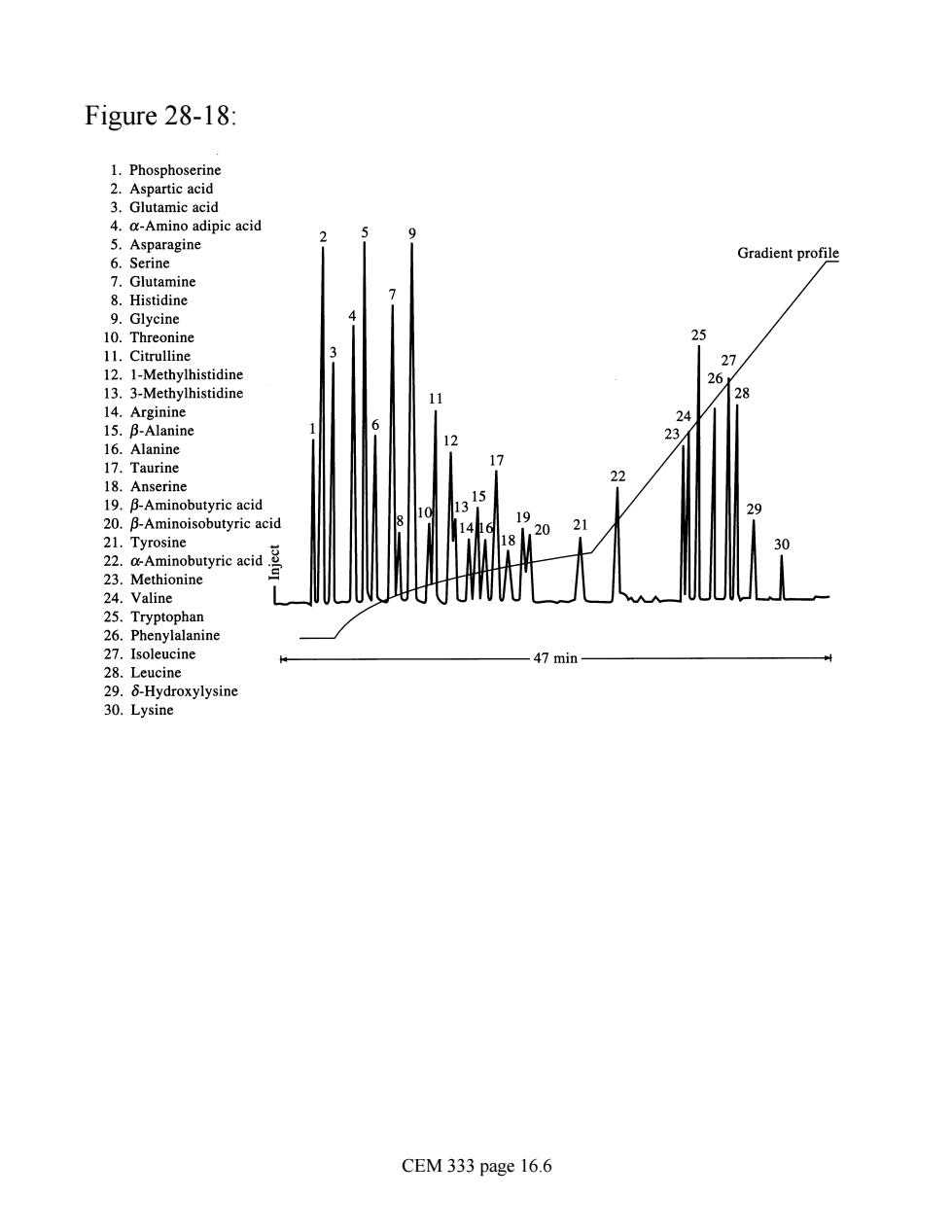
Figure 28-18: 1.Phosphoserine 2.Aspartic acid Glutamic acic ipicacid 5 Ac 6.Serine Gradient profile Glutamine 25 1.Citrulline 14 Arg 15.B-Alanine 16.Alanine 19.B-Aminobutyric acid 20.B-Aminoisobutyric acid 24.Valine 28.Leucine 29.8-Hydroxylysine 30.Lysine CEM 333 page 16.6
Figure 28-18: CEM 333 page 16.6
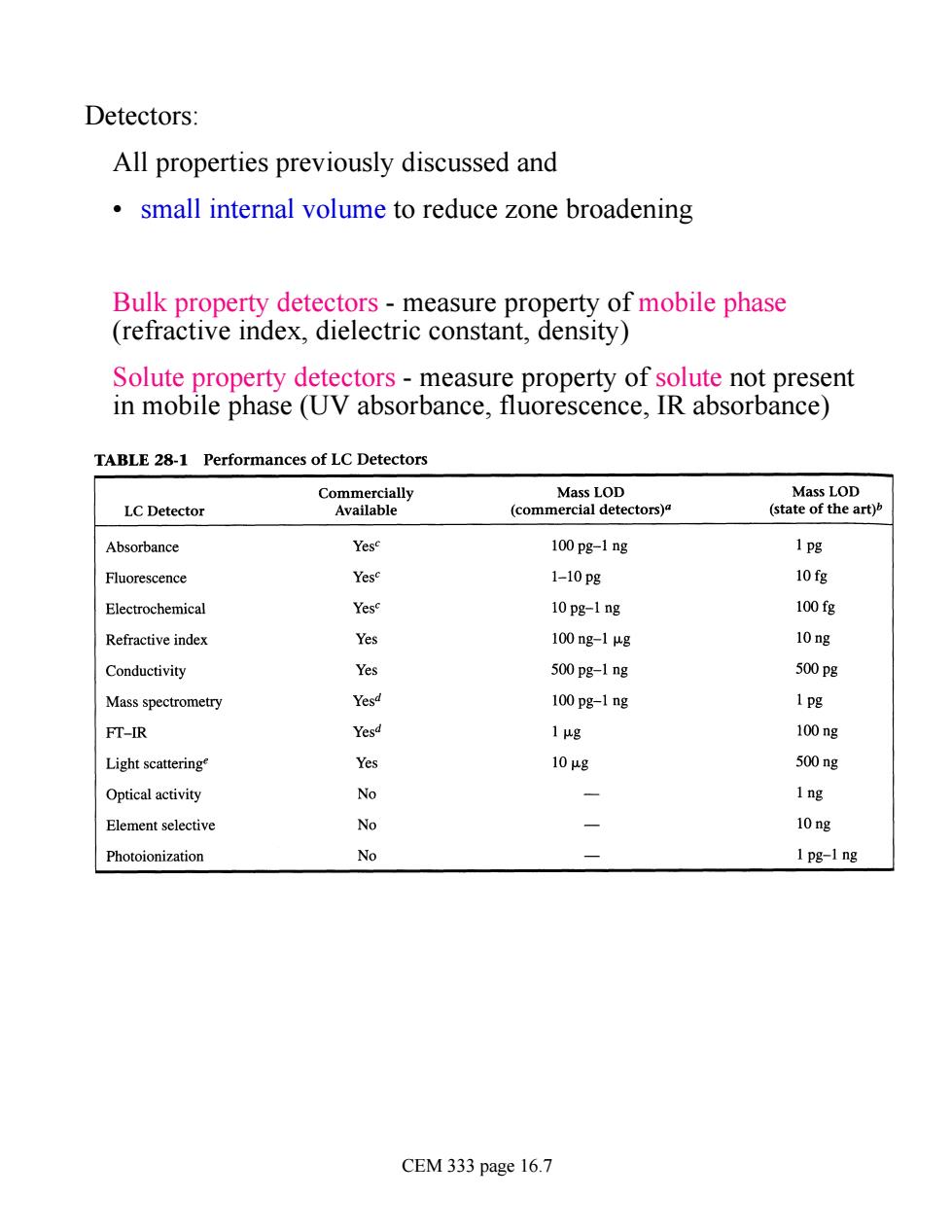
Detectors: All properties previously discussed and small internal volume to reduce zone broadening Bulk property detectors-measure property of mobile phase (refractive index,dielectric constant,density) Solute property detectors-measure property of solute not present in mobile phase (UV absorbance.fluorescence.IR absorbance) TABLE 28-1 Performances of LC Detectors Commercially Mass LOD Mass LOD LC Detector Available (commercial detectors) (state of the art) Absorbance 100pg-1g 1p Fluorescence se 1-10pg 10fg Electrochemical 。 10pg-1 ng 100fg Refractive index 4 100g-1g 10g Conductivity Yes 500 pg-1 ng 500Pg Mass spectrometry Yesd 100 pg-1 ng 1pg FT-IR Yesd 1ug 100ng Light scattering Yes 10ug 500ng Optical activity 名 1ng Element selective 名 10g Photoionization No 1 pg-1 ng CEM 333 page 16.7
Detectors: All properties previously discussed and • small internal volume to reduce zone broadening Bulk property detectors - measure property of mobile phase (refractive index, dielectric constant, density) Solute property detectors - measure property of solute not present in mobile phase (UV absorbance, fluorescence, IR absorbance) CEM 333 page 16.7
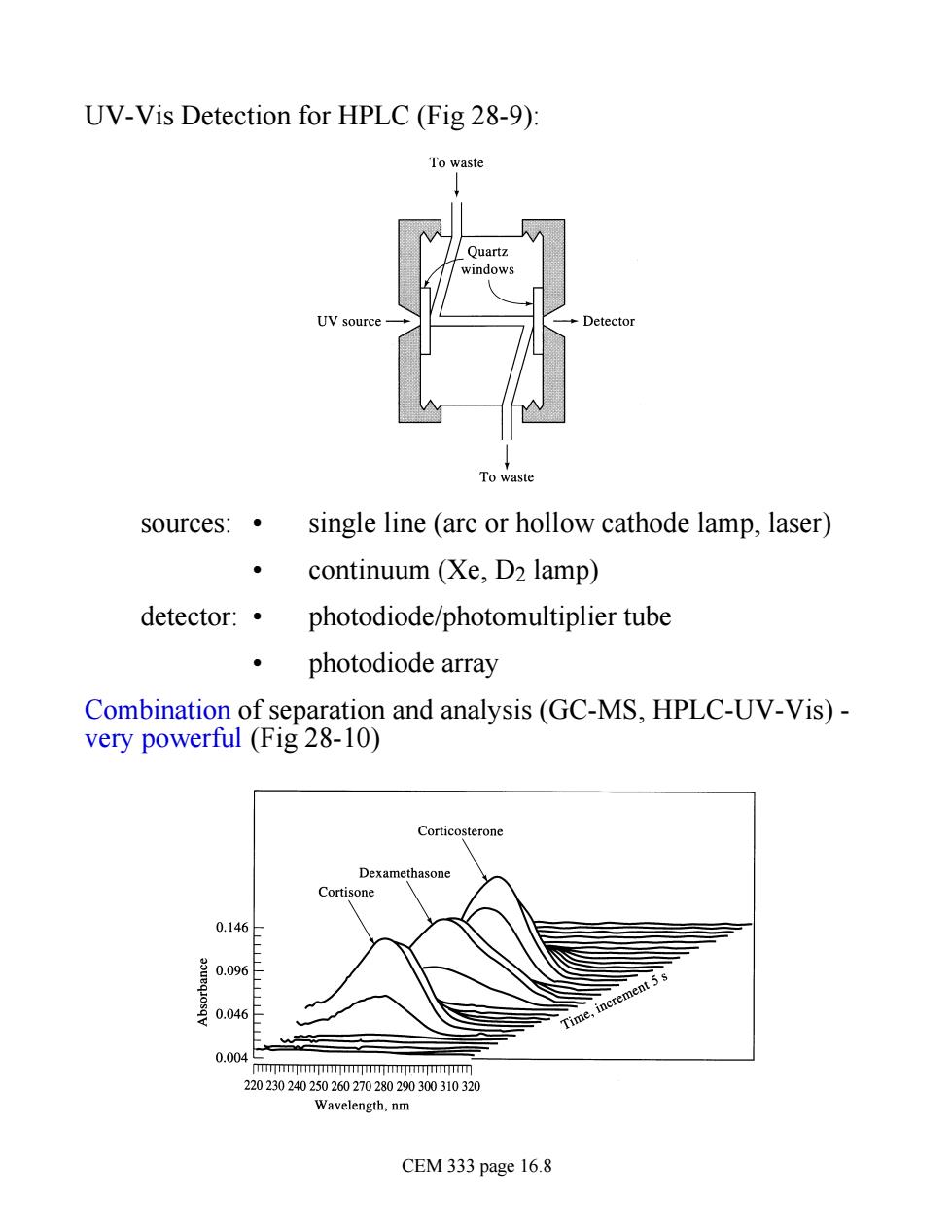
UV-Vis Detection for HPLC(Fig 28-9): To waste sources:.single line (arc or hollow cathode lamp,laser) continuum (Xe,D2 lamp) detector:· photodiode/photomultiplier tube photodiode array Combination of separation and analysis(GC-MS,HPLC-UV-Vis)- very powerful(Fig 28-10) Cor 0.146 0.09 0.046 0.004 22023024 elength,nm CEM 333 page 16.8
UV-Vis Detection for HPLC (Fig 28-9): sources: • single line (arc or hollow cathode lamp, laser) • continuum (Xe, D2 lamp) detector: • photodiode/photomultiplier tube • photodiode array Combination of separation and analysis (GC-MS, HPLC-UV-Vis) - very powerful (Fig 28-10) CEM 333 page 16.8

Partition Chromatography: ·Most popular method Low molecular weight(mw<3000)analytes ·Polar or non-polar Bonded stationary phase column (liquid chemically bonded to support particles) 3,5 or 10 um hydrolyzed silica particles coated with siloxanes R2 Normal phase HPLC nonpolar solvent/polar column Reversed phase HPLC polar solvent/nonpolar column CEM 333 page 16.9
Partition Chromatography: • Most popular method • Low molecular weight (mw<3000) analytes • Polar or non-polar • Bonded stationary phase column (liquid chemically bonded to support particles) 3, 5 or 10 mm hydrolyzed silica particles coated with siloxanes Si O * R1 R2 n Normal phase HPLC nonpolar solvent/polar column Reversed phase HPLC polar solvent/nonpolar column CEM 333 page 16.9
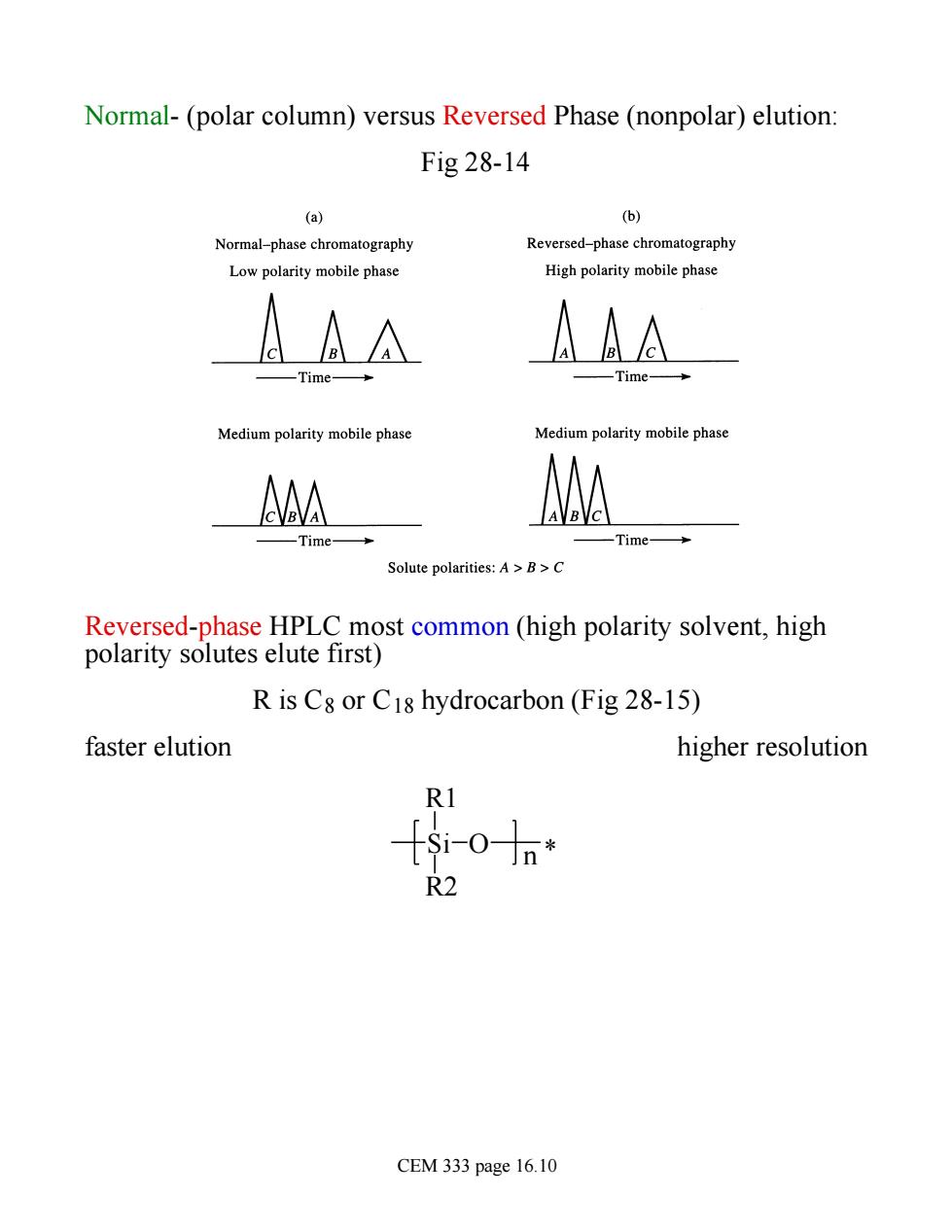
Normal-(polar column)versus Reversed Phase(nonpolar)elution: Fig28-14 (a) (6) Normal-phase chromatography Reversed-phase chromatography Low polarity mobile phase High polarity mobile phase AA AAA -Time 一Time+ Medium polarity mobile phase Medium polarity mobile phase A AVBVC -Time- -Time→ Solute polarities:A>B>C Reversed-phase HPLC most common (high polarity solvent,high polarity solutes elute first) R is Cg or C18 hydrocarbon (Fig 28-15) faster elution higher resolution Jn¥ CEM 333 page 16.10
Normal- (polar column) versus Reversed Phase (nonpolar) elution: Fig 28-14 Reversed-phase HPLC most common (high polarity solvent, high polarity solutes elute first) R is C8 or C18 hydrocarbon (Fig 28-15) faster elution higher resolution Si O * R1 R2 n CEM 333 page 16.10